This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Exosome
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (10 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Exosome== | ==Exosome== | ||
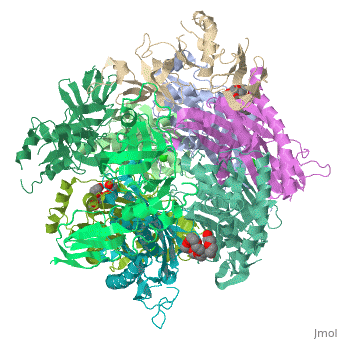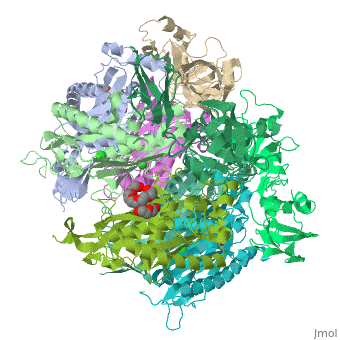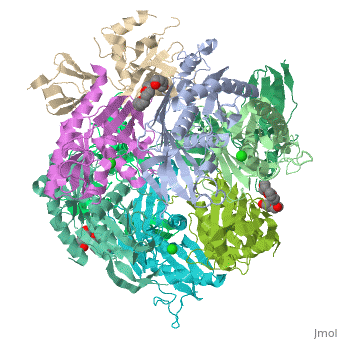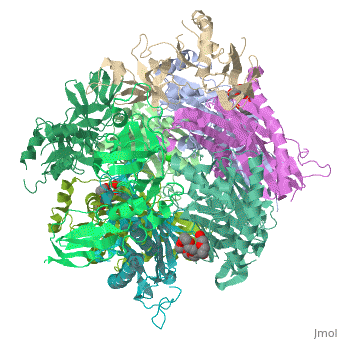
| - | <StructureSection load=' | + | <StructureSection load='2je6' size='340' side='right' caption='Exosome complex containing exonuclease 1 (green), exonuclease 2 (grey) and exosome complex RNA-binding protein 1 (wheat) complex with PEG400 (pdb code [[2je6]]).' scene=''> |
| - | The Exosome complex (or just- Exosome) is a multi-protein complex capable of degrading various types of RNA molecules. The Exosome complex is found in eukaryotic cell, and also in archaea, while in bacteria it is found as a simpler complex (but it has the same function). <ref>http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Exosome_complex#Structure</ref> | + | The '''Exosome complex''' (or just- Exosome) is a multi-protein complex capable of degrading various types of RNA molecules. The Exosome complex is found in eukaryotic cell, and also in archaea, while in bacteria it is found as a simpler complex (but it has the same function). <ref>http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Exosome_complex#Structure</ref> |
| + | |||
| + | Some of the exosome components are:<br /> | ||
| + | *'''MTR3''' and '''SKI6''' are part of RNase PH domain-containing subunits proposed to form a central channel which threads RNA for degradation.<br /> | ||
| + | *'''MTR4''' interacts with Nop53 and together they have a role in the maturation of 5.8S rRNA<ref>PMID:28883156</ref>.<br /> | ||
| + | *'''M-phase phosphoprotein 6''' is involved in the 3'-processing of the 7S pre-RNA to the mature 5.8S rRNA. | ||
| + | |||
| + | __TOC__ | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
In order to see the structure of the protein complex, press <scene name='60/609824/2nn6/8'>Exosome</scene>. | In order to see the structure of the protein complex, press <scene name='60/609824/2nn6/8'>Exosome</scene>. | ||
| - | + | ===Enzymatic function=== | |
The exosome is primarily a 3'-5' exoribonuclease, meaning that it degrades RNA molecules from their 3' end. In eukaryotes it also have an endoribonucleolytic function, meaning it cleaves RNA at sites within the molecule. | The exosome is primarily a 3'-5' exoribonuclease, meaning that it degrades RNA molecules from their 3' end. In eukaryotes it also have an endoribonucleolytic function, meaning it cleaves RNA at sites within the molecule. | ||
| - | + | ===Substrates=== | |
The exosome is involved in the degradation and processing of a wide variety of RNA species. Substrates of the exosome include messenger RNA, ribosomal RNA, and many species of small RNAs. | The exosome is involved in the degradation and processing of a wide variety of RNA species. Substrates of the exosome include messenger RNA, ribosomal RNA, and many species of small RNAs. | ||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
| - | + | ===Autoimmunity=== | |
The exosome complex is the target of autoantibodies, which are known to be found in people that suffer from various autoimmune diseases (especially PM/Scl overlap syndrome). In the autoimune diseases, antibodies are mainly directed against two of the proteins of the complex, called PM/Scl-100 and PM/Scl-75. | The exosome complex is the target of autoantibodies, which are known to be found in people that suffer from various autoimmune diseases (especially PM/Scl overlap syndrome). In the autoimune diseases, antibodies are mainly directed against two of the proteins of the complex, called PM/Scl-100 and PM/Scl-75. | ||
| - | + | ===Cancer treatment=== | |
The Exosome is found to be inhibited by a cancer chemotherapy drug, which called antimetabolite fluorouracil. This drug is one of the most successful drugs for treating solid tumors. | The Exosome is found to be inhibited by a cancer chemotherapy drug, which called antimetabolite fluorouracil. This drug is one of the most successful drugs for treating solid tumors. | ||
| - | + | ===Neurological disorders=== | |
Mutations in Exosome component 3 cause pontocerebellar hypoplasia and spinal motor neuron disease. | Mutations in Exosome component 3 cause pontocerebellar hypoplasia and spinal motor neuron disease. | ||
| Line 28: | Line 35: | ||
The core of the Exosome complex is made of a ring, which is consisting of six RNases proteins (Rnase PH-like proteins), and other proteins are attached. | The core of the Exosome complex is made of a ring, which is consisting of six RNases proteins (Rnase PH-like proteins), and other proteins are attached. | ||
You can also view the complex in a <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/2">ribbon view</scene>. | You can also view the complex in a <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/2">ribbon view</scene>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==3D structures of exosome== | ||
| + | [[Exosome 3D structures]] | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| + | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| + | [[Category: Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
Exosome
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Exosome_complex#Structure
- ↑ Falk S, Tants JN, Basquin J, Thoms M, Hurt E, Sattler M, Conti E. Structural insights into the interaction of the nuclear exosome helicase Mtr4 with the pre-ribosomal protein Nop53. RNA. 2017 Sep 7. pii: rna.062901.117. doi: 10.1261/rna.062901.117. PMID:28883156 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1261/rna.062901.117