This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox bcce14
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (12 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | ==BCCE14: | + | ==BCCE14: The amazing protein== |
| - | <StructureSection load=' | + | <StructureSection load='1pgb' size='300' side='right' caption='BCCE14' scene=''> |
This is a default text for your page '''Sandbox bcce14'''. Click above on '''edit this page''' to modify. Be careful with the < and > signs. | This is a default text for your page '''Sandbox bcce14'''. Click above on '''edit this page''' to modify. Be careful with the < and > signs. | ||
You may include any references to papers as in: the use of JSmol in Proteopedia <ref>DOI 10.1002/ijch.201300024</ref> or to the article describing Jmol <ref>PMID:21638687</ref> to the rescue. | You may include any references to papers as in: the use of JSmol in Proteopedia <ref>DOI 10.1002/ijch.201300024</ref> or to the article describing Jmol <ref>PMID:21638687</ref> to the rescue. | ||
| - | [[Image: | + | [[Image:picture.jpg]] |
== Function == | == Function == | ||
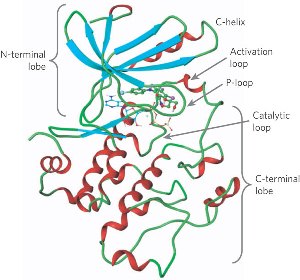
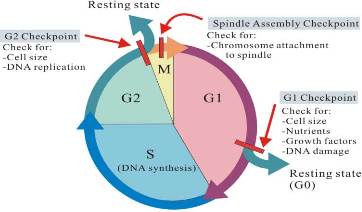
| - | This protein is a tyrosine kinase that is active in the progression of a cell through the G2/M checkpoint. | + | This protein is a tyrosine kinase that is active in the progression of a cell through the G2/M checkpoint. |
| + | [[Image:Cell_cycle_check_points.jpg]] | ||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
Mutations in the C terminal end of the protein have been associated with excessive kinase activity. It has been implicated in aggressive forms of breast cancer. | Mutations in the C terminal end of the protein have been associated with excessive kinase activity. It has been implicated in aggressive forms of breast cancer. | ||
| Line 12: | Line 13: | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| + | <scene name='59/596448/N_to_c_rainbow/2'>N to C sequence</scene> | ||
| + | {{Template:ColorKey_Amino2CarboxyRainbow}} | ||
| + | <scene name='59/596448/Secondary_structure/1'>Secondary Structures</scene> | ||
| + | {{Template:ColorKey_Helix}} | ||
| + | {{Template:ColorKey_Strand}} | ||
| + | {{Template:ColorKey_Turn}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <scene name='59/596448/Hydrophobic_hydrophilic_residu/1'>hydrophobic and hydrophilic residues</scene> | ||
| + | {{Template:ColorKey_Hydrophobic}}, {{Template:ColorKey_Polar}} | ||
This is a sample scene created with SAT to <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/1">color</scene> by Group, and another to make <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/2">a transparent representation</scene> of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes. | This is a sample scene created with SAT to <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/1">color</scene> by Group, and another to make <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/2">a transparent representation</scene> of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes. | ||
Current revision
BCCE14: The amazing protein
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644