We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox bcce04
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (13 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
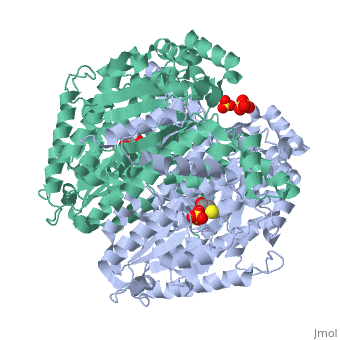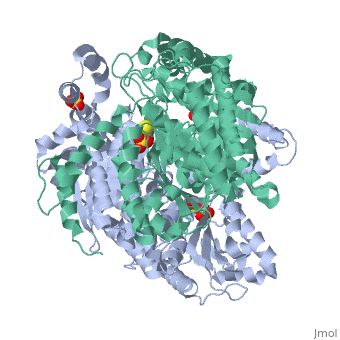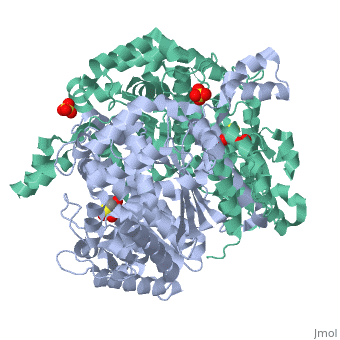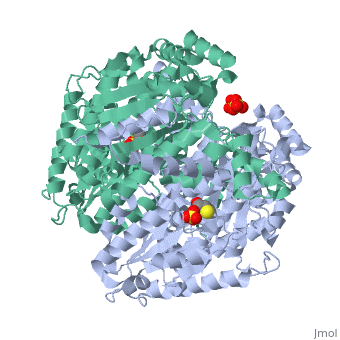
<StructureSection load='1iat' size='450' side='right' scene='' caption=''> | <StructureSection load='1iat' size='450' side='right' scene='' caption=''> | ||
| - | '''Imaginaryase''' (alternatively known as '''imaginary isomerase''' or '''imaginary- | + | '''Imaginaryase''' (alternatively known as '''imaginary isomerase''' or '''imaginary-6-phosphate isomerase''') are a group of enzymes of the isomerase family ([[EC]] 5.3.a.b), so named for their main function in metabolism. In this pathway imaginary isomerase (IGI) is used to inter-convert imaginary-6-phosphate and reality-6-phosphate. |
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
* Something my prof thinks is cool <ref>4</ref>. | * Something my prof thinks is cool <ref>4</ref>. | ||
* Something really boring <ref>5</ref>. | * Something really boring <ref>5</ref>. | ||
| - | + | ||
=='''Structure'''== | =='''Structure'''== | ||
| - | [[Image:Align.jpg|thumb|left|'''Figure 1.''' Multiple alignment IGI - ''Geobacillus stearothermophilus'' (white),'' Homo sapiens'' (pink), ''Oryctolagus cuniculus'' (blue)<ref> Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, Couch GS, Greenblatt DM, Meng EC, Ferrin TE. UCSF Chimera--a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem. 2004 Oct;25(13):1605-12. </ref>]] | ||
| - | |||
| - | Imaginary isomerase exists in the cell usually as a <scene name='Stancu_Phosphoglucoisomerase_Sandbox_1/Dimer/1'>homodimer</scene>, nevertheless outside of the cell, it has been isolated as a <scene name='Stancu_Phosphoglucoisomerase_Sandbox_1/Monomer/1'>monomeric</scene> structure. IGI has essentially an identical fold in all of the characterized species (see '''Figure 1'''). The <scene name='Stancu_Phosphoglucoisomerase_Sandbox_1/Sec_struct/1'>secondary structure</scene> of imaginary isomerase is charaterized by an αβα conformation, on each of its two domains. The smaller domain is characterized by 5 parallel β-sheets, while the larger domain if formed out of 6 parallel/antiparallel β-sheets. Furthermore, another characteristic trait is a residue extension at the C-terminus, which wraps around the other monomer in the dimeric conformation. A "hook" that can potentially be involved in the previously mentioned extracellular activities. | ||
| - | |||
| - | Imaginary isomerase has a monomer molecular mass of proximately 55 kDa. | ||
| - | |||
| + | Imaginary isomerase exists in cells usually as a <scene name='Stancu_Phosphoglucoisomerase_Sandbox_1/Dimer/1'>homodimer</scene>, nevertheless outside of cells, it has been isolated as a <scene name='Stancu_Phosphoglucoisomerase_Sandbox_1/Monomer/1'>monomeric</scene> structure. The <scene name='Stancu_Phosphoglucoisomerase_Sandbox_1/Sec_struct/1'>secondary structure</scene> of imaginary isomerase is characterized by a conformation, on each of its two domains. Fill in the information here to give more detail. | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
=='''Mechanism'''== | =='''Mechanism'''== | ||
