Sandbox Reserved 824
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (17 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | == | + | == Human SRP54 M-domain == |
<StructureSection load='1qb2' size='450' side='right'caption='Dimer of human SRP54M, (PDB code [[1qb2]]) ' scene='56/568022/Hsrp54m_dimer/1' > | <StructureSection load='1qb2' size='450' side='right'caption='Dimer of human SRP54M, (PDB code [[1qb2]]) ' scene='56/568022/Hsrp54m_dimer/1' > | ||
| + | == Context == | ||
SRP54 is a 54kDa cytosolic protein part of the Signal Recognition Particle (SRP). | SRP54 is a 54kDa cytosolic protein part of the Signal Recognition Particle (SRP). | ||
SRP54 bacterial homologous can be referred to as Ffh (Fifty Four Homologous). | SRP54 bacterial homologous can be referred to as Ffh (Fifty Four Homologous). | ||
| - | SRP is a ribonucleoprotein particle essential for the translation and integration in membranes of signal peptide-bearing proteins. | + | |
| - | For example Mammalian SRP are formed of the RNA 7S and | + | SRP is a ribonucleoprotein particle essential for the translation and integration in membranes of signal peptide-bearing proteins. It is composed of an RNA backbone, on which bind different proteins. |
| + | For example Mammalian SRP are formed of the RNA 7S and SRP 9-14-19-54-68-72. | ||
SRP54 and regions of RNA 7S are highly conserved in every organism and it was found that these two components are sufficient to form a minimal SRP. | SRP54 and regions of RNA 7S are highly conserved in every organism and it was found that these two components are sufficient to form a minimal SRP. | ||
| + | |||
The role of SRP is to : | The role of SRP is to : | ||
*Bind signal peptide bearing proteins at the beginning of their translation by the ribosome (at this step we call the ribosome and the protein it began to translate the Ribosome Nascent Chain – RNC) | *Bind signal peptide bearing proteins at the beginning of their translation by the ribosome (at this step we call the ribosome and the protein it began to translate the Ribosome Nascent Chain – RNC) | ||
| Line 13: | Line 16: | ||
SRP54 is a 504 aminoacids protein,composed of 3 domains: | SRP54 is a 504 aminoacids protein,composed of 3 domains: | ||
| - | + | *N-terminal domain with 4 alpha-helices; | |
| - | + | *G domain, central, with a GTPase activity | |
| - | + | *M domain ( for Methionin Rich). | |
The 1QB2 structure is the M-domain of the human SRP54. It includes the aminoacids 322 to 441. | The 1QB2 structure is the M-domain of the human SRP54. It includes the aminoacids 322 to 441. | ||
| Line 24: | Line 27: | ||
SRP54M is a 120 aminoacids long polypeptide. 1QB2 is a <scene name='56/568022/Hsrp54m_dimer/1'>dimer of SRP54M</scene>, since the studied polypeptide has the interesting property to dimerize in solution. | SRP54M is a 120 aminoacids long polypeptide. 1QB2 is a <scene name='56/568022/Hsrp54m_dimer/1'>dimer of SRP54M</scene>, since the studied polypeptide has the interesting property to dimerize in solution. | ||
| - | Note : | + | ''Note : for a readability purpose the structures enlighten in the Jmol applet will focus only on one SRP54. The same structures are present in the second SRP54M of the dimer.'' |
| - | The secondary structure of | + | The secondary structure of human SRP54M is formed of <scene name='56/568022/Hsrp54m_h1_to_h7/1'>7 alpha helixes (H1 to H7)</scene>. The helices 2 to 7 form the <scene name='56/568022/Hsrp54m_core_and_h1v2/2'>Core structure</scene>, stabilized by hydrophobic, hydrogen and ionic interactions. |
