Poly (ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (13 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
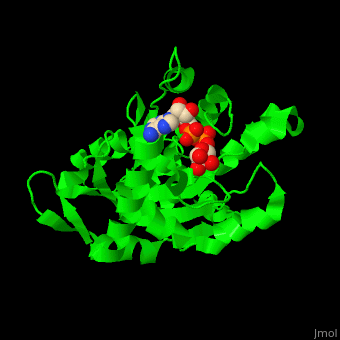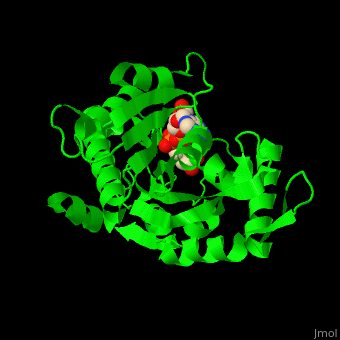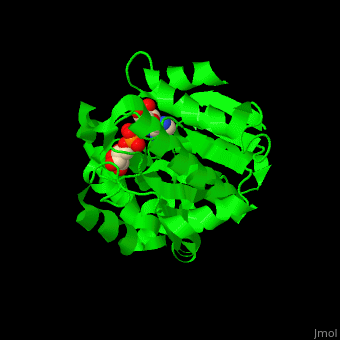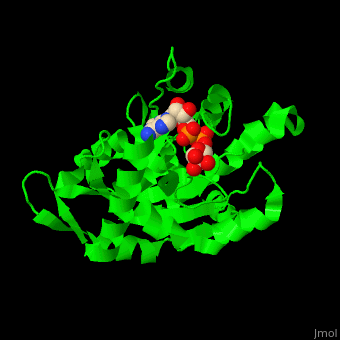
| - | <StructureSection load=' | + | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of human poly (ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase catalytic domain complex with ADP-ribose (PDB code [[3sig]]). ' scene='59/595759/Cv/1'> |
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | '''Poly (ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase''' (PARG) hydrolizes the ribose-ribose bonds in poly (ADP-ribose). Poly (ADP-ribose) are synthesized after DNA damage. PARG acts as both endo- and exoglycosidase and releases poly (ADP-ribose) of different lengths including monomers. | + | '''Poly (ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase''' (PARG) hydrolizes the ribose-ribose bonds in poly (ADP-ribose). Poly (ADP-ribose) are synthesized after DNA damage. PARG acts as both endo- and exoglycosidase and releases poly (ADP-ribose) of different lengths including monomers<ref>PMID:11376691</ref>. |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
== Relevance == | == Relevance == | ||
| - | PARG deficiency leads to cell death. | + | PARG deficiency leads to cell death. Over-activation of PARP due to oxidative stress culminates in cell dysfunction and necrosis. PARP inhibitors have anti-inflammatory effect<ref>PMID:12223530</ref>. |
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| + | The <scene name='59/595759/Cv/4'>active site</scene> of PARG contains <scene name='59/595759/Cv/5'>two catalytic glutamic acid residues</scene><ref>PMID:21892188</ref>. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. | ||
== 3D Structures of poly (ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase == | == 3D Structures of poly (ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase == | ||
| + | [[Poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase 3D structures]] | ||
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Herceg Z, Wang ZQ. Functions of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) in DNA repair, genomic integrity and cell death. Mutat Res. 2001 Jun 2;477(1-2):97-110. PMID:11376691
- ↑ Virag L, Szabo C. The therapeutic potential of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors. Pharmacol Rev. 2002 Sep;54(3):375-429. PMID:12223530
- ↑ Slade D, Dunstan MS, Barkauskaite E, Weston R, Lafite P, Dixon N, Ahel M, Leys D, Ahel I. The structure and catalytic mechanism of a poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase. Nature. 2011 Sep 4. doi: 10.1038/nature10404. PMID:21892188 doi:10.1038/nature10404