Potassium channel toxin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (9 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
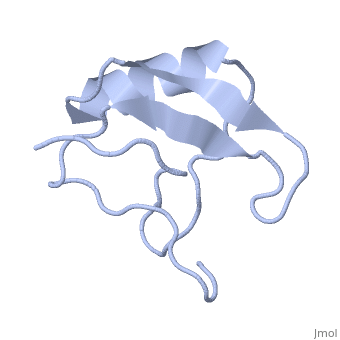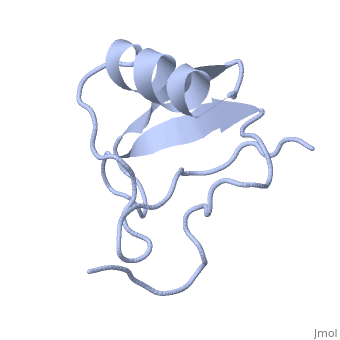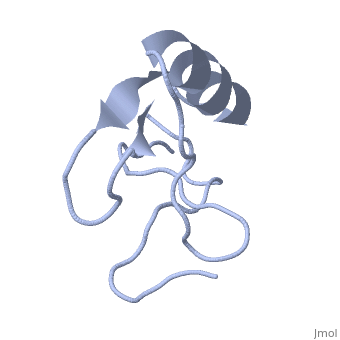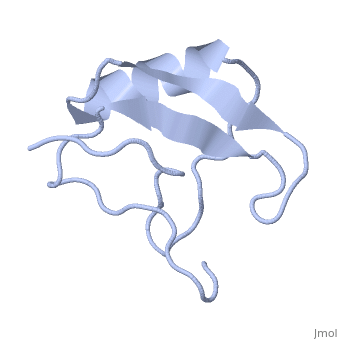
| - | <StructureSection load='1lqh' size=" | + | <StructureSection load='1lqh' size="350" color="" spin="on" Scene= caption='Scorpion potassium channel toxin, [[1lqh]]' > |
| + | __TOC__ | ||
| + | == Function == | ||
| + | '''Potassium channel toxins''' are various venoms which block the transport of potassium ions across the plasma membrane through potassium channels<ref>PMID:2181489</ref>. | ||
| - | + | See also [[Vm24 Scorpion Toxin]]. | |
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
| - | Scorpion toxins are 61- to 76-residue long proteins that modulate the gating properties of voltage-gated sodium channels. According to their mode of action and binding properties, | + | Scorpion toxins are 61- to 76-residue long proteins that modulate the gating properties of voltage-gated sodium channels. According to their mode of action and binding properties, scorpion toxins are divided into two major classes, α- and β- toxins. |
LqhαIT is a 64-residue scorpion α-toxin from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Deathstalker_scorpion Leiurus quinquestriatus hebraeus] (yellow scorpion) venom. Scorpion α-toxins prolong the action potential by inhibiting channel inactivation. The binding site of scorpion α-neurotoxins on voltage-gated sodium channels is named neurotoxin receptor site-3. | LqhαIT is a 64-residue scorpion α-toxin from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Deathstalker_scorpion Leiurus quinquestriatus hebraeus] (yellow scorpion) venom. Scorpion α-toxins prolong the action potential by inhibiting channel inactivation. The binding site of scorpion α-neurotoxins on voltage-gated sodium channels is named neurotoxin receptor site-3. | ||
| Line 16: | Line 19: | ||
NMR studies of LqhαIT with a peptide derived from part of neurotoxin receptor site-3 (D4S3-S4) identified residues <scene name='1lqh/Nmr/1'>Lys8, Asn9, Cys12, Val13, Arg18, Trp38, Ala39 and Arg58</scene> of LqhαIT as participating in binding to that extra-cellular part of the sodium channel (3). | NMR studies of LqhαIT with a peptide derived from part of neurotoxin receptor site-3 (D4S3-S4) identified residues <scene name='1lqh/Nmr/1'>Lys8, Asn9, Cys12, Val13, Arg18, Trp38, Ala39 and Arg58</scene> of LqhαIT as participating in binding to that extra-cellular part of the sodium channel (3). | ||
Both methods led to the identification of two regions on the surface of LqhαIT that participate in binding of the toxin to neurotoxin receptor site-3 on sodium channels. | Both methods led to the identification of two regions on the surface of LqhαIT that participate in binding of the toxin to neurotoxin receptor site-3 on sodium channels. | ||
| - | </StructureSection> | ||
==3D structures of potassium channel toxins== | ==3D structures of potassium channel toxins== | ||
| + | [[Potassium channel toxin 3D structures]] | ||
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | == References == | |
| - | + | <references/> | |
| - | + | [[Category:Topic Page]] | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||