We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Ribosome
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (33 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | <StructureSection load='4v42' size='450' side='right' scene='User:Wayne_Decatur/SandboxRibosome/Bothmodels6/1' caption='The Ribosome ([[4v42]])'> | ||
| + | __TOC__ | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
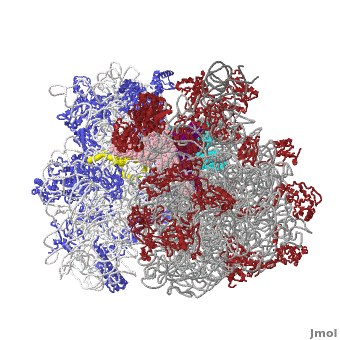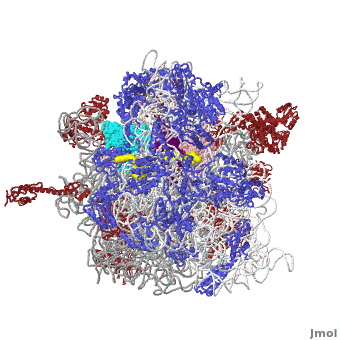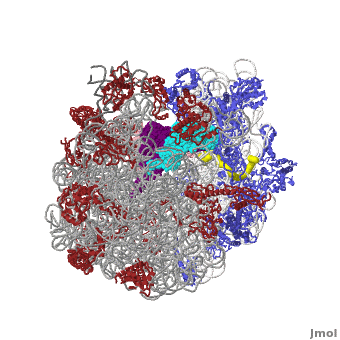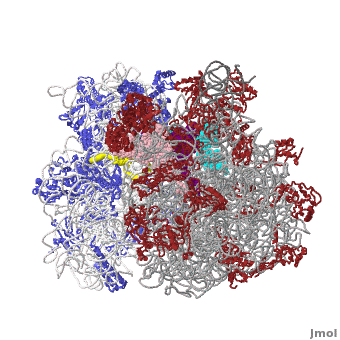
| - | <table width='550' align='right' cellpadding='5'><tr><td rowspan='2'> </td><td bgcolor='#eeeeee'><applet load='1jgo1giy.gz.pdb' size='540' frame='true' align='right' scene='User:Wayne_Decatur/SandboxRibosome/Bothmodels6/1' /></td></tr><tr><td bgcolor='#eeeeee'><center>'''The Ribosome''' ([[1jgo]] and [[1giy]]), resolution 5.5Å (<scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/SandboxRibosome/Bothmodels6/1'>initial scene</scene>). <br> | ||
| - | ·· {{Link Toggle 70SribotRNAs}} ·· {{Link Toggle 70SribomRNA}} ·· {{Link Toggle 70SriborRNA}} ·· {{Link Toggle 70SriboProtein}} ··<br> | ||
| - | ·· {{Link Toggle 70SriboAsitetRNA}} ·· {{Link Toggle 70SriboPsitetRNA}} ·· {{Link Toggle 70SriboEsitetRNA}} ·· <br> | ||
| - | ·· {{Link Toggle 70SriboLSU}} ·· {{Link Toggle 70SriboSSU}} ·· {{Link Toggle BlackWhiteBackground}} ·· <br></center></td></tr></table> | ||
The [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ribosome ribosome] is a complex composed of RNA and protein that adds up to several million daltons in size and plays a critical role in the process of decoding the genetic information stored in the genome into protein as outlined in what is now known as [http://sandwalk.blogspot.com/2009/10/ribosome-and-central-dogma-of-molecular.html the Central Dogma of Molecular Biology]. Specifically, the ribosome carries out the process of translation, decoding the genetic information encoded in messenger RNA, one amino acid at a time, into newly synthesized polypeptide chains. | The [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ribosome ribosome] is a complex composed of RNA and protein that adds up to several million daltons in size and plays a critical role in the process of decoding the genetic information stored in the genome into protein as outlined in what is now known as [http://sandwalk.blogspot.com/2009/10/ribosome-and-central-dogma-of-molecular.html the Central Dogma of Molecular Biology]. Specifically, the ribosome carries out the process of translation, decoding the genetic information encoded in messenger RNA, one amino acid at a time, into newly synthesized polypeptide chains. | ||
| + | *'''30S ribosome''' - prokaryote small subunit | ||
| + | *'''40S ribosome''' - eukaryote small subunit | ||
| + | *'''pre-40S ribosome''' - eukaryote small subunit with associated assembly factors | ||
| + | *'''43S ribosome''' - eukaryote preinitiation small subunit containing eIF3, eIF1 and eIF1A | ||
| + | *'''48S ribosome''' - eukaryote small subunit initiation complex containing Met-tRNA | ||
| + | *'''50S ribosome''' - prokaryote large subunit | ||
| + | *'''60S ribosome''' - eukaryote large subunit | ||
| + | *'''pre-60S ribosome''' - eukaryote nucleolar large subunit with associated assembly factors | ||
| + | *'''70S ribosome''' - prokaryote full ribosome containing small and large subunits | ||
| + | *'''80S ribosome''' - eukaryote full ribosome containing small and large subunits | ||