| - | The proposed reaction mechanism of PGI for the reversible conversion of glucose-6-phosphate to fructose 6-phosphate involves an acid/base catalysis by the enzyme. The basic mechanism involves the isomerization of an aldose to a ketose. This is performed by a ring opening, followed by an isomeration of the opened ring, then a ring closing. A detailed step by step mechanism of this process can be seen as follows <ref> Voet D, Voet J, and Pratt C. Fundamentals of Biochemistry Life at the Molecular Level. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 2008. Print.</ref>: | ||
| - | |||
| - | '''Step 1.''' The substrate binds to the enzyme. | ||
| - | |||
| - | '''Step 2.''' The residue Lys518 (or His388b) acts as an enzymatic acid catalyzing the opening of the ring. | ||
| - | |||
| - | '''Step 3.''' Conserved Glu357 abstracts the acidic proton from C2 forming a cis-enendiol intermediate. | ||
| - | |||
| - | '''Step 4.''' Glu357 donates back the proton at the C1 position. | ||
| - | |||
| - | '''Step 5.''' Lys518 (or His388b) abstracts back the proton from the sugar ring oxygen, resulting in a ring closure, to give the product. | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[Image:Mech.png]] | ||
=='''Regulation and Inhibition'''== | =='''Regulation and Inhibition'''== | ||
| - | '''Regulation''' of phosphoglucoisomerase is only done by the relative concentrations of glucose-6-phosphate and fructose 6-phosphate, towards equilibrium. Nevertheless, it was found that the kinetic parameters of PGI does depend on the pH and temperature of the environment. | ||
| - | The following kinetic parameters are proposed for rabbit PGI at pH 8.5 and 30°C <ref>PMID: 5647261</ref> | ||
| + | ==3D structures of Imaginary isomerase== | ||
| - | + | ==Additional Resources== | |
| - | |||
| - | It is interesting to point the regulation of PGI in other aspects that are not involved in metabolism. For example, PGI acts as a "cytokine" outside the cell in that it can be used as a cell signalling protein. PGI has been found to to be associated with AMF cells, which is found to regulate tumor cell motility. Regulation of these extracellular "cytokine" PGI/AMF can be seen. The amount of PGI/AMF that is secreted inside and outside the cell based on infection <ref> Funasaka T, Hu H, Yanagawa T, Hogan V, Raz A. Down-Regulation of Phosphoglucose Isomerase/Autocrine Motility Factors Results in Mesenchymal-to-Epithelial Transition of Human Lung Fibrosarcoma Cells. (2007) Cancer Res, 76(9) </ref>. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | '''Inhibition''' of the phosphoglucoisomerase regulated reaction of glucose-6-phosphate to fructose-6-phosphate can also occur. Competitive competition can take place from inhibitors such as 5PAH. 5PAH resembles PGI, differing only in a nitrogen atom at the first carbon position. 5PAH is reported to have a Ki of .0000002 M <ref> Arsenieva D, Hardre R, Salmon L, Jeffery CJ. The crystal structure of rabbit phosphoglucose isomerase complex with 5-phospho-D-arabinonohydroxamic acid. (2002),PNAS, 99(9) </ref>. | ||
| - | =='''Links'''== | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | * Crystal Structure of human phosphoglucose isomerase (PDB=[[1iat]]) | ||
| - | |||
| - | * Crystal Structure of rabbit phosphoglucose isomerase complexed fructose 6-phosphate (PDB=[[1hox]]<ref>PMID:11425306</ref>) | ||
| - | |||
| - | * Other available structures [[1dqr]], [[1g98]], [[1gzd]], [[1gzv]], [[1hm5]], [[1iri]], [[1jiq]], [[1jlh]], [[1koj]], [[1n8t]], [[1nuh]], [[1xtb]]. | ||
| - | |||
| - | ==3D structures of phosphoglucose isomerase== | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===PGI=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[2pgi]], [[1b0z]] – GsPGI – ''Geobacillus stearothermophilus''<br /> | ||
