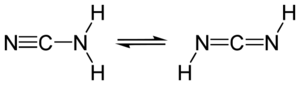Sandbox Reserved 964
From Proteopedia
| (33 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Sandbox_ESBS}}<!-- PLEASE ADD YOUR CONTENT BELOW HERE --> | {{Sandbox_ESBS}}<!-- PLEASE ADD YOUR CONTENT BELOW HERE --> | ||
| - | == | + | |
| - | <StructureSection load='1f2w' size='340' side='right' caption=' | + | ==1f2w Cyanamide-Carbonic Anhydrase II EC 4.2.1.1== |
| - | This is a | + | <StructureSection load='1f2w' size='340' side='right' caption='Structure of carbonic anhydrase II' scene=''> |
| - | + | ||
| + | ==Introduction== | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1f2w is a human protein from the Carbonic anhydrase II (gene name CA2) sub-sub-family, which is one of the fourteen isoforms of human α carbonic anhydrases. | ||
| + | |||
| + | This enzyme is a lyase, which is able to break C-N links, and needs its cofactor, the zinc ion, to be activated. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Carbonic anhydrase II is located in the cytosol, and normally catalyzes the reversible hydration of CO2 into bicarbonate: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:D7423ca6daa1149f361c10b977acad36.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | But in this representation, we observe the carbonic anhydrase II bound to its suicide substrate, the cyanamide, which is hydrated by the enzyme, forming urea. The urea-carbonic anhydrase II complex leads to the inactivation of the enzyme. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Cyanamide is an organic compound, which formula is : | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:620px-Cyanamide.svg.png|300px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Cyanamide is a toxic compound mainly found in pesticides or drugs. It exists as two tautomers, the NCNH2 form dominating the other one. Cyanamide is produced by hydrolysis of calcium cyanamide. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Structure== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The carbonic anhydrase II is composed of 259 amino acids, and its dimensions are 42Å x 42Å x 72Å. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The protein is composed of : | ||
| + | |||
| + | - 5 <scene name='60/604483/Alpha_helix/2'>α helix