| + | *'''90S pre-ribosome''' - eukaryote an early biogenesis ribosome intermediate containing assembly factors and small nucleolar RNAs. | ||
| + | *'''100S ribosome''' - a dimer of prokaryote full ribosomes | ||
| + | |||
| - | __TOC__ | ||
==Nobel Prize Winners and Other Contributors== | ==Nobel Prize Winners and Other Contributors== | ||
Venkatraman Ramakrishnan of the M.R.C. Laboratory of Molecular Biology in Cambridge, England; Thomas A. Steitz of Yale University; and Ada E. Yonath of the Weizmann Institute of Science in Rehovot, Israel have been awarded the [http://nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/chemistry/laureates/2009/ the 2009 Nobel Prize in Chemistry]<ref>[[Nobel Prizes for 3D Molecular Structure]].</ref> for their landmark work revealing the atomic details of the molecular machine that make proteins in all cells, [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ribosome the ribosome]. Their findings are the gloriously enlightening culmination of years of work<ref>PMID: 19833925</ref>, first heralded by Ada Yonath's report of crystals in 1980<ref>Yonath A, Mussig J, Tesche B, Lorenz S, Erdmann VA, Wittmann HG. Crystallization of the large ribosomal subunits from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Biochem. Internat. 1980 1:428-435.</ref>. Others made significant contributions to the detailed structure of this machine, as poignantly summarized by [https://loop.nigms.nih.gov/index.php/2009/10/07/2009-chemistry-nobel-prize-recognizes-the-determination-of-the-ribosomes-three-dimensional-structure/ Jeremy Berg, current Director of National Institute of General Medical Sciences, in his announcement] | Venkatraman Ramakrishnan of the M.R.C. Laboratory of Molecular Biology in Cambridge, England; Thomas A. Steitz of Yale University; and Ada E. Yonath of the Weizmann Institute of Science in Rehovot, Israel have been awarded the [http://nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/chemistry/laureates/2009/ the 2009 Nobel Prize in Chemistry]<ref>[[Nobel Prizes for 3D Molecular Structure]].</ref> for their landmark work revealing the atomic details of the molecular machine that make proteins in all cells, [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ribosome the ribosome]. Their findings are the gloriously enlightening culmination of years of work<ref>PMID: 19833925</ref>, first heralded by Ada Yonath's report of crystals in 1980<ref>Yonath A, Mussig J, Tesche B, Lorenz S, Erdmann VA, Wittmann HG. Crystallization of the large ribosomal subunits from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Biochem. Internat. 1980 1:428-435.</ref>. Others made significant contributions to the detailed structure of this machine, as poignantly summarized by [https://loop.nigms.nih.gov/index.php/2009/10/07/2009-chemistry-nobel-prize-recognizes-the-determination-of-the-ribosomes-three-dimensional-structure/ Jeremy Berg, current Director of National Institute of General Medical Sciences, in his announcement] | ||
| Line 18: | Line 28: | ||
==Ribosome Components== | ==Ribosome Components== | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | ·· {{Link Toggle 70SribotRNAs}} ·· {{Link Toggle 70SribomRNA}} ·· {{Link Toggle 70SriborRNA}} ·· {{Link Toggle 70SriboProtein}} ·· {{Link Toggle 70SriboAsitetRNA}} ·· {{Link Toggle 70SriboPsitetRNA}} ·· {{Link Toggle 70SriboEsitetRNA}} ·· {{Link Toggle 70SriboLSU}} ·· {{Link Toggle 70SriboSSU}} ·· {{Link Toggle BlackWhiteBackground}} ·· | ||
