This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
3vjp
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (2 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | |||
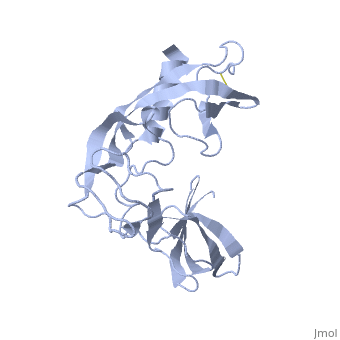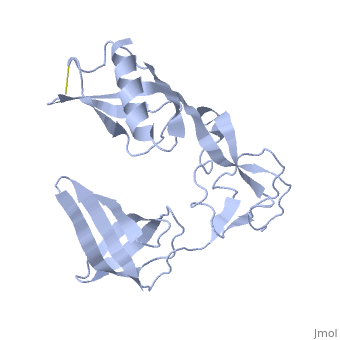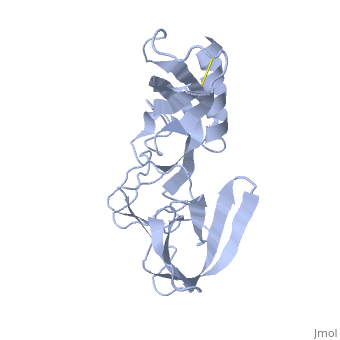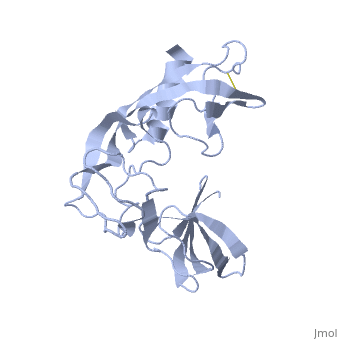
==Orthorhombic Crystal Structure of Salmonella FlgA in closed form== | ==Orthorhombic Crystal Structure of Salmonella FlgA in closed form== | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='3vjp' size='340' side='right' caption='[[3vjp]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.70Å' scene=''> | + | <StructureSection load='3vjp' size='340' side='right'caption='[[3vjp]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.70Å' scene=''> |
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| - | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[3vjp]] is a 2 chain structure with sequence from [ | + | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[3vjp]] is a 2 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/"bacillus_typhimurium"_loeffler_1892 "bacillus typhimurium" loeffler 1892]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=3VJP OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=3VJP FirstGlance]. <br> |
</td></tr><tr id='NonStdRes'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Non-Standard_Residue|NonStd Res:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='pdbligand=MSE:SELENOMETHIONINE'>MSE</scene></td></tr> | </td></tr><tr id='NonStdRes'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Non-Standard_Residue|NonStd Res:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='pdbligand=MSE:SELENOMETHIONINE'>MSE</scene></td></tr> | ||
| - | <tr id='related'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Related_structure|Related:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">[[3tee|3tee]]</td></tr> | + | <tr id='related'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Related_structure|Related:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><div style='overflow: auto; max-height: 3em;'>[[3tee|3tee]]</div></td></tr> |
| - | <tr id='gene'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Gene|Gene:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">flgA ([ | + | <tr id='gene'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Gene|Gene:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">flgA ([https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&srchmode=5&id=90371 "Bacillus typhimurium" Loeffler 1892])</td></tr> |
| - | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[ | + | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=3vjp FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=3vjp OCA], [https://pdbe.org/3vjp PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=3vjp RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/3vjp PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=3vjp ProSAT]</span></td></tr> |
</table> | </table> | ||
| + | == Function == | ||
| + | [[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/FLGA_SALTY FLGA_SALTY]] Involved in the assembly process of the P-ring formation. It may associate with FlgF on the rod constituting a structure essential for the P-ring assembly or may act as a modulator protein for the P-ring assembly. | ||
| + | <div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | ||
| + | == Publication Abstract from PubMed == | ||
| + | A periplasmic flagellar chaperone protein, FlgA, is required for P-ring assembly in bacterial flagella of taxa such as Salmonella enterica or Escherichia coli. The mechanism of chaperone-mediated P-ring formation is poorly understood. Here we present the open and closed crystal structures of FlgA from Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium, grown under different crystallization conditions. An intramolecular disulfide cross-linked form of FlgA caused a dominant negative effect on motility of the wild-type strain. Pull-down experiments support a specific protein-protein interaction between FlgI, the P-ring component protein, and the C-terminal domain of FlgA. Surface plasmon resonance and limited-proteolysis indicate that flexibility of the domain is reduced in the covalently closed form. These results show that the structural flexibility of the C-terminal domain of FlgA, which is related to the structural difference between the two crystal forms, is intrinsically associated with its molecular chaperone function in P-ring assembly. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Structural flexibility of the periplasmic protein, FlgA, regulates flagellar P-ring assembly in Salmonella enterica.,Matsunami H, Yoon YH, Meshcheryakov VA, Namba K, Samatey FA Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 7;6:27399. doi: 10.1038/srep27399. PMID:27273476<ref>PMID:27273476</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <div class="pdbe-citations 3vjp" style="background-color:#fffaf0;"></div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==See Also== | ||
| + | *[[Flagellar protein 3D structures|Flagellar protein 3D structures]] | ||
| + | *[[Flagellar proteins|Flagellar proteins]] | ||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
[[Category: Bacillus typhimurium loeffler 1892]] | [[Category: Bacillus typhimurium loeffler 1892]] | ||
| + | [[Category: Large Structures]] | ||
[[Category: Matsunami, H]] | [[Category: Matsunami, H]] | ||
[[Category: Namba, K]] | [[Category: Namba, K]] | ||
Current revision
Orthorhombic Crystal Structure of Salmonella FlgA in closed form
| |||||||||||