Sandbox reserved 916
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (7 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Monoglyceride Lipase (MGL)== | ==Monoglyceride Lipase (MGL)== | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='' size='450' side='right' scene='58/580299/Human_monoglyceride_lipase/1' caption=' | + | <StructureSection load='' size='450' side='right' scene='58/580299/Human_monoglyceride_lipase/1' caption='Monoglyceride Lipase (PDB code [[3JWE]])'> |
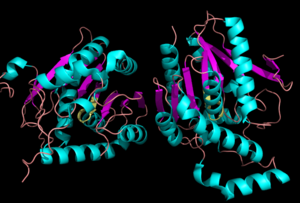
[[Image:Complete_crystal_structure.png|left|300px|thumb|Crystal Structure of MGL]] | [[Image:Complete_crystal_structure.png|left|300px|thumb|Crystal Structure of MGL]] | ||
==Background== | ==Background== | ||
| - | Monoglyceride lipase is part of the α/β hydrolase family, having a Ser-His-Asp catalytic triad (Celemnte et al. 2012). MGL terminates the signaling of a primary endocannabinoid, 2-AG (Savinainen et al 2010). MGL is | + | Monoglyceride lipase is part of the α/β hydrolase family, having a Ser-His-Asp catalytic triad (Celemnte et al. 2012). This enzyme is present in most cells, providing the rate limiting step for MG (Taschler et al 2011). MGL terminates the signaling of a primary endocannabinoid, 2-AG (Savinainen et al 2010). MGL is the main enzyme respondsible for hydrolyzing 2-arachidonoylglycerol into arachidonic acid and glycerol ''in vivo'' (Bertrand et al. 2010). One of the key features of MGL is the hydrophobic tunnel, which has been suggested to provide a model for drug research. |
===Metabolic Role=== | ===Metabolic Role=== | ||
| - | Monoglyceride lipase is able to hydrolyze monoacylglycerols into fatty acids and glycerol (Taschler et al. 2011). MGL degrades sn-1 and 2-MG at identical specific rates as a part of its metabolic role (Taschler et al. 2011). | + | Monoglyceride lipase is able to hydrolyze monoacylglycerols into fatty acids and glycerol, which are able to then be used for energy production (Taschler et al. 2011). MGL degrades sn-1 and 2-MG at identical specific rates as a part of its metabolic role (Taschler et al. 2011). |
===Component of Endocannabinoid System=== | ===Component of Endocannabinoid System=== | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
==Structure== | ==Structure== | ||
| - | MGL has eight-stranded β-sheet protein fold with seven parallel and one <scene name='58/580299/Beta_sheets/1'> antiparallel strand </scene> (Bertrand et al. 2010). | + | Representation of the <scene name='58/580298/Overall_structure/3'>Overall Structure</scene>. MGL has eight-stranded β-sheet protein fold with seven parallel and one <scene name='58/580299/Beta_sheets/1'> antiparallel strand </scene> (Bertrand et al. 2010). |
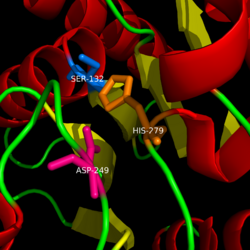
== Catalytic triad == | == Catalytic triad == | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
====Binding==== | ====Binding==== | ||
| - | The ligand binding pocket of MGL has a large hydrophobic region with a polar bottom (Bertrand et al. 2010). Bertrand found that in MGL the binding pocket is not adjusted to the ligands shape. 2-archidonylglycerol are ligands for cannabinoid receptors (Clemente et al. 2012). Inhibition of MGL leads to increase in 2-AG levels since AG is broken down by MGL (Clemente et al. 2012). Through covalent interactions with a Cys residue, NAM, one of the many possible inhibitors, is able to inhibit MGL (Bertrand et al. 2010). | ||
==Ligand Binding Site== | ==Ligand Binding Site== | ||
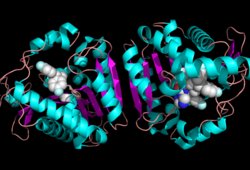
[[Image:Overall_ligand.png|left|250px|thumb|Ligand within the Overall Structure of MGL]] | [[Image:Overall_ligand.png|left|250px|thumb|Ligand within the Overall Structure of MGL]] | ||
| - | + | <scene name='58/580298/Ligand/1'>Ligand binding site</scene> | |
| + | The <scene name='58/580299/Ligand_binding_pocket_take_3/1'> ligand binding pocket </scene> of MGL has a large hydrophobic region with a polar bottom (Bertrand et al. 2010). Bertrand found that in MGL the binding pocket is not adjusted to the ligands shape. 2-archidonylglycerol are ligands for cannabinoid receptors (Clemente et al. 2012). Inhibition of MGL leads to increase in 2-AG levels since AG is broken down by MGL (Clemente et al. 2012). Through covalent interactions with a Cys residue, NAM, one of the many possible inhibitors, is able to inhibit MGL (Bertrand et al. 2010). | ||
==Overall Reaction== | ==Overall Reaction== | ||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
| - | Savinainen, Juha R., Megumi Yoshino, Anna Minkkilä, Tapio Nevalainen, and Jarmo T. Laitinen. "Characterization of Binding Properties of Monoglyceride Lipase Inhibitors by a Versatile Fluorescence-based Technique." Analytical Biochemistry 399.1 (2010): 132-34 | + | -Clemente, J. C., E. Nulton, M. Nelen, M. J. Todd, D. Maguire, C. Schalk-Hihi, L. C. Kuo, S.-P. Zhang, C. M. Flores, and J. K. Kranz. "Screening and Characterization of Human Monoglyceride Lipase Active Site Inhibitors Using Orthogonal Binding and Functional Assays." Journal of Biomolecular Screening 17.5 (2012): 629-40. |
| + | |||
| + | -Savinainen, Juha R., Megumi Yoshino, Anna Minkkilä, Tapio Nevalainen, and Jarmo T. Laitinen. "Characterization of Binding Properties of Monoglyceride Lipase Inhibitors by a Versatile Fluorescence-based Technique." Analytical Biochemistry 399.1 (2010): 132-34 | ||
| + | |||
| + | -Taschler, U., F. P. W. Radner, C. Heier, R. Schreiber, M. Schweiger, G. Schoiswohl, K. Preiss-Landl, D. Jaeger, B. Reiter, H. C. Koefeler, J. Wojciechowski, C. Theussl, J. M. Penninger, A. Lass, G. Haemmerle, R. Zechner, and R. Zimmermann. "Monoglyceride Lipase Deficiency in Mice Impairs Lipolysis and Attenuates Diet-induced Insulin Resistance." Journal of Biological Chemistry 286.20 (2011): 17467-7477 | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Current revision
Monoglyceride Lipase (MGL)
| |||||||||||