We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Bromelain
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (12 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
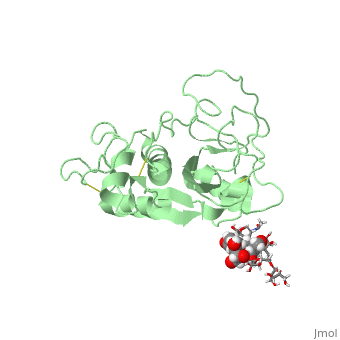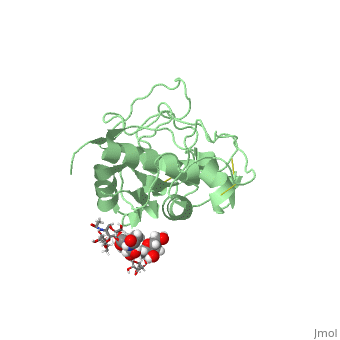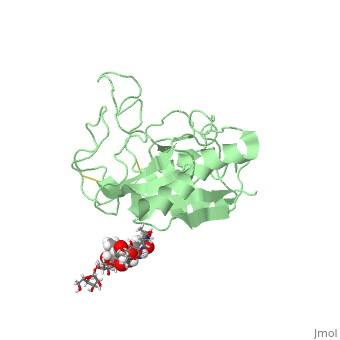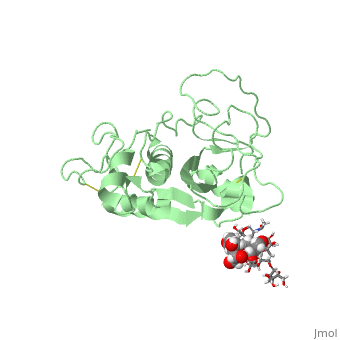
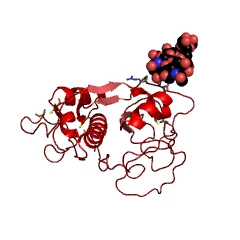
| - | <StructureSection load=' | + | <StructureSection load='1w0q' size='350' side='right' scene='' caption='Pineapple bromelain (PDB code [[1w0q]])'> |
| - | Bromelain is a protein extract derived from the stems of pineapples.The extract has a history of folk medicine use. As a culinary ingredient, it may be used as a meat tenderizer. | + | '''Bromelain''' is a protein extract derived from the stems of pineapples.The extract has a history of folk medicine use. As a culinary ingredient, it may be used as a meat tenderizer. |
Bromelain may refer to either of two protease enzymes extracted from the plants of the family Bromeliaceae, or it may refer to a combination of those enzymes along with other compounds produced in an extract. | Bromelain may refer to either of two protease enzymes extracted from the plants of the family Bromeliaceae, or it may refer to a combination of those enzymes along with other compounds produced in an extract. | ||
Although tested in a variety of research models for its possible efficacy against diseases, bromelain has no established research evidence as a nutraceutical or drug.Limited evidence exists for possible effectiveness of a product used to reduce pain from osteoarthritis that combines bromelain with trypsin and rutin. | Although tested in a variety of research models for its possible efficacy against diseases, bromelain has no established research evidence as a nutraceutical or drug.Limited evidence exists for possible effectiveness of a product used to reduce pain from osteoarthritis that combines bromelain with trypsin and rutin. | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
<table> | <table> | ||
| - | + | ||
== Image of Protein == | == Image of Protein == | ||
[[Image:1w0q.jpg]] | [[Image:1w0q.jpg]] | ||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
At the optimum temperature, the enzyme acts the fastest, but (at least the fruit variant) is destroyed within few minutes. After an hour at 50 °C (122 °F), 83% of the enzyme remains, while at 40 °C (104 °F), practically 100% remains. As a result of this, the optimum temperature for maximum cumulated activity over time is 35-45 °C. At room temperature, the enzyme can survive at least a week even under multiple freeze-thaw cycles. | At the optimum temperature, the enzyme acts the fastest, but (at least the fruit variant) is destroyed within few minutes. After an hour at 50 °C (122 °F), 83% of the enzyme remains, while at 40 °C (104 °F), practically 100% remains. As a result of this, the optimum temperature for maximum cumulated activity over time is 35-45 °C. At room temperature, the enzyme can survive at least a week even under multiple freeze-thaw cycles. | ||
| - | == | + | ==How it works== |
| - | + | Bromelain is a cysteine protease. The <scene name='60/609840/Active_site/1'>active site</scene> contains a cysteine residue. A neighboring histidine increases the ionization of the cysteine, making it a better nucleophile. | |
| + | |||
| + | == 3D Structures of bromelain == | ||
| + | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | ||
| + | [[1w0q]] - pineapple - model<br /> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||