This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Heat Shock Proteins
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (37 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | + | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' scene='Journal:JBSD:30/Cv/5' caption=''> | |
| - | [[Heat Shock Proteins]] (Hsp). The Hsp are proteins which are expressed when cells are exposed to stresses like heat. Hsp60, Hsp70, Hsp90 etc. are named according to their molecular weights. Their function is to provide protection from stress. | + | == Function == |
| - | See also [[Chaperones]]. | + | [[Heat Shock Proteins]] (Hsp). The Hsp are proteins which are expressed when cells are exposed to stresses like heat. Hsp60, Hsp70, Hsp90 etc. are named according to their molecular weights. Their function is to provide protection from stress<ref>PMID:18432918</ref>. Hsp contains a nucleotide-binding domain (NBD), a substrate-binding domain (SBD) and C-terminal lid domain (lid). In ''E. coli'' there are additional Hsp – HslV (19kD), HslJ and HslU (50kD). The heat-inducible Hsp is called '''heat shock cognate protein''' (Hsc). '''Hsp70''' from ''E. coli'' is called '''DnaK'''. '''Hsp70 family protein 5''' or '''endoplasmic reticulum chaperone BIP''' is located in the lumen of the ER and its synthesis is markedly induced under conditions that lead to the accumulation of unfolded polypeptides in the ER<ref>apmid;10597629</ref> '''Hsp90B1''' is also called '''endoplasmin''' and '''grp94'''. '''DegP''' is a dual-function chaperon and protease. It degrades peripasmic proteins under stress conditions<ref>PMID:31738379</ref>. |
| + | See also<br /> | ||
| + | * [[Chaperones]]<br /> | ||
| + | * [[Hsp100]]<br /> | ||
| + | * [[Hsp40]] | ||
| + | * [[Hsp70]] | ||
| + | * [[Molecular Playground/DnaK]] for Hsp70 in ''E. coli'' | ||
| + | * [[Molecular Playground/sHSP]] for small Hsp | ||
| + | * [[Molecular Playground/Hsp70-Hsp90]] | ||
| - | == | + | == Conformational dynamics of full-length inducible human Hsp70 derived from microsecond molecular dynamics simulations in explicit solvent <ref>doi 10.1080/07391102.2012.726190</ref> == |
| - | + | '''1. Hsp70, molecular chaperone''' | |
| - | + | The 70 kDa heat shock proteins (Hsp70s) are major ATP-dependent molecular chaperones involved in the general folding assisted pathways and are present in all eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. Hsp70s assist a wide range of folding processes; including the folding of newly synthesized proteins and the refolding of misfolded and aggregated proteins. Other functions of Hsp70s include protein degradation, translocation of peptides across the cell membrane, formation of protein complexes, and inhibition of the programmed cell death. Consistent with the fact that Hsp70s interact with hundreds of client proteins of the intracellular environment and with its key role in the “conformational homeostasis” of cellular proteins, human Hsp70 (hHsp70) are involved in numerous diseases, such as neurodegenerative diseases and cancer. The diversity of hHsp70 implications in these diseases explains that they become recently an important target for the development of new therapeutic strategies. | |
| - | * | + | == Structure of Hsp70 == |
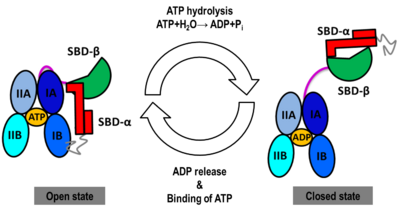
| + | All Hsp70s are comprised of two main domains, a <scene name='Journal:JBSD:30/Cv/6'>N-terminal Nucleotide Binding Domain (NBD)</scene> of 45 kDa and a <scene name='Journal:JBSD:30/Cv/7'>C-terminal substrate binding domain (SBD)</scene> of 25 kDa. The NBD is divided into two rather <scene name='Journal:JBSD:30/Cv/8'>symmetrical lobes, I and II</scene>, each divided into two <scene name='Journal:JBSD:30/Cv/9'>subdomains A and B</scene>. The two lobes form the two arms of a V-shaped structure in which the nucleotide (ADP or ATP) is bound at the center. The <scene name='Journal:JBSD:30/Cv/10'>SBD is further divided</scene> into a β sandwich subdomain (SBD-β) which has a hydrophobic peptide binding pocket, and a α-helical “lid” subdomain (SBD-α) which regulates the access of the substrate to the SBD-β. The NBD and the SBD are connected by a conserved hydrophobic linker. Final color code: | ||
| + | *<font color='blue'><b>NBD-IA is in blue</b></font> | ||
| + | *<span style="color:deepskyblue;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">NBD-IB is in deepskyblue</span> | ||
| + | *<span style="color:lightsteelblue;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">NBD-IIA is in lightsteelblue</span> | ||
| + | *<span style="color:cyan;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">NBD-IIB is in cyan</span> | ||
| + | *<font color='magenta'><b>Linker is in magenta</b></font> | ||
| + | *<span style="color:lime;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">SBD-β is in green</span> | ||
| + | *<font color='red'><b>SBD-α is in red</b></font> | ||
| + | *<span style="color:darkgray;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">C-terminal is in gray</span> | ||
| - | + | == The Hsp70 functional cycle == | |
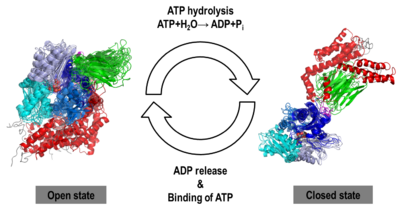
