Ketosteroid Isomerase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (17 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
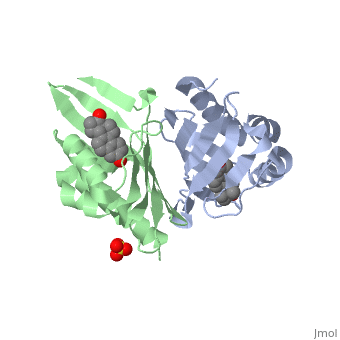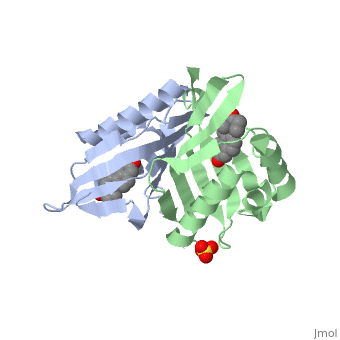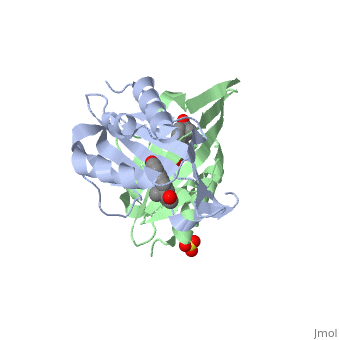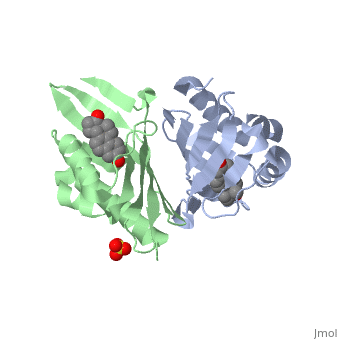
| - | <StructureSection load='1qjg' size=' | + | <StructureSection load='1qjg' size='350' side='right' scene='' caption='Ketosteroid isomerase complex with transition state analog equilenin and sulfate (PDB code [[1qjg]])'> |
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
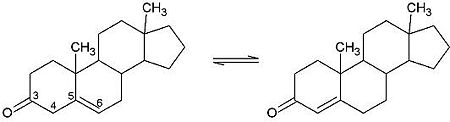
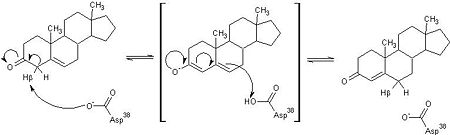
| - | <scene name='User:Laura_M._Haynes/Sandbox_1/Ksi/4'>Ketosteroid isomerase</scene> (KSI, EC#5.3.3.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the isomerization of 3-oxo-Δ<sup>5</sup> ketosteroids to their hormonally active Δ<sup>4</sup>-conjugated isomers, as illustrated below.<ref name="Pollack">PMID:15381400</ref>, <ref name="Talalay">PMID:13276386 </ref> | + | <scene name='User:Laura_M._Haynes/Sandbox_1/Ksi/4'>Ketosteroid isomerase</scene> (KSI, EC#5.3.3.1) or '''steroid delta-isomerase''' is an enzyme that catalyzes the isomerization of 3-oxo-Δ<sup>5</sup> ketosteroids to their hormonally active Δ<sup>4</sup>-conjugated isomers, as illustrated below.<ref name="Pollack">PMID:15381400</ref>, <ref name="Talalay">PMID:13276386 </ref> |
[[Image:Reaction.jpg|left|450px|thumb]] | [[Image:Reaction.jpg|left|450px|thumb]] | ||
| - | This reaction is essential in the biosynthesis of steroids in mammals where KSI is a membrane-bound complex.<ref name="Ha">PMID:11751047</ref> In bacteria, however, KSI exists as a soluble protein is involves in catabolism of steroids.<ref name="Ha" /> It was first isolated in and has been extensively studied in [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Comamonas_testosteroni ''Commamonas tetosteroni''] (TI), a bacteria that is capable of growth with testosterone as its sole carbon source.<ref name="Stanier1966">PMID:11751047</ref> Structural and kinetic studies of this and its homolog from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pseudomonas_putida ''Pseudomonas putida''] with which it shares 34% sequence and near identical structural homology.<ref name="Pollack" />,<ref name="Ha" /> It is one of the most efficient known enzymes with an essentially diffusion limited rate of catalysis.<ref name="Talalay" />,<ref name="Wu">PMID:9103200 </ref> It is capable of increasing the catalytic rate by eleven orders of magnitude.<ref name="Murzin">PMID:9666335 </ref> The high degree of efficiency is believed to be due to a preference for the transition state to move towards products rather than reactants although the exact mechanism of this preference is unclear.<ref name="Pollack" /> Its high catalytic efficiency and unique active site geometry have made it fertile ground for examining the validity of the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Low-barrier_hydrogen_bond low barrier hydrogen bond] hypothesis<ref name="Cleland1998">PMID:9748211 </ref> and electrostatic preorganization.<ref name="Kraut2006">PMID:16602823 </ref>. | + | This reaction is essential in the biosynthesis of steroids in mammals where KSI is a membrane-bound complex.<ref name="Ha">PMID:11751047</ref> In bacteria, however, KSI exists as a soluble protein is involves in catabolism of steroids.<ref name="Ha" /> It was first isolated in and has been extensively studied in [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Comamonas_testosteroni ''Commamonas tetosteroni''] (TI), a bacteria that is capable of growth with testosterone as its sole carbon source.<ref name="Stanier1966">PMID:11751047</ref> Structural and kinetic studies of this and its homolog from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pseudomonas_putida ''Pseudomonas putida''] with which it shares 34% sequence and near identical structural homology.