We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Molecular Playground/CLOCK:BMAL1 heterodimer complex
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (3 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
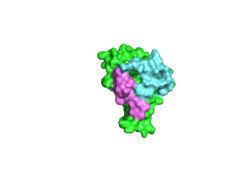
| - | <StructureSection load='4F3L' size='340' side='right' caption='mouse CLOCK:BMAL1 heterodimer complex' scene='60/609802/Clock_bmal1/1'> | + | <StructureSection load='4F3L' size='340' side='right' caption='mouse CLOCK:BMAL1 heterodimer complex (PDB code [[4f3l]]).' scene='60/609802/Clock_bmal1/1'> |
The <scene name='60/609802/Clock_bmal1/1'>CLOCK:BMAL1 heterodimer complex</scene> is a vital regulatory component of the circadian rhythm protein regulation system. CLOCK (''Circadian Locomotor Output Cycles Kaput'') and BMAL1 (''Brain and muscle Arnt-like protein-1'') are <scene name='60/609802/Bhlh_ex/1'>the basic helix-loop-helix</scene> PER-ARNT-SIM (bHLH-PAS) proteins. (The structure highlighted in yellow is a portion of bHLH structure in CLOCK) The CLOCK:BMAL1 heterodimer is the main transcriptional activator in the mammalian circadian mechanism.<ref>DOI: 10.1126/science.280.5369.1564</ref> The binding between CLOCK and BMAL1 involves the N-terminal bHLH, PAS-A and PAS-B domains of both proteins. Each domain (bHLH, PAS-A, PAS-B) binds to its corresponding equivalent in the other protein. Though both proteins contain the same types of domains with similar primary amino acid sequences in each, the overall heterodimer is surprisingly asymmetrical due to differences in the spatial orientation of the domains in each protein. Since this heterodimer complex involves the binding of all of the major domains in both participating proteins, the overall binding affinity is very high. | The <scene name='60/609802/Clock_bmal1/1'>CLOCK:BMAL1 heterodimer complex</scene> is a vital regulatory component of the circadian rhythm protein regulation system. CLOCK (''Circadian Locomotor Output Cycles Kaput'') and BMAL1 (''Brain and muscle Arnt-like protein-1'') are <scene name='60/609802/Bhlh_ex/1'>the basic helix-loop-helix</scene> PER-ARNT-SIM (bHLH-PAS) proteins. (The structure highlighted in yellow is a portion of bHLH structure in CLOCK) The CLOCK:BMAL1 heterodimer is the main transcriptional activator in the mammalian circadian mechanism.<ref>DOI: 10.1126/science.280.5369.1564</ref> The binding between CLOCK and BMAL1 involves the N-terminal bHLH, PAS-A and PAS-B domains of both proteins. Each domain (bHLH, PAS-A, PAS-B) binds to its corresponding equivalent in the other protein. Though both proteins contain the same types of domains with similar primary amino acid sequences in each, the overall heterodimer is surprisingly asymmetrical due to differences in the spatial orientation of the domains in each protein. Since this heterodimer complex involves the binding of all of the major domains in both participating proteins, the overall binding affinity is very high. | ||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
The PSA-B domains of CLOCK and BMAL1 are stacked in parallel conformation. The β-sheet on PSA-B domain of BMAL1 contact the helical face of CLOCK PSA-B domain. The <scene name='60/609802/Clock_bmal1_if_2/1'>contact interface</scene> bury some hydrophobic residues on both subunits, including Try310, Val315, and Leu318 of CLOCK and Phe423, Trp427, and Val435 of BMAL1. | The PSA-B domains of CLOCK and BMAL1 are stacked in parallel conformation. The β-sheet on PSA-B domain of BMAL1 contact the helical face of CLOCK PSA-B domain. The <scene name='60/609802/Clock_bmal1_if_2/1'>contact interface</scene> bury some hydrophobic residues on both subunits, including Try310, Val315, and Leu318 of CLOCK and Phe423, Trp427, and Val435 of BMAL1. | ||
| + | [[Image:Binding.png|250 px|thumb|Fig. 1 The overlap structure of CLOCK:BMAL1 complex with bHLH Myc:Max-DNA complex (pdb: 1NKP). The figure is generated by Pymol]] | ||
===The binding interface between CLOCK:BMAL1 and E-box element=== | ===The binding interface between CLOCK:BMAL1 and E-box element=== | ||
| - | + | As shown in Fig. 1, the four-helical bHLH bundle in the CLOCK:BMAL1 heterodimer overlaps with the bHLH Myc:Max-DNA complex (pdb: 1NKP, in wheat). This four-helical bundle is highly hydrophobic, which indicating that dimerization of the bHLH domains should help stabilize the CLOCK:BMAL1 complex.<ref>DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(02)01284-9</ref> This bHLH conformation is also important for the E-box recognition. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | As shown in Fig. 1, the four-helical bHLH bundle in the CLOCK:BMAL1 heterodimer overlaps with the bHLH Myc:Max-DNA complex (pdb: 1NKP). | + | |
Current revision
CLOCK:BMAL1 heterodimer complex
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.280.5369.1564
- ↑ Silver R, Kriegsfeld LJ. Circadian rhythms have broad implications for understanding brain and behavior. Eur J Neurosci. 2014 Jun;39(11):1866-80. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12593. Epub 2014 May 5. PMID:24799154 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/ejn.12593
- ↑ Huang N, Chelliah Y, Shan Y, Taylor CA, Yoo SH, Partch C, Green CB, Zhang H, Takahashi JS. Crystal structure of the heterodimeric CLOCK:BMAL1 transcriptional activator complex. Science. 2012 Jul 13;337(6091):189-94. Epub 2012 May 31. PMID:22653727 doi:10.1126/science.1222804
- ↑ Lowrey PL, Takahashi JS. Genetics of circadian rhythms in Mammalian model organisms. Adv Genet. 2011;74:175-230. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-387690-4.00006-4. PMID:21924978 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-387690-4.00006-4
- ↑ doi: https://dx.doi.org/http
- ↑ Stevens RG. Circadian disruption and breast cancer: from melatonin to clock genes. Epidemiology. 2005 Mar;16(2):254-8. doi: 10.1097/01.ede.0000152525.21924.54. PMID:15703542 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.ede.0000152525.21924.54
- ↑ Ramsey KM, Yoshino J, Brace CS, Abrassart D, Kobayashi Y, Marcheva B, Hong HK, Chong JL, Buhr ED, Lee C, Takahashi JS, Imai S, Bass J. Circadian clock feedback cycle through NAMPT-mediated NAD+ biosynthesis. Science. 2009 May 1;324(5927):651-4. doi: 10.1126/science.1171641. Epub 2009 Mar , 19. PMID:19299583 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.1171641
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Hui-Hsien Lin, Joseph Hardie, Michael Mingroni, Michal Harel