Molecular Playground/E. coli ClpP
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (4 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | Here in the Chien lab, we study how [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Proteolysis proteolysis] plays a large part in protein quality control. The maintenance and timely destruction of protein levels plays an important role during cell homeostasis and cell transitions/differentiation, yet much of what governs these processes has | + | Here, in the Chien lab of the University of Massachusetts-Amherst, we study how [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Proteolysis proteolysis] plays a large part in protein quality control. The maintenance and timely destruction of protein levels plays an important role during cell homeostasis and cell transitions/differentiation, yet much of what governs these processes has to be fully understood. |
<StructureSection load='1yg6' size='340' side='right' caption='Caption for this structure' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='1yg6' size='340' side='right' caption='Caption for this structure' scene=''> | ||
== ClpP Introduction == | == ClpP Introduction == | ||
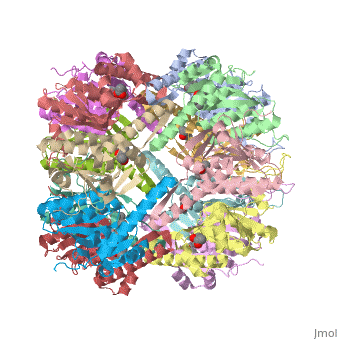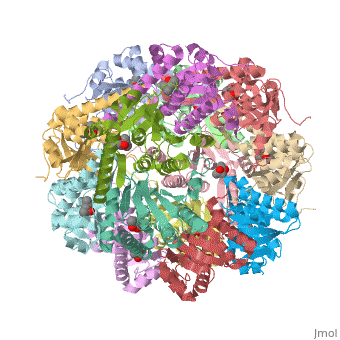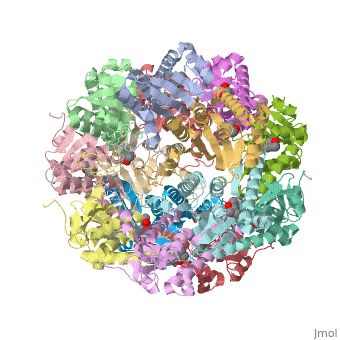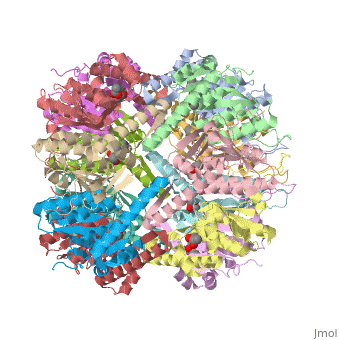
| - | ''E. coli'' Casein lytic proteinase P (ClpP) is a double ring [http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/tetradecamer tetradecameric] homo oligomer compartmentalized peptidase [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=ClpP%3A+A+structurally+dynamic+protease+regulated+by+AAA%2B+proteins]. ClpP requires the use of ATP dependent regulatory elements that independently bind to ClpP in order for substrates to have access the active core [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15037252][http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20236930][http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19038348]. Here, proteins that are translocated by regulatory elements into the peptidase core are cleaved into smaller amino acid chains approximately on average 6-8aa in length [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16229481]. | + | ''E. coli'' Casein lytic proteinase P (<scene name='60/609790/Clpp-2/2'>ClpP</scene>) is a double ring [http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/tetradecamer tetradecameric] homo oligomer compartmentalized peptidase [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=ClpP%3A+A+structurally+dynamic+protease+regulated+by+AAA%2B+proteins]. ClpP requires the use of ATP dependent regulatory elements that independently bind to ClpP in order for substrates to have access the active core [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15037252][http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20236930][http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19038348]. Here, proteins that are translocated by regulatory elements into the peptidase core are cleaved into smaller amino acid chains approximately on average 6-8aa in length [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16229481]. |
== Tetradecameric Structure == | == Tetradecameric Structure == | ||
ClpP is a serine protease which consists of fourteen monomers situated into two [http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/heptamer heptameric] rings seated on top of each other. In the center of the barrel-shaped chamber lies a core of fourteen peptide-cleaving active sites, restricted by the narrow entrance called the <scene name='60/609790/Clpp_axial_pore/4'>axial pore</scene>. As peptides are [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Processivity processively] threaded in the pore by the regulatory elements, the peptides are then degraded into smaller fragments as a result from ClpP cleavage. Smaller peptides are then released through small openings found around the <scene name='60/609790/Clpp_equator_pore/2'>equatorial interface</scene> of the two stacked rings. | ClpP is a serine protease which consists of fourteen monomers situated into two [http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/heptamer heptameric] rings seated on top of each other. In the center of the barrel-shaped chamber lies a core of fourteen peptide-cleaving active sites, restricted by the narrow entrance called the <scene name='60/609790/Clpp_axial_pore/4'>axial pore</scene>. As peptides are [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Processivity processively] threaded in the pore by the regulatory elements, the peptides are then degraded into smaller fragments as a result from ClpP cleavage. Smaller peptides are then released through small openings found around the <scene name='60/609790/Clpp_equator_pore/2'>equatorial interface</scene> of the two stacked rings. | ||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
== Acknowledgements== | == Acknowledgements== | ||
Kamal Joshi, Joanne Lau, Jing Liu, Rob Vass | Kamal Joshi, Joanne Lau, Jing Liu, Rob Vass | ||
| + | |||
| + | PDB id:1YG6 from [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1yg6 Bewley, MC ''et. al'' (2006 J.Struct.Biol.)] | ||
Current revision
Here, in the Chien lab of the University of Massachusetts-Amherst, we study how proteolysis plays a large part in protein quality control. The maintenance and timely destruction of protein levels plays an important role during cell homeostasis and cell transitions/differentiation, yet much of what governs these processes has to be fully understood.
| |||||||||||
References
6. Clp P represents a unique family of serine proteases. Maurizi MR et. al (1990 J Biolchem)
Acknowledgements
Kamal Joshi, Joanne Lau, Jing Liu, Rob Vass
PDB id:1YG6 from Bewley, MC et. al (2006 J.Struct.Biol.)