<ref name="Pollack" />,<ref name="Ha" /> It is one of the most efficient known enzymes with an essentially diffusion limited rate of catalysis.<ref name="Talalay" />,<ref name="Wu">PMID:9103200 </ref> It is capable of increasing the catalytic rate by eleven orders of magnitude.<ref name="Murzin">PMID:9666335 </ref> The high degree of efficiency is believed to be due to a preference for the transition state to move towards products rather than reactants although the exact mechanism of this preference is unclear.<ref name="Pollack" /> Its high catalytic efficiency and unique active site geometry have made it fertile ground for examining the validity of the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Low-barrier_hydrogen_bond low barrier hydrogen bond] hypothesis<ref name="Cleland1998">PMID:9748211 </ref> and electrostatic preorganization.<ref name="Kraut2006">PMID:16602823 </ref>. See also [[Isomerases]]. |
==Structure== | ==Structure== | ||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
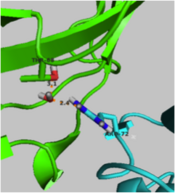
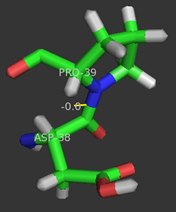
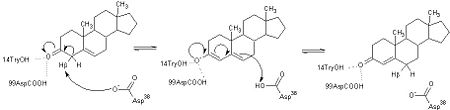
Although the <scene name='User:Laura_M._Haynes/Sandbox_1/Active_site_1isk/1'>active site</scene> of KSI is notably hydrophobic, it contains several hydrophilic residues believed to be important to the enzymatic function of the protein. The hydrophobic active site of KSI contains an aspartate residue at position 99 and a tyrosine residue at position 14 (according to the numbering for the ''Commamonas tetosteroni'' protein, which will be used throughout) that are capable of forming hydrogen bonds with the 3-position carbonyl of the steroid and form an active site oxyanion hole.<ref name="Pollack" />,<ref name="Sigala2008">PMID:18808119 </ref> Additionally, the active site contains an aspartate residue at position 38 that is participates in the catalytic activity of KSI.<ref name="Pollack" /> [[Image:cis.png|thumb|left|'''Cis-Pro39.''']] | Although the <scene name='User:Laura_M._Haynes/Sandbox_1/Active_site_1isk/1'>active site</scene> of KSI is notably hydrophobic, it contains several hydrophilic residues believed to be important to the enzymatic function of the protein. The hydrophobic active site of KSI contains an aspartate residue at position 99 and a tyrosine residue at position 14 (according to the numbering for the ''Commamonas tetosteroni'' protein, which will be used throughout) that are capable of forming hydrogen bonds with the 3-position carbonyl of the steroid and form an active site oxyanion hole.<ref name="Pollack" />,<ref name="Sigala2008">PMID:18808119 </ref> Additionally, the active site contains an aspartate residue at position 38 that is participates in the catalytic activity of KSI.<ref name="Pollack" /> [[Image:cis.png|thumb|left|'''Cis-Pro39.''']] | ||
| - | Upon substrate binding the the three α-helices become more tightly packed with the "front face" of the β-sheet. This in turn allows Tyr14 to approach Asp99 and the substrate. | + | <html5media height=“315” width=“560”>https://www.youtube.com/embed/o6XSjDNyGdw</html5media> |
| - | + | ||
| + | <br>Upon substrate binding the the three α-helices become more tightly packed with the "front face" of the β-sheet. This in turn allows Tyr14 to approach Asp99 and the substrate. | ||
===Cis-Peptide Bond=== | ===Cis-Peptide Bond=== | ||
| Line 113: | Line 114: | ||
Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | ||
| + | {{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | ||
| - | + | *Ketosteroid isomerase | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | **[[1isk]] – CtKSI – ''Comamonas testosteroni'' - NMR<BR /> | |
| + | **[[8cho]] – CtKSI<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[1ocv]], [[3nxj]], [[3mhe]], [[3mki]], [[3myt]], [[3nm2]], [[3t8u]], [[3unl]], [[4l7k]], [[4k1u]], [[4k1v]], [[5dre]] – CtKSI (mutant) <BR /> | ||