| + | |||
The small subunit of the prokaryotic ribosome sediments at 30S<ref>[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Svedberg Svedberg unit] in Wikipedia</ref>. It is composed of a 16S chain of RNA about 1,500 bases long (~500 kDa), plus about 20 protein chains. The proteins in the first small subunit determined range from about 3 kDa to 29 kDa. | The small subunit of the prokaryotic ribosome sediments at 30S<ref>[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Svedberg Svedberg unit] in Wikipedia</ref>. It is composed of a 16S chain of RNA about 1,500 bases long (~500 kDa), plus about 20 protein chains. The proteins in the first small subunit determined range from about 3 kDa to 29 kDa. | ||
| - | The large subunit of the prokaryotic ribosome sediments at 50S. It is composed of two chains of RNA, a 23S chain (~3000 bases long, 946 kDa) and a 5S chain (~120 bases long, 39 kDa). Assembled with the RNA are about 30 protein chains. The proteins in the first large subunit determined range from 6 kDa to 37 kDa. See also [[Large Ribosomal Subunit of Haloarcula]]. | + | The large subunit of the prokaryotic ribosome sediments at 50S. It is composed of two chains of RNA, a 23S chain (~3000 bases long, 946 kDa) and a 5S chain (~120 bases long, 39 kDa). Assembled with the RNA are about 30 protein chains. The proteins in the first large subunit determined range from 6 kDa to 37 kDa. See also [[Large Ribosomal Subunit of Haloarcula]]. The large subunit contains several [[Kink-turn motif]]s. |
| + | |||
| + | The ''mitochindrial ribosome'' or '''mitoribosome''' is smaller than the the cytoplasmic ribosome with a small subunit which sediments at 28S and a large subunit which sediments at 39S. The whole mitoribosome sediments at 55S. | ||
Other macromolecules in a functioning ribosome include three transfer RNA molecules, messenger RNA, and the nascent protein chain. | Other macromolecules in a functioning ribosome include three transfer RNA molecules, messenger RNA, and the nascent protein chain. | ||
| Line 38: | Line 53: | ||
*<b>Yonath lab original atomic-resolution structures</b><ref>PMID: 11007480</ref><ref>PMID: 11733066</ref>: <em>Thermus thermophilus</em> small ribosomal subunit - [[1fka]], improved in [[1i94]], [[1i95]], [[1i96]], and [[1i97]]. <em>Thermus thermophilus</em> is a [[Extremophiles|thermophilic]] eubacteria. <em>Deinococcus radiodurans</em> large ribosomal subunit - [[1nkw]], later refined to give [[2zjr]]. <em>Deinococcus radiodurans</em> is a mesophilic eubacteria.<br> | *<b>Yonath lab original atomic-resolution structures</b><ref>PMID: 11007480</ref><ref>PMID: 11733066</ref>: <em>Thermus thermophilus</em> small ribosomal subunit - [[1fka]], improved in [[1i94]], [[1i95]], [[1i96]], and [[1i97]]. <em>Thermus thermophilus</em> is a [[Extremophiles|thermophilic]] eubacteria. <em>Deinococcus radiodurans</em> large ribosomal subunit - [[1nkw]], later refined to give [[2zjr]]. <em>Deinococcus radiodurans</em> is a mesophilic eubacteria.<br> | ||
| - | *<b>Ramakrishnan lab original atomic-resolution structures</b><ref>PMID: 11014182</ref><ref>PMID: 11014183</ref>: <em>Thermus thermophilus</em> small ribosomal subunit | + | *<b>Ramakrishnan lab original atomic-resolution structures</b><ref>PMID: 11014182</ref><ref>PMID: 11014183</ref>: <em>Thermus thermophilus</em> small ribosomal subunit in [[1j5e]]. Related: in complex with the antibiotics streptomycin, spectinomycin, and paromomycin in [[1fjg]]; in complex with tetracycline in [[1hnw]], pactamycin in [[1hnx]], hygromycin B in [[1hnz]]. |