| - | Several residues important to maintain the Core structure were identified. | + | Several residues important to maintain the Core structure were identified. Among them the <scene name='56/568022/Hsrp54m_core_and_h1/2'>Methionine 382,Glutamine 386, Arginine 402 and Arginine 405.</scene> |
| - | Among them the <scene name='56/568022/Hsrp54m_core_and_h1/2'>Methionine 382,Glutamine 386, Arginine 402 and Arginine 405.</scene> | + | |
Met382 is invariable while Glu386, Arg402 and Arg405 are well-conserved but not systemically found in the SRP54M of different organisms. | Met382 is invariable while Glu386, Arg402 and Arg405 are well-conserved but not systemically found in the SRP54M of different organisms. | ||
| - | The remaining helix, <scene name='56/568022/ | + | The remaining helix, <scene name='56/568022/Hsrp54m_core_and_h1v2/1'>H1</scene>, is not part of the Core and protrudes from it. |
Between the helices are loops of various importance. | Between the helices are loops of various importance. | ||
| - | The loop including the aminoacids 349 to 365, besides having an important role in SRP54 function, has the particularity to have two phenylalanine residues, <scene name='56/568022/Hsrp54m_phe355_and_phe359/1'>Phe355 and Phe359</scene>, stacking their aromatic cycles. The function of this loop will be developed in the next part. | + | The loop including the <scene name='56/568022/Hsrp54m_loop_349-365/2'>aminoacids 349 to 365</scene>, besides having an important role in SRP54 function, has the particularity to have two phenylalanine residues, <scene name='56/568022/Hsrp54m_phe355_and_phe359/1'>Phe355 and Phe359</scene>, stacking their aromatic cycles. The function of this loop will be developed in the next part. |
==Fonction== | ==Fonction== | ||
| Line 48: | Line 50: | ||
Theses similarities might come from the fact that the H1 helix is near the hydrophobic groove of its own SRP54M, and that conformational changes (in a full SRP54 protein) might bring H1 into the groove in order to protect it from solvent interaction in the absence of signal peptide. | Theses similarities might come from the fact that the H1 helix is near the hydrophobic groove of its own SRP54M, and that conformational changes (in a full SRP54 protein) might bring H1 into the groove in order to protect it from solvent interaction in the absence of signal peptide. | ||
| - | It was therefore | + | It was therefore hypothesized that the binding of H1 into the groove of another SRP54M provides a possible model of the interaction between the signal peptide and SRP54M in vivo. |
It also explains the dimerization of SRP54M in solution. | It also explains the dimerization of SRP54M in solution. | ||
| Line 56: | Line 58: | ||
SRP54M binds the SRP RNA 7S by electrostatic interactions. | SRP54M binds the SRP RNA 7S by electrostatic interactions. | ||
| - | The residues responsible for this interaction are localized in <scene name='56/568022/Hsrp54m_rna_bindv3/1'>helices 4,5, 6 and 7</scene>, but most particularly in helices 5 and 6. | + | The residues responsible for this interaction are localized in <scene name='56/568022/Hsrp54m_rna_bindv3/1'>helices 4, 5, 6 and 7</scene>, but most particularly in helices 5 and 6. |
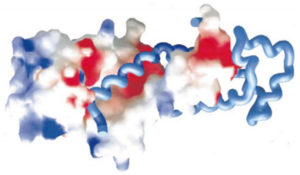
| - | A large part of the top is therefore positively charged to bind with the negatively charged 7S RNA. | + | A large part of the top of SRP54M is therefore positively charged to bind with the negatively charged 7S RNA. |
| - | [[Image:Proteopedia charge.png|300px|center|thumb| | + | [[Image:Proteopedia charge.png|300px|center|thumb| The helices 4, 5, 6 and 7 surfaces are colored in blue on the spacefill model (left) of SRP54M in this picture. For more details see figure 7 of reference 1.]] |