| - | [[1dqr]], [[1hm5]], [[1n8t]] – rPGI – rabbit<br /> | ||
| - | [[1iat]], [[1jlh]] – hPGI – human<br /> | ||
| - | [[1qxj]], [[1x8e]], [[3sxw]] – PfPGI – ''Pyrococcus furiosus''<br /> | ||
| - | [[1j3p]], [[1j3q]] – TlPGI – ''Thermococcus litoralis''<br /> | ||
| - | [[1q50]] – LmPGI – ''Leishmania Mexicana''<br /> | ||
| - | [[1u0e]], [[2cvp]] – mPGI – mouse<br /> | ||
| - | [[2q8n]] – PGI – ''Thermotoga maritima''<br /> | ||
| - | [[3hjb]] – PGI – ''Vibrio cholera''<br /> | ||
| - | [[3ifs]] – PGI – ''Bacillus anthracis''<br /> | ||
| - | [[2wu8]] – PGI – ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis''<br /> | ||
| - | [[3ljk]] – FtPGI (mutant) – ''Francisella tularensis''<br /> | ||
| - | [[3nbu]] – PGI – ''Escherichia coli'' | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===PGI complex with fructose-6-phosphate=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[1hox]] – rPGI + fructose-6-phosphate<br /> | ||
| - | [[1t10]] - LmPGI + fructose-6-phosphate<br /> | ||
| - | [[2gc2]] - PfPGI + fructose-6-phosphate<br /> | ||
| - | [[2cxs]], [[2cxt]] - mPGI + fructose-6-phosphate<br /> | ||
| - | [[3m5p]] - FtPGI (mutant) + fructose-6-phosphate<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===PGI complex with sorbitol-6-phosphate=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[1xtb]] - rPGI + sorbitol-6-phosphate<br /> | ||
| - | [[2gc1]] - PfPGI + sorbitol-6-phosphate<br /> | ||
| - | [[2cxq]] - mPGI + sorbitol-6-phosphate<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===PGI complex with phosphoarabinose=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[1gzd]], [[1gzv]] – PGI + phosphoarabinose – pig<br /> | ||
| - | [[1c7r]] - GsPGI + phosphoarabinose<br /> | ||
| - | [[2cxp]] – mPGI + phosphoarabinose<br /> | ||
| - | [[1nuh]] - hPGI + phosphoarabinose<br /> | ||
| - | [[1qsr]], [[1x7n]], [[1x82]] - PfPGI + phosphoarabinose<br /> | ||
| - | [[2gc0]] - PfPGI + phosphoarabinose derivative<br /> | ||
| - | [[1koj]] – rPGI + phosphoarabinose derivative | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===PGI complex with gluconate-6-phosphate=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[1qy4]] - PfPGI + gluconate-6-phosphate<br /> | ||
| - | [[1j3r]] - TlPGI + gluconate-6-phosphate<br /> | ||
| - | [[2cxr]] - mPGI + gluconate-6-phosphate<br /> | ||
| - | [[3q7i]] - FtPGI (mutant) + gluconate-6-phosphate<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===PGI complex with glucose-6-phosphate=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[1u0f]] - mPGI + glucose-6-phosphate<br /> | ||
| - | [[3ff1]] - PGI + glucose-6-phosphate – ''Staphylococcus aureus''<br /> | ||
| - | [[2o2c]] - TbPGI + glucose-6-phosphate – ''Trypanosoma brucei'' | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===Other PGI binary complexes=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[2o2d]] – TbPGI + citrate<br /> | ||
| - | [[1u0g]], [[2cxo]] - mPGI + erythrose-4-phosphate<br /> | ||
| - | [[3q88]] – FtPGI (mutant) + ribose bisphosphate<br /> | ||
| - | [[1c7q]] – GsPGI + phosphate inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | [[2cxn]], [[2cxu]] – mPGI + phosphate<br /> | ||
| - | [[1g98]] – rPGI + transition state analog<br /> | ||
| - | [[2gc3]] - PfPGI + mannose-6-phosphate<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | ==Additional Resources== | ||
| - | For additional information, see: [[Carbohydrate Metabolism]] | ||
| - | <br /> | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Current revision
Imaginary Protein
| |||||||||||