| + | **[[1opy]], [[3vsy]], [[6u1z]], [[6ucw]] – PpKSI – ''Pseudomonas putida''<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[1c7h]], [[1dmm]], [[1dmn]], [[1dmq]], [[1e97]], [[1ea2]], [[1k41]], [[1vzz]], [[1w01]], [[1w02]], [[1w6y]], [[1w00]], [[3sed]], [[3ox9]], [[3oxa]], [[3t8n]], [[3rgr]], [[5d81]], [[5d82]], [[5d83]], [[6f4y]], [[6f50]], [[6f53]], [[6f54]], [[6uad]], [[6uae]], [[7rxf]], [[7rxk]] – PpKSI (mutant) <BR /> | ||
| + | **[[5z3r]] – KSI – ''Mycobacterium neoaurum'' <BR /> | ||
| + | **[[6p3l]] – MhKSI – ''Mycobacterium hassiacum'' <BR /> | ||
| + | **[[7epn]] – MsKSI – ''Mycobacterium smegmatis'' <BR /> | ||
| - | + | *Ketosteroid isomerase complexes | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | **[[1buq]] – CtKSI (mutant) + steroid - NMR<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[1qjg]], [[1ogz]], [[3m8c]], [[3ov4]], [[5ugi]] – CtKSI (mutant) + equilenin <BR /> | ||
| + | **[[3nbr]], [[3nhx]], [[3nuv]] – CtKSI (mutant) + androgen derivative <BR /> | ||
| + | **[[1qjg]] – PtKSI (mutant) + equilenin – ''Pseudomonas testosteroni''<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[1e3r]] – PpKSI (mutant) + androgen derivative <BR /> | ||
| + | **[[1oh0]] – PpKSI + equilenin <BR /> | ||
| + | **[[1gs3]], [[1ogx]], [[1cqs]], [[1oho]], [[3fzw]], [[3ipt]], [[3ows]], [[3owu]], [[3owy]], [[5ai1]], [[5g2g]], [[5kp1]], [[5kp3]], [[5kp4]] – PpKSI (mutant) + equilenin <BR /> | ||
| + | **[[6tzd]], [[6ubq]], [[6ucy]] – PpKSI + androstenedione <BR /> | ||
| + | **[[6ufs]] – PpKSI + dihydronandrolone <BR /> | ||
| + | **[[6u4i]], [[6ucn]] – PpKSI + equilenin <BR /> | ||
| + | **[[1e3v]], [[4cdl]] – PpKSI + inhibitor <BR /> | ||
| + | **[[2pzv]], [[2inx]], [[3cpo]], [[3vgn]], [[6c17]], [[6c1j]], [[6c1x]] – PpKSI (mutant) + phenol derivative<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[7ry4]] – PpKSI (mutant) + transition state analog<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[6p44]] – MhKSI (mutant) + phenol derivative<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[1ohp]] – CtKSI (mutant) + estrogen derivative <BR /> | ||
| + | **[[1ohs]] – CtKSI (mutant) + androgen derivative <BR /> | ||
| + | **[[7epo]] – MsKSI + benzoxazole derivative <BR /> | ||
| + | }} | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
3D structures of ketosteroid isomerase
Updated on 13-June-2023
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 Pollack RM. Enzymatic mechanisms for catalysis of enolization: ketosteroid isomerase. Bioorg Chem. 2004 Oct;32(5):341-53. PMID:15381400 doi:10.1016/j.bioorg.2004.06.005
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 TALALAY P, WANG VS. Enzymic isomerization of delta5-3-ketosteroids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1955 Oct;18(2):300-1. PMID:13276386
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 3.8 Ha NC, Choi G, Choi KY, Oh BH. Structure and enzymology of Delta5-3-ketosteroid isomerase. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2001 Dec;11(6):674-8. PMID:11751047
- ↑ Ha NC, Choi G, Choi KY, Oh BH. Structure and enzymology of Delta5-3-ketosteroid isomerase. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2001 Dec;11(6):674-8. PMID:11751047
- ↑ 5.00 5.01 5.02 5.03 5.04 5.05 5.06 5.07 5.08 5.09 5.10 Wu ZR, Ebrahimian S, Zawrotny ME, Thornburg LD, Perez-Alvarado GC, Brothers P, Pollack RM, Summers MF. Solution structure of 3-oxo-delta5-steroid isomerase. Science. 1997 Apr 18;276(5311):415-8. PMID:9103200
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Murzin AG. How far divergent evolution goes in proteins. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1998 Jun;8(3):380-7. PMID:9666335
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Cleland WW, Frey PA, Gerlt JA. The low barrier hydrogen bond in enzymatic catalysis. J Biol Chem. 1998 Oct 2;273(40):25529-32. PMID:9748211
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Kraut DA, Sigala PA, Pybus B, Liu CW, Ringe D, Petsko GA, Herschlag D. Testing electrostatic complementarity in enzyme catalysis: hydrogen bonding in the ketosteroid isomerase oxyanion hole. PLoS Biol. 2006 Apr;4(4):e99. Epub 2006 Mar 28. PMID:16602823 doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0040099
- ↑ Cho HS, Choi G, Choi KY, Oh BH. Crystal structure and enzyme mechanism of Delta 5-3-ketosteroid isomerase from Pseudomonas testosteroni. Biochemistry. 1998 Jun 9;37(23):8325-30. PMID:9622484 doi:10.1021/bi9801614
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Aurora R, Rose GD. Helix capping. Protein Sci. 1998 Jan;7(1):21-38. PMID:9514257 doi:10.1002/pro.5560070103
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Kim DH, Jang DS, Nam GH, Choi KY. Folding mechanism of ketosteroid isomerase from Comamonas testosteroni. Biochemistry. 2001 Apr 24;40(16):5011-7. PMID:11305917
- ↑ Massiah MA, Abeygunawardana C, Gittis AG, Mildvan AS. Solution structure of Delta 5-3-ketosteroid isomerase complexed with the steroid 19-nortestosterone hemisuccinate. Biochemistry. 1998 Oct 20;37(42):14701-12. PMID:9778345 doi:10.1021/bi981447b
- ↑ Kim SW, Cha SS, Cho HS, Kim JS, Ha NC, Cho MJ, Joo S, Kim KK, Choi KY, Oh BH. High-resolution crystal structures of delta5-3-ketosteroid isomerase with and without a reaction intermediate analogue. Biochemistry. 1997 Nov 18;36(46):14030-6. PMID:9369474 doi:10.1021/bi971546+
- ↑ Sigala PA, Kraut DA, Caaveiro JM, Pybus B, Ruben EA, Ringe D, Petsko GA, Herschlag D. Testing geometrical discrimination within an enzyme active site: constrained hydrogen bonding in the ketosteroid isomerase oxyanion hole. J Am Chem Soc. 2008 Oct 15;130(41):13696-708. Epub 2008 Sep 23. PMID:18808119 doi:10.1021/ja803928m
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 Nam GH, Cha SS, Yun YS, Oh YH, Hong BH, Lee HS, Choi KY. The conserved cis-Pro39 residue plays a crucial role in the proper positioning of the catalytic base Asp38 in ketosteroid isomerase from Comamonas testosteroni. Biochem J. 2003 Oct 15;375(Pt 2):297-305. PMID:12852789 doi:10.1042/BJ20030263
- ↑ Cho HS, Ha NC, Choi G, Kim HJ, Lee D, Oh KS, Kim KS, Lee W, Choi KY, Oh BH. Crystal structure of delta(5)-3-ketosteroid isomerase from Pseudomonas testosteroni in complex with equilenin settles the correct hydrogen bonding scheme for transition state stabilization. J Biol Chem. 1999 Nov 12;274(46):32863-8. PMID:10551849
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 Zhao Q, Abeygunawardana C, Talalay P, Mildvan AS. NMR evidence for the participation of a low-barrier hydrogen bond in the mechanism of delta 5-3-ketosteroid isomerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Aug 6;93(16):8220-4. PMID:8710850
- ↑ Zhao Q, Abeygunawardana C, Talalay P, Mildvan AS. NMR evidence for the participation of a low-barrier hydrogen bond in the mechanism of delta 5-3-ketosteroid isomerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Aug 6;93(16):8220-4. PMID:8710850
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 Kraut DA, Sigala PA, Fenn TD, Herschlag D. Dissecting the paradoxical effects of hydrogen bond mutations in the ketosteroid isomerase oxyanion hole. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Feb 2;107(5):1960-5. Epub 2010 Jan 11. PMID:20080683
- ↑ Sigala PA, Caaveiro JM, Ringe D, Petsko GA, Herschlag D. Hydrogen bond coupling in the ketosteroid isomerase active site. Biochemistry. 2009 Jul 28;48(29):6932-9. PMID:19469568 doi:10.1021/bi900713j
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 Cherney MM, Garen CR, James MN. Crystal structure of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rv0760c at 1.50 A resolution, a structural homolog of Delta(5)-3-ketosteroid isomerase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Nov;1784(11):1625-32. Epub 2008 Jun 6. PMID:18589008 doi:10.1016/j.bbapap.2008.05.012
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Laura M. Haynes, Michal Harel, Joel L. Sussman, Alexander Berchansky