| - | It was also shown that the SRP54M - SRP RNA interaction is highly dependent of the structural integrity of the <scene name='56/568022/ | + | It was also shown that the SRP54M - SRP RNA interaction is highly dependent of the structural integrity of the <scene name='56/568022/Hsrp54m_core_and_h1v2/2'>Core structure</scene>. |
Experiments conducted with shorter versions of the M-domain, lacking some aminoacids of the Core, showed a loss in SRP RNA binding activity. | Experiments conducted with shorter versions of the M-domain, lacking some aminoacids of the Core, showed a loss in SRP RNA binding activity. | ||
| Line 78: | Line 80: | ||
[[1mfq]] – hSRP19 + hSRP54 M domain + 7S RNA S domain | [[1mfq]] – hSRP19 + hSRP54 M domain + 7S RNA S domain | ||
| - | == | + | ==References== |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | # Clemons, W M, Jr, K Gowda, S D Black, C Zwieb, and V Ramakrishnan. “Crystal Structure of the Conserved Subdomain of Human Protein SRP54M at 2.1 A Resolution: Evidence for the Mechanism of Signal Peptide Binding.” Journal of Molecular Biology 292, no. 3 (September 24, 1999): 697–705. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1999.3090. | ||
| + | # Halic, Mario, Thomas Becker, Martin R. Pool, Christian M. T. Spahn, Robert A. Grassucci, Joachim Frank, and Roland Beckmann. “Structure of the Signal Recognition Particle Interacting with the Elongation-Arrested Ribosome.” Nature 427, no. 6977 (February 26, 2004): 808–814. doi:10.1038/nature02342. | ||
| + | # Huang, Qiaojia, Sayran Abdulrahman, Jiaming Yin, and Christian Zwieb. “Systematic Site-Directed Mutagenesis of Human Protein SRP54: Interactions with Signal Recognition Particle RNA and Modes of Signal Peptide Recognition.” Biochemistry 41, no. 38 (September 24, 2002): 11362–11371. | ||
==Contributors== | ==Contributors== | ||
| - | + | Gregoire de Claviere and Hamelin Baptiste</StructureSection><!-- PLEASE DO NOT DELETE THIS TEMPLATE --> | |
{{Sandbox_Reserved_ESBS}} | {{Sandbox_Reserved_ESBS}} | ||
<!-- PLEASE ADD YOUR CONTENT BELOW HERE --> | <!-- PLEASE ADD YOUR CONTENT BELOW HERE --> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | ==Scènes à intégrer== | ||
| - | |||
| - | <scene name='56/568022/Hsrp54m_dimer/1'>hSRP54M Dimer</scene> | ||
| - | <scene name='56/568022/Hsrp54m_h1_to_h7/1'>hSRP54M and its 7 alpha helixes</scene> | ||
| - | <scene name='56/568022/Hsrp54m_core_and_h1/1'>Core and H1</scene> | ||
| - | <scene name='56/568022/Hsrp54m_conserved_residues/1'>Conserved residues</scene> | ||
| - | <scene name='56/568022/Hsrp54m_conserved_residues/2'>Conserved residues 2</scene> | ||
| - | <scene name='56/568022/Hsrp54m_core_and_h1/2'>Conserved residues 3</scene> | ||
| - | <scene name='56/568022/Hsrp54m_groove/1'>Hydrophobic groove</scene> | ||
| - | <scene name='56/568022/Hsrp54m_groove_with_h1/1'>Groove with H1</scene> | ||
| - | <scene name='56/568022/Hsrp54m_rna_bind/1'>Helixes involved in RNA binding</scene> | ||
| - | <scene name='56/568022/Hsrp54m_phe355_and_phe359/1'>Phe355 and Phe359</scene> | ||
| - | <scene name='56/568022/Hsrp54m_arg402_and_arg405/1'>Arg402 and Arg405</scene> | ||
| - | <scene name='56/568022/Hsrp54m_groovev2/1'>hydrophobic groovev2</scene> | ||
| - | <scene name='56/568022/Hsrp54m_rna_bindv2/1'>helices 4,5, 6 and 7</scene> | ||
| - | <scene name='56/568022/Hsrp54m_core_and_h1v2/1'>TextToBeDisplayed</scene> | ||
Current revision
Human SRP54 M-domain
| |||||||||||
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 06/12/2018, through 30/06/2019 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1480 through Sandbox Reserved 1543. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |