We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Hepatocyte growth factor
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (11 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
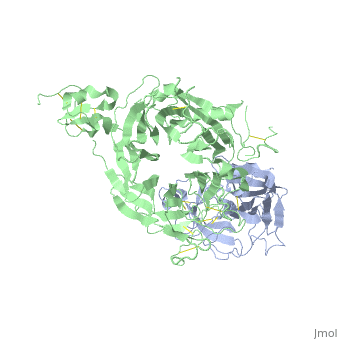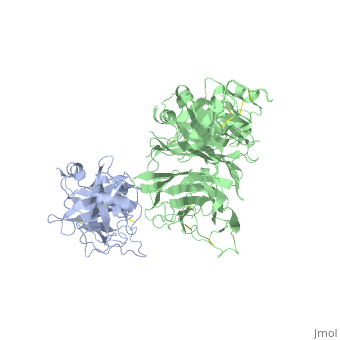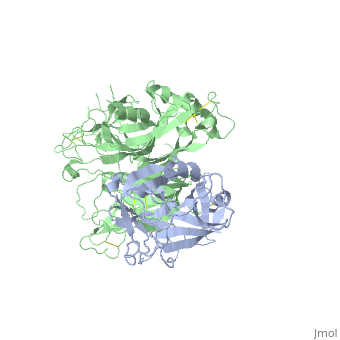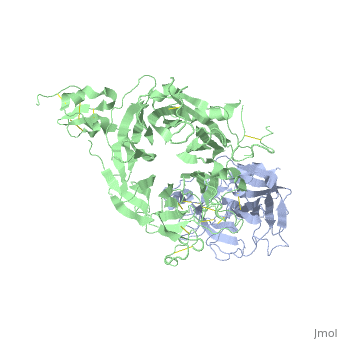
<StructureSection load='1shy' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of human HGF β chain (grey) complex with HGF receptor Sema and ψ domains (green) (PDB entry [[1shy]])' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='1shy' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of human HGF β chain (grey) complex with HGF receptor Sema and ψ domains (green) (PDB entry [[1shy]])' scene=''> | ||
| + | == Function == | ||
| + | '''Hepatocyte growth factor''' (HGF) regulates cell growth, motility and morphogenesis. HGF binds to proto-oncogene c-Met receptor and activates a tyrosine kinase signaling cascade. HGF precursor is cleaved by serine protease to α (69 kD) and β (34 kD) chains which form a disulfide bond to produce the active heterodimer<ref>PMID:1838014</ref>. '''HGF α chain''' contains an N-terminal hairpin and 4 kringle domains. The kringle domain participates in protein-protein interaction and its structure is of a large loop which is stabilized by 3 Cys-Cys bonds. '''HGF β chain''' is catalytically inactive serine protease-like. '''HGF NK1''' - a natural splice variant is comprised of residues 28-210 containing the N-terminus and the first kringle domain of HGF<ref>PMID:9488442</ref>. '''HGF NK2''' variant is comprised of residues 28-289 containing the N-terminus and the first 2 kringle domains of HGF. See also [[Hepatocyte growth factor receptor]]. | ||
| - | + | == Relevance == | |
| + | High levels of HGF are associated with liver diseases<ref>PMID:7806142</ref>, lung diseases, acute cardiac infraction, vascular diseases, renal failure, neurologic diseases like Alzheimer Disease, pancreatic diseases, several types of cancer and diabetes type II<ref>PMID:19154948</ref><ref>PMID:7806142</ref>. HGF administration can reverse liver chirrosis<ref>PMID:12482615</ref>. | ||
| + | </StructureSection> | ||
==3D structures of hepatocyte growth factor== | ==3D structures of hepatocyte growth factor== | ||
Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | ||
| + | {{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | ||
| - | + | *HGF full length 1-728 | |
| - | [[ | + | **[[7mo7]], [[7mo8]], [[7mo9]], [[7moa]], [[7mob]] – hHGF + hHGFR – human – Cryo EM <br /> |
| - | [[ | + | |
| - | [[ | + | |
| - | + | *HGF N terminal 28-126 | |
| - | [[ | + | **[[2hgf]] – hHGF N terminal – human - NMR <br /> |
| - | [[ | + | **[[3hms]], [[3hmt]] – hHGF N terminal <br /> |
| + | **[[3hmr]] – mHGF N terminal – mouse <br /> | ||
