Introduction
Heparin is a type of glycosaminoglycan chain that is secreted by human mast cell. Heparin exists in many isoforms and is often sulfated at specific sites. Because of the heterogeneity in structure and distribution of negative charge within those sulfate groups, heparin can bind multiple types of proteins and participate in many different biological processes, such as anti-coagulation. Therefore polysaccharides, the low molecular weight products that are originated from digested heparin was often used in the therapy of many diseases such as atrial fibrillation and thrombosis.
Heparin is usually localized on the surface of cells and the complex with matrix proteins. This interesting discovery suggests that heparin exists in the form of “immobile phase” attaching antithrombin and activates its function as an anticoagulant factor in the circulation system. In an anticoagulant process, antithrombin needs to bind to some coagulant proteases such as Factor Xa or thrombin and “neutralizes” their activity. There are several hypotheses to explain how the heparin chains activate this process. A simple model is that a long heparin chain could be a scaffold to improve the possibility of antithrombin contacting with other proteins.[1] Another direct model is that specific sulfate-containing heparin fragments (oligosaccharides) can allosterically enhance the binding affinity between antithrombin and thrombin or Factor Xa. We are going to describe the structural basis of the second model in the rest of contexts.[2]
Structure features and activation of latent antithrombin
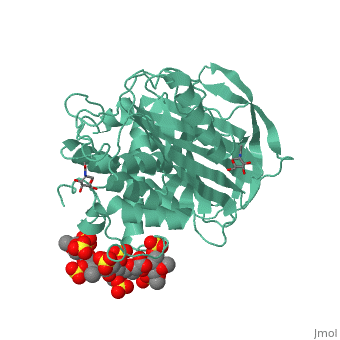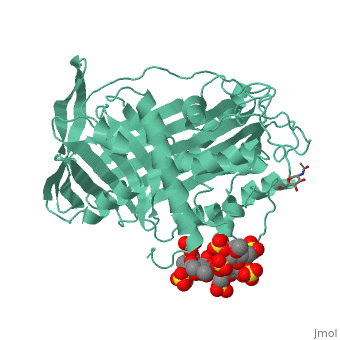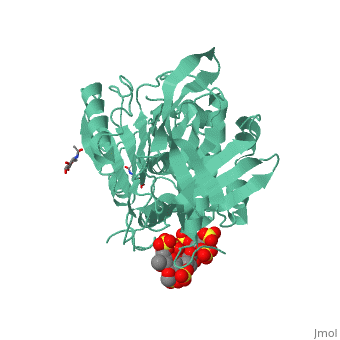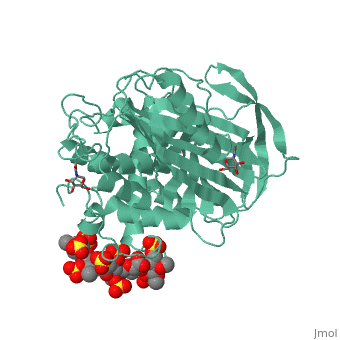
Antithrombin is a natural inhibitor of many serine proteases and it contains an exposed inhibitory loop (shown in blue color in figure 1) to intrude the catalytic site of proteases. The peptide bond between R393-S394 (shown as the sphere model in figure 1) plays a critical role in the inhibitory binding. However, the exposure of the inhibitory loop requires a conformational change during activation. In the latent state of antithrombin, this loop is fully buried in the four-strands beta sheet to form a new five-strands beta sheet. This reversible conformation change effectively switch antithrombin between on- and off-state.
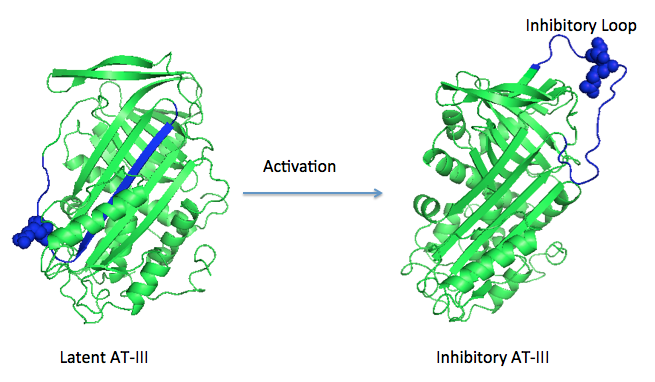
Figure 1 The mechanism of latent antithrombin highlighted by a remarkable conformational rearrangement of the inhibitory loop.
The allosteric mechanism of heparin-based anticoagulant activation
A model of anticoagulant activation of antithrombin by heparin was described as an allosteric mechanism. In another word, heparin chain binds to antithrombin and stabilizes the inhibitory conformation (the inhibitory loop is outward) or alters the antithrombin conformation to facilitate the antithrombin-protease interaction. Early published crystal structure of pentasaccharide-bond antithrombin provided many details of the interaction and validated this hypothesis to some extents.[3] Pentasaccharide binds to the distal to the inhibitory loop, which is pushed outward to make the contact with protease (eg. thrombin or factor Xa) easier. Although the plenty of charge on heparin strongly suggests that majority of interaction between antithrombin and heparin in solution is the electrostatic force, the distance between those two appears to be very close when heparin approaches AT-III during crystallization. This short distance implies that multiple hydrogen bond could be formed on the interface with helical region, supported by the crystal structure. The residues from the helical region of heparin-binding domain that contribute to interaction include Arg129, Lys125, Lys 11, Lys114, Arg13, Asn45, Arg46, Arg47 and Glu113 (shown in lime). Most of those residues are positively charged and can potentially attract the negative charges on sulfate groups of heparin to initialize those sidechains orientation. Interestingly, if comparing with the non-heparin structure of AT-III, some conformation differences are observed in pentasaccharide-binding structure. For example, the attachment of pentasaccharide to the helical region induces a unique . Three positively charged sidechains Lys133, Lys136 and Arg136 on the extended helix are most possible to be affected by the pentasaccharide-bindng. Those secondary structures rearrangement may offer some torsion forces and finally lead the inhibitory loop to shift allosterically.
References
- ↑ Lane DA, Denton J, Flynn AM, Thunberg L, Lindahl U. Anticoagulant activities of heparin oligosaccharides and their neutralization by platelet factor 4. Biochem J. 1984 Mar 15;218(3):725-32. PMID:6721831
- ↑ Olson ST, Bjork I, Sheffer R, Craig PA, Shore JD, Choay J. Role of the antithrombin-binding pentasaccharide in heparin acceleration of antithrombin-proteinase reactions. Resolution of the antithrombin conformational change contribution to heparin rate enhancement. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):12528-38. PMID:1618758
- ↑ Jin L, Abrahams JP, Skinner R, Petitou M, Pike RN, Carrell RW. The anticoagulant activation of antithrombin by heparin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Dec 23;94(26):14683-8. PMID:9405673