| - | + | The Hsp70s assists in the folding of other proteins through cycles of binding and release of unfolded polypeptide chains in the SBD (Figure 1). The cycle is governed by the nucleotide-binding status of the NBD: in the ATP-bound Hsp70, the SBD is opened with fast binding and release of the protein substrate and the SBD and the NBD are docked, whereas in the ADP-bound and nucleotide-free states (APO), the SBD is assumed to be closed with low binding and release rate of the protein substrate, with the SBD and the NBD undocked. The transition between the ATP (open conformation) and the ADP states of Hsp70 (closed conformation) is triggered by the ATP binding to the NBD, which induces a conformational change of the interdomain linker, and the opening of the SBD through an allosteric mechanism which is not fully elucidated (see static image below). The ATP hydrolysis restores the closed conformation of the SBD. Rebinding of ATP to the nucleotide-free Hsp70 restarts the cycle of the chaperone. In vivo, the ATP hydrolysis and nucleotide exchange rates are increased by co-chaperones. Because of their critical roles in many cellular processes and based on evidence that their mechanisms involve cycles of conformational changes, there has been a strong interest in elucidating the structures of human Hsp70 in its two main conformations, i.e. ATP and ADP-bound. Structures of human Hsp70 are of first interest for the design of drugs in new cancer therapies. However, only the structure of the NBD of hHsp70 was solved by X-ray. Truncated structures comprising both the NBD and the SBD were solved for the bacterial E. coli Hsp70 homolog in the closed state (PDB ID: [[2kho]]) and for the yeast ''S. cerevisiae'' Hsp110 homolog in the open state (PDB ID: [[3c7n]]). | |
| - | + | [[Image:JBSD30.png|left|400px|thumb|<font color='blue'><b>NBD-IA is in blue</b></font>, <span style="color:deepskyblue;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">NBD-IB is in deepskyblue</span>, <span style="color:lightsteelblue;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">NBD-IIA is in lightsteelblue</span>, <span style="color:cyan;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">NBD-IIB is in cyan</span>, <font color='magenta'><b>Linker is in magenta</b></font>, <span style="color:lime;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">SBD-β is in green</span>, <font color='red'><b>SBD-α is in red</b></font>, <span style="color:darkgray;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">C-terminal is in gray</span>]] | |
| - | + | {{Clear}} | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | == Conformational heterogeneity observed in MD simulations == | |
| - | + | Prompted by the absence of detailed atomic experimental structures, we carried out the task of generating computer models of the human Hsp70 in its open and closed states by homology modeling and by molecular dynamics (MD) simulations on a unprecedented micro-second timescale, using the templates PDB ID: [[3c7n]] and PDB ID: [[2kho]], respectively. The sequence of human inducible Hsp70 (UniProt ID: P08107) was chosen for modeling purposes because it has been reported as a new target for cancer therapies. | |
| - | + | We obtained stable structures by using six and three different initial conditions in the molecular dynamics (MD) simulations of the open and closed models, respectively. In the six MD trajectories (see static image below), the <scene name='Journal:JBSD:30/Cv/11'>open model</scene> adopted a stable conformation in which the lid was open, the SBD-α was docked to the NBD and the linker was bound to a cleft between subdomains IA and IIA of the NBD. Different stable binding positions sites were found for the SBD-α on the lobe I of the NBD. The conformational heterogeneity of the <scene name='Journal:JBSD:30/Cv/12'>closed model</scene>, probed by three MD trajectories corresponded to a rotation of the SBD around the NBD, in agreement with NMR data. | |
| - | + | We found that human Hsp70, <scene name='Journal:JBSD:30/Cv/13'>both in its open and closed states</scene>, was better represented by an ensemble of conformations on a μs timescale, corresponding to different local minima of its free-energy landscape in good agreement with low-resolution experimental data of Hsp70s homologs (Small Angle Xray-Scattering and single-molecule Förster Resonance Energy Transfer) to which the MD simulations were compared in details. These structural ensembles represent the first attempt to model the conformational heterogeneity of a full-length molecular chaperone at the atomic scale. | |
| - | + | [[Image:JBSD30a.png|left|400px|thumb|<font color='blue'><b>NBD-IA is in blue</b></font>, <span style="color:deepskyblue;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">NBD-IB is in deepskyblue</span>, <span style="color:lightsteelblue;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">NBD-IIA is in lightsteelblue</span>, <span style="color:cyan;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">NBD-IIB is in cyan</span>, <font color='magenta'><b>Linker is in magenta</b></font>, <span style="color:lime;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">SBD-β is in green</span>, <font color='red'><b>SBD-α is in red</b></font>, <span style="color:darkgray;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">C-terminal is in gray</span>]] | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | == 3D Structures of Heat Shock Proteins == | |
| - | + | [[Heat Shock Protein structures]] | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
| - | + | == References == | |
| - | + | <references/> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Li Z, Srivastava P. Heat-shock proteins. Curr Protoc Immunol. 2004 Feb;Appendix 1:Appendix 1T. doi:, 10.1002/0471142735.ima01ts58. PMID:18432918 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/0471142735.ima01ts58
- ↑ apmid;10597629
- ↑ Zhang S, Cheng Y, Ma J, Wang Y, Chang Z, Fu X. Degp degrades a wide range of substrate proteins in Escherichia coli under stress conditions. Biochem J. 2019 Dec 12;476(23):3549-3564. PMID:31738379 doi:10.1042/BCJ20190446
- ↑ Nicolai A, Delarue P, Senet P. Conformational dynamics of full-length inducible human Hsp70 derived from microsecond molecular dynamics simulations in explicit solvent. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2012 Oct 17. PMID:23075261 doi:10.1080/07391102.2012.726190