The <em>Thermus thermophilus</em> small ribosomal subunit is composed of a 16S chain of RNA about 1,522 bases long (494 kDa), plus 20 protein chains (S2-S20, THX). The protein chains range from 26 (THX, 3 kDa) to 256 amino acids (S2, 29 kDa). | The <em>Thermus thermophilus</em> small ribosomal subunit is composed of a 16S chain of RNA about 1,522 bases long (494 kDa), plus 20 protein chains (S2-S20, THX). The protein chains range from 26 (THX, 3 kDa) to 256 amino acids (S2, 29 kDa). | ||
| Line 46: | Line 61: | ||
*[[Large Ribosomal Subunit of Haloarcula|The Large Ribosomal Subunit]] as solved by the Steitz & Moore labs.<br> | *[[Large Ribosomal Subunit of Haloarcula|The Large Ribosomal Subunit]] as solved by the Steitz & Moore labs.<br> | ||
*[[User:Wayne Decatur/Interactions between Antibiotics and the Ribosome|Interactions between Antibiotics and the Ribosome]]<br> | *[[User:Wayne Decatur/Interactions between Antibiotics and the Ribosome|Interactions between Antibiotics and the Ribosome]]<br> | ||
| + | *[[Large Ribosomal Subunit of Haloarcula]]<br /> | ||
*[[User:Wayne_Decatur/Haloarcula Large Ribosomal Subunit With Azithromycin|Azithromycin bound to the Large Ribosomal Subunit of Haloarcula marismortui]]<br> | *[[User:Wayne_Decatur/Haloarcula Large Ribosomal Subunit With Azithromycin|Azithromycin bound to the Large Ribosomal Subunit of Haloarcula marismortui]]<br> | ||
| + | *[[Azithromycin]]<br /> | ||
| + | *[[Clarithromycin]]<br /> | ||
| + | *[[Doxycycline]]<br /> | ||
| + | *[[40S rRNA and proteins and P/E tRNA for eukaryotic ribosome]]<br /> | ||
| + | *[[Ribosomal A Site Binding Paromomycin: A Morph]]<br /> | ||
| + | *[[Large Ribosomal Subunit of Haloarcula|The Large Ribosomal Subunit]]<br /> | ||
| + | *[[Ribosome structure]]<br /> | ||
| + | *[[Ribosome structure (Spanish)]]<br /> | ||
| + | *[[Ribosome (Czech)]]<br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Ribosome 3D structures== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Ribosome 3D structures]] | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
| - | + | ||
* [[Nobel Prizes for 3D Molecular Structure]] | * [[Nobel Prizes for 3D Molecular Structure]] | ||
* [[Highest impact structures]] of all time | * [[Highest impact structures]] of all time | ||
| Line 55: | Line 84: | ||
* [[DNA Replication, Transcription and Translation]] | * [[DNA Replication, Transcription and Translation]] | ||
* [[tRNA]] | * [[tRNA]] | ||
| - | * [[Large Ribosomal Subunit of Haloarcula|The Large Ribosomal Subunit]] | ||
* [[LepA|Escherichia coli LepA, the ribosomal back translocase]] | * [[LepA|Escherichia coli LepA, the ribosomal back translocase]] | ||
* [[Extremophiles]] | * [[Extremophiles]] | ||
| - | *[[RNA]] | + | * [[RNA]] |
* [[Ribozyme]] | * [[Ribozyme]] | ||
| + | * For Spanish see [[Ribosoma 70S]] | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| Line 74: | Line 103: | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
[[Category:Translation]] | [[Category:Translation]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Ribosome]] | ||
| + | [[Category: BioMolViz]] | ||
| + | [[Category: Macromolecular Assemblies]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Wayne Decatur, Michal Harel, Jaime Prilusky, Eric Martz, Alexander Berchansky, Joel L. Sussman, Eran Hodis, David Canner, Margaret Franzen