Lotem haleva/test page
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (8 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Trypsin== | ==Trypsin== | ||
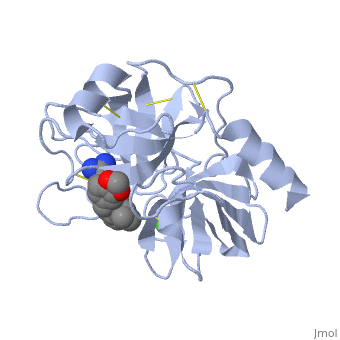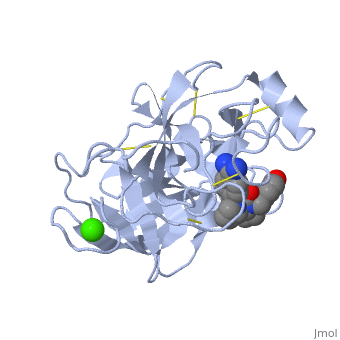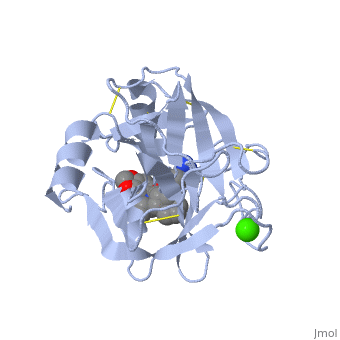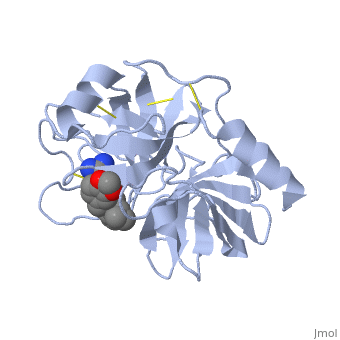
| - | <StructureSection load='1y3v' size='340' side='right' caption=' | + | <StructureSection load='1y3v' size='340' side='right' caption='Bovine trypsine complex with inhibitor and Ca+2 ion (green) (PDB code [[1y3v]])' scene=''> |
| - | Trypsin is a serine protease | + | '''Trypsin''' is a serine protease that found in the digestive system of many vertebrates, where it hydrolyses proteins<ref>doi:10.1016/0076-6879(94)44004-2</ref>. |
| - | Trypsin is produced in the pancreas as the inactive protease trypsinogen. | + | Trypsin is produced in the pancreas as the inactive zymogen protease called trypsinogen. trypsinogen secreted into the small intestine where it activates trypsinogen into trypsin by the enzyme Antrookinaz using proteolytic decomposition. |
| - | Trypsin Break peptide chains | + | Trypsin Break peptide chains at the carboxyl side of the amino acids lysine or arginine, |
except when it is followed by proline. . | except when it is followed by proline. . | ||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
== Structure and Mechanism == | == Structure and Mechanism == | ||
| - | Trypsin is a medium size globular protein that contains either <scene name='60/607865/Helix/1'>alpha helix</scene> | + | Trypsin is a medium size globular protein that contains either <scene name='60/607865/Helix/1'>alpha helix</scene> and <scene name='60/607865/Sheets/1'>beta sheets</scene>. |
| - | The enzymatic mechanism of Trypsin is similar to the other serine proteases. These enzymes contain a catalytic triad consisting of <scene name='60/607865/Active_site/2'>histidine-57, aspartate-102, and serine-195</scene>, These three residues | + | The enzymatic mechanism of Trypsin is similar to the other serine proteases. These enzymes contain a catalytic triad consisting of <scene name='60/607865/Active_site/2'>histidine-57, aspartate-102, and serine-195</scene>, These three residues makes the active site serine nucleophilic <ref>doi:10.1007/s00018-005-5160-x</ref>. |
Trypsin contains an "oxyanion hole" formed by the backbone amide hydrogen atoms of <scene name='60/607865/Oxyanion_hole/1'>Gly-193 and Ser-195</scene> , which serves to stabilize the developing negative charge on the carbonyl oxygen atom of the cleaved amides. | Trypsin contains an "oxyanion hole" formed by the backbone amide hydrogen atoms of <scene name='60/607865/Oxyanion_hole/1'>Gly-193 and Ser-195</scene> , which serves to stabilize the developing negative charge on the carbonyl oxygen atom of the cleaved amides. | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| - | There are different ways to present the protein structure<scene name='60/607865/Balls_and_stik/1'>balls and stick</scene> and <scene name='60/607865/Backbone/1'>Backbone</scene>.Another way to view the protein is <scene name='60/607865/Rainbow_n_to_c/1'>Rainbow</scene> that show the protein from the N (blue) to C terminal (green) | + | There are different ways to present the protein structure :<scene name='60/607865/Balls_and_stik/1'>balls and stick</scene>, <scene name='60/607865/Surface/1'>surface</scene> and <scene name='60/607865/Backbone/1'>Backbone</scene>. Another way to view the protein is <scene name='60/607865/Rainbow_n_to_c/1'>Rainbow</scene> that show the protein from the N (blue) to C terminal (green). |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Current revision
Trypsin
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Rawlings ND, Barrett AJ. Families of serine peptidases. Methods Enzymol. 1994;244:19-61. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(94)44004-2. PMID:7845208 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0076-6879(94)44004-2
- ↑ Polgar L. The catalytic triad of serine peptidases. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2005 Oct;62(19-20):2161-72. PMID:16003488 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00018-005-5160-x
- ↑ Rodriguez J, Gupta N, Smith RD, Pevzner PA. Does trypsin cut before proline? J Proteome Res. 2008 Jan;7(1):300-5. Epub 2007 Dec 8. PMID:18067249 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/pr0705035