| - | + | *HGF NK1 variant 28-210 | |
| - | [[ | + | **[[1bht]], [[1gp9]], [[1nk1]], [[2qj2]], [[2qj4]] – hHGF NK1 <br /> |
| - | [[ | + | **[[5coe]], [[5cs1]], [[5cs5]], [[5cs9]] – hHGF NK1 (mutant) <br /> |
| - | [[ | + | **[[1gmn]], [[1gmo]], [[3mkp]] – hHGF NK1 (mutant) + heparin<br /> |
| + | **[[5cp9]], [[5ct1]], [[5ct2]], [[5ct3]], [[5cs3]], [[5csq]] – hHGF NK1 (mutant) + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4d3c]] – hHGF NK1 (mutant) + antibody<br /> | ||
| - | + | *HGF NK2 variant 28-289 | |
| - | [[ | + | **[[3hn4]] – hHGF NK2 <br /> |
| - | [[ | + | **[[3sp8]] – hHGF NK2 (mutant) + heparin<br /> |
| + | **[[4iua]] – mHGF NK2 (mutant) <br /> | ||
| - | + | * HGF α chain (69 kD) 495-728 | |
| + | |||
| + | **[[1si5]] – hHGF α chain (mutant) <br /> | ||
| + | **[[1shy]] – hHGF α chain (mutant) + HGF receptor Sema and ψ domains<br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *HGF β chain 25-567 | ||
| + | |||
| + | **[[4o3t]], [[4o3u]] – hHGF β chain (mutant) + HGF receptor Sema and ψ domains + zymogen activator peptide<br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *HGF α+β chain | ||
| + | |||
| + | **[[4k3j]] – hHGF α (mutant) + β + antibody <br /> | ||
| + | **[[6lz9]] – hHGF α (mutant) + K4 domain 388-494 + antibody <br /> | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
| - | [[4k3j]] – hHGF α (mutant) + β + antibody <br /> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
3D structures of hepatocyte growth factor
Updated on 25-August-2025
References
- ↑ Nakamura T. Structure and function of hepatocyte growth factor. Prog Growth Factor Res. 1991;3(1):67-85. PMID:1838014
- ↑ Jakubczak JL, LaRochelle WJ, Merlino G. NK1, a natural splice variant of hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor, is a partial agonist in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1998 Mar;18(3):1275-83. PMID:9488442
- ↑ Shiota G, Okano J, Kawasaki H, Kawamoto T, Nakamura T. Serum hepatocyte growth factor levels in liver diseases: clinical implications. Hepatology. 1995 Jan;21(1):106-12. PMID:7806142
- ↑ Anan F, Masaki T, Yonemochi H, Takahashi N, Nakagawa M, Eshima N, Saikawa T, Yoshimatsu H. Hepatocyte growth factor levels are associated with the results of 123I-metaiodobenzylguanidine myocardial scintigraphy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism. 2009 Feb;58(2):167-73. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2008.09.009. PMID:19154948 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2008.09.009
- ↑ Shiota G, Okano J, Kawasaki H, Kawamoto T, Nakamura T. Serum hepatocyte growth factor levels in liver diseases: clinical implications. Hepatology. 1995 Jan;21(1):106-12. PMID:7806142
- ↑ Funakoshi H, Nakamura T. Hepatocyte growth factor: from diagnosis to clinical applications. Clin Chim Acta. 2003 Jan;327(1-2):1-23. PMID:12482615