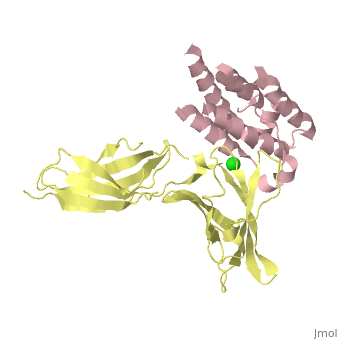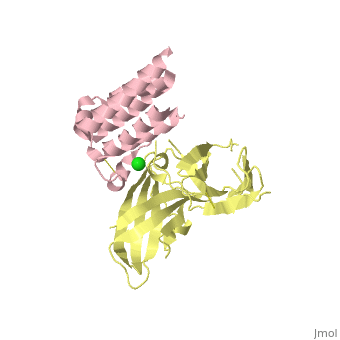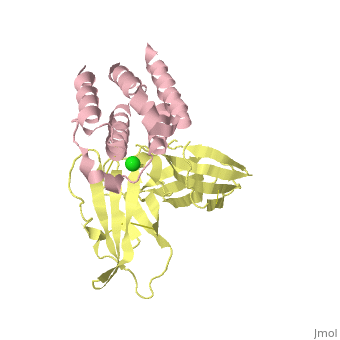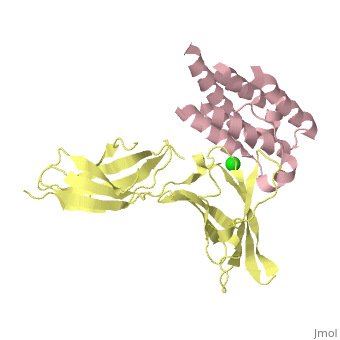|
|
| (2 intermediate revisions not shown.) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| | + | |
| | ==binary complex between IFNa2 and IFNAR2== | | ==binary complex between IFNa2 and IFNAR2== |
| - | <StructureSection load='3s9d' size='340' side='right' caption='[[3s9d]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.00Å' scene=''> | + | <StructureSection load='3s9d' size='340' side='right'caption='[[3s9d]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.00Å' scene=''> |
| | == Structural highlights == | | == Structural highlights == |
| - | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[3s9d]] is a 4 chain structure with sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=3S9D OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=3S9D FirstGlance]. <br> | + | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[3s9d]] is a 4 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=3S9D OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=3S9D FirstGlance]. <br> |
| - | </td></tr><tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='pdbligand=CL:CHLORIDE+ION'>CL</scene></td></tr> | + | </td></tr><tr id='method'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Empirical_models|Method:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="methodDat">X-ray diffraction, [[Resolution|Resolution]] 1.9999Å</td></tr> |
| - | <tr id='related'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Related_structure|Related:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">[[3s8w|3s8w]], [[3s98|3s98]]</td></tr>
| + | <tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="ligandDat"><scene name='pdbligand=CL:CHLORIDE+ION'>CL</scene></td></tr> |
| - | <tr id='gene'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Gene|Gene:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">IFNA2 ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&srchmode=5&id=9606 Homo sapiens]), IFNAR2, IFNABR, IFNARB ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&srchmode=5&id=9606 Homo sapiens])</td></tr> | + | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=3s9d FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=3s9d OCA], [https://pdbe.org/3s9d PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=3s9d RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/3s9d PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=3s9d ProSAT]</span></td></tr> |
| - | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=3s9d FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=3s9d OCA], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=3s9d RCSB], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/3s9d PDBsum]</span></td></tr> | + | |
| | </table> | | </table> |
| | == Function == | | == Function == |
| - | [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/IFNA2_HUMAN IFNA2_HUMAN]] Produced by macrophages, IFN-alpha have antiviral activities. [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/INAR2_HUMAN INAR2_HUMAN]] Associates with IFNAR1 to form the type I interferon receptor. Receptor for interferons alpha and beta. Involved in IFN-mediated STAT1, STAT2 and STAT3 activation. Isoform 1 and isoform 2 are directly involved in signal transduction due to their association with the TYR kinase, JAK1. Isoform 3 is a potent inhibitor of type I IFN receptor activity.<ref>PMID:8181059</ref> <ref>PMID:7665574</ref> <ref>PMID:7759950</ref> <ref>PMID:11682488</ref> <ref>PMID:12105218</ref> | + | [https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/IFNA2_HUMAN IFNA2_HUMAN] Produced by macrophages, IFN-alpha have antiviral activities. |
| - | <div style="background-color:#fffaf0;">
| + | |
| - | == Publication Abstract from PubMed ==
| + | |
| - | Type I Interferons (IFNs) are important cytokines for innate immunity against viruses and cancer. Sixteen human type I IFN variants signal through the same cell-surface receptors, IFNAR1 and IFNAR2, yet they can evoke markedly different physiological effects. The crystal structures of two human type I IFN ternary signaling complexes containing IFNalpha2 and IFNomega reveal recognition modes and heterotrimeric architectures that are unique among the cytokine receptor superfamily but conserved between different type I IFNs. Receptor-ligand cross-reactivity is enabled by conserved receptor-ligand "anchor points" interspersed among ligand-specific interactions that "tune" the relative IFN-binding affinities, in an apparent extracellular "ligand proofreading" mechanism that modulates biological activity. Functional differences between IFNs are linked to their respective receptor recognition chemistries, in concert with a ligand-induced conformational change in IFNAR1, that collectively control signal initiation and complex stability, ultimately regulating differential STAT phosphorylation profiles, receptor internalization rates, and downstream gene expression patterns.
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | Structural linkage between ligand discrimination and receptor activation by type I interferons.,Thomas C, Moraga I, Levin D, Krutzik PO, Podoplelova Y, Trejo A, Lee C, Yarden G, Vleck SE, Glenn JS, Nolan GP, Piehler J, Schreiber G, Garcia KC Cell. 2011 Aug 19;146(4):621-32. PMID:21854986<ref>PMID:21854986</ref>
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br>
| + | |
| - | </div>
| + | |
| | | | |
| | ==See Also== | | ==See Also== |
| - | *[[Interactive 3D Complements in Proteopedia|Interactive 3D Complements in Proteopedia]] | + | *[[Interferon 3D structures|Interferon 3D structures]] |
| - | *[[Interferon|Interferon]]
| + | |
| | *[[Interferon receptor|Interferon receptor]] | | *[[Interferon receptor|Interferon receptor]] |
| | + | *[[Interferon receptor 3D structures|Interferon receptor 3D structures]] |
| | *[[Multiple sclerosis|Multiple sclerosis]] | | *[[Multiple sclerosis|Multiple sclerosis]] |
| - | == References == | |
| - | <references/> | |
| | __TOC__ | | __TOC__ |
| | </StructureSection> | | </StructureSection> |
| | [[Category: Homo sapiens]] | | [[Category: Homo sapiens]] |
| - | [[Category: Garcia, K C]] | + | [[Category: Large Structures]] |
| - | [[Category: Thomas, C]] | + | [[Category: Garcia KC]] |
| - | [[Category: Human]] | + | [[Category: Thomas C]] |
| - | [[Category: Ifna2]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Ifnar2]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Signaling protein-receptor complex]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Sub-complex of the interferon signaling complex]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Type i interferon]]
| + | |