We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Atropine
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (2 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='1th6' size=' | + | <StructureSection load='1th6' size='350' side='right' scene='' caption='Phospholipase A2 complex with atropine and sulfate (PDB code [[1th6]])'> |
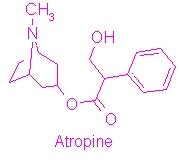
[[Image:Atropine structure.jpg|thumb|right|1000px|Structure of Atropine]] | [[Image:Atropine structure.jpg|thumb|right|1000px|Structure of Atropine]] | ||
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
The proper dose of atropine is approximately 0.1 mg/ml in adults and 0.05 mg/ml in children when taken orally or given intravenously <ref>Atropine. http://www.rxlist.com/atropine-drug.htm </ref>. Atropine can be given orally, intravenously, rectally, or topically, and in veterinary medicine, it can be given intramuscularly or subcutaneously. | The proper dose of atropine is approximately 0.1 mg/ml in adults and 0.05 mg/ml in children when taken orally or given intravenously <ref>Atropine. http://www.rxlist.com/atropine-drug.htm </ref>. Atropine can be given orally, intravenously, rectally, or topically, and in veterinary medicine, it can be given intramuscularly or subcutaneously. | ||
| - | == '''Interaction of Atropine with Phospholipase | + | == '''Interaction of Atropine with Phospholipase A2''' == |
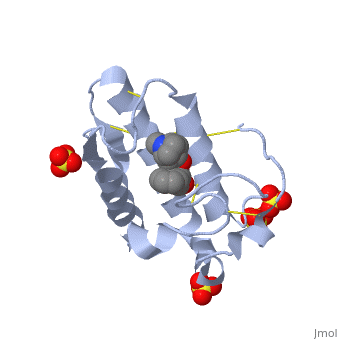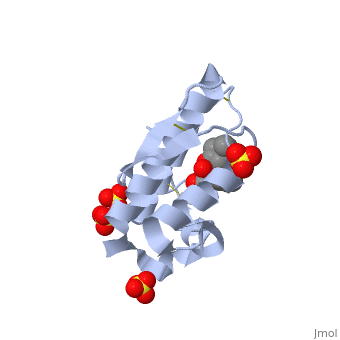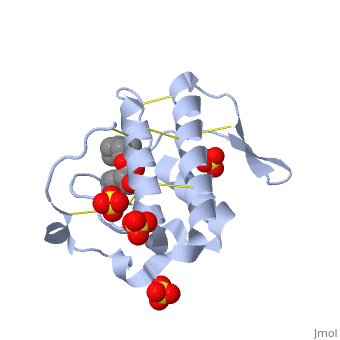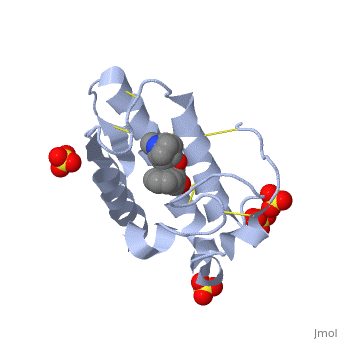
<scene name='42/420811/Cv/1'>Atropine in complex with phospholipase A2</scene> ([[1th6]]). | <scene name='42/420811/Cv/1'>Atropine in complex with phospholipase A2</scene> ([[1th6]]). | ||
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
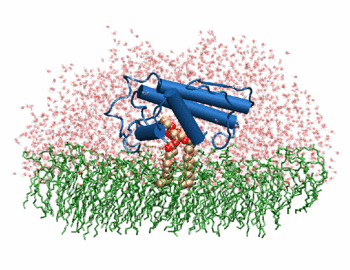
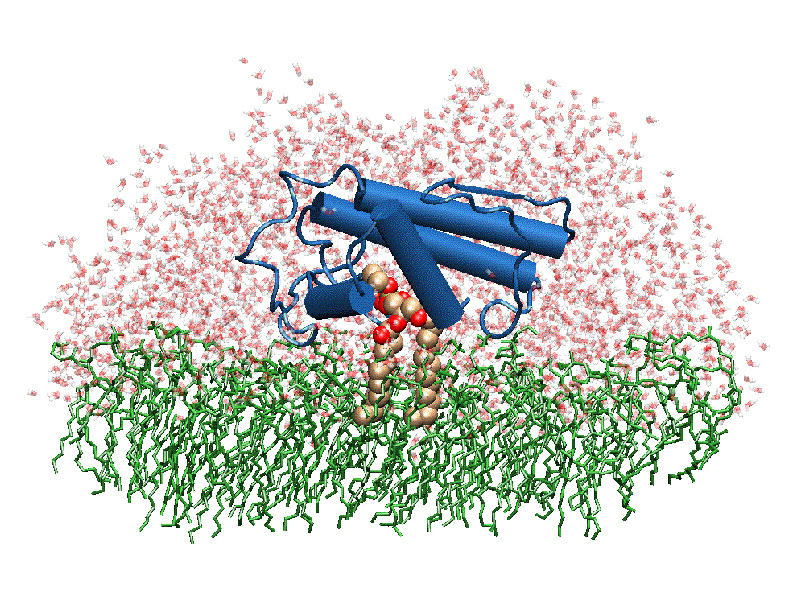
The image to the above shows the membrane-bound phospholipase A2 in blue <ref> pla2. http://www.ks.uiuc.edu/Research/smd_imd/pla2/pla2.gif </ref>. | The image to the above shows the membrane-bound phospholipase A2 in blue <ref> pla2. http://www.ks.uiuc.edu/Research/smd_imd/pla2/pla2.gif </ref>. | ||
| - | ==== '''Atropine in the Active Site of Phospholipase | + | ==== '''Atropine in the Active Site of Phospholipase A2''' ==== |
Atropine is an inhibitor of phospholipase 2A, and can be seen in complex with this enzyme on the left. The <scene name='Sandbox_53/Atropine_structure/1'>structure of atropine</scene> can be seen more clearly in gray using the ball-and stick representation of the drug and protein. It can also be seen in green in this <scene name='Sandbox_53/Phospholipase2a_composition/1'>space-filling model</scene>, where protein appears in brown, ligands appear in green, and solvents appear in blue. Finally, the | Atropine is an inhibitor of phospholipase 2A, and can be seen in complex with this enzyme on the left. The <scene name='Sandbox_53/Atropine_structure/1'>structure of atropine</scene> can be seen more clearly in gray using the ball-and stick representation of the drug and protein. It can also be seen in green in this <scene name='Sandbox_53/Phospholipase2a_composition/1'>space-filling model</scene>, where protein appears in brown, ligands appear in green, and solvents appear in blue. Finally, the | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Atropine. Encyclopedia Brittanica. http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/42015/atropine
- ↑ Atropine. New World Encyclopedia. http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Atropine
- ↑ Atropine. New World Encyclopedia. http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Atropine
- ↑ Atropine. New World Encyclopedia. http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Atropine
- ↑ Atropine. New World Encyclopedia. http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Atropine
- ↑ Gnagey, Ann L; Seidenberg, Margret; Ellis, John; Site-directed mutagenesis reveals two epitopes involved in the subtype selectivity of the allosteric interactions of gallamine at muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Molecular Pharmocology, 56:1245-1253, 1999
- ↑ Atropine. New World Encyclopedia. http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Atropine
- ↑ Parker, Julie C; Sarkar, Deboshree; Quick, Michael W; Lester, Robin A. Interactions of Atropine with heterologously expressed and native alpha3 subunit-containing nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. British Journal of Pharmacology. 138:5. p801-810. 2009.
- ↑ Image from: http://www.neurevolution.net/category/history/page/2/
- ↑ Atropine. New World Encyclopedia. http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Atropine
- ↑ Atropine. New World Encyclopedia. http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Atropine
- ↑ Atropine. New World Encyclopedia. http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Atropine
- ↑ Atropine. New World Encyclopedia. http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Atropine
- ↑ Atropine Diphenoxylate. http://www.everydayhealth.com/drugs/atropine-diphenoxylate
- ↑ Riviere, Jim E. Papich, Mark G. Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 9th Edition. John Wiley and Sons, 2009.
- ↑ ATROPINE- ORAL. http://www.medicinenet.com/atropine-oral/article.htm
- ↑ ATROPINE- ORAL. http://www.medicinenet.com/atropine-oral/article.htm
- ↑ Atropine. http://www.rxlist.com/atropine-drug.htm
- ↑ Kumar, Jainendra; Bala, Priti; Vihwal, Preeti. Analysis of Interaction of atropine with phospholipase A2 (1th6.pdb). Department of Botany and Biotechnlogy, College of Commerce, Patna, India.
- ↑ Phospholipase A2. http://www.worldlingo.com/ma/enwiki/en/Phospholipase_A2
- ↑ Phospholipase A2. http://www.worldlingo.com/ma/enwiki/en/Phospholipase_A2
- ↑ Phospholipase A2. http://www.worldlingo.com/ma/enwiki/en/Phospholipase_A2
- ↑ pla2.
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Lindsey Hayes, David Canner, Alexander Berchansky, Michal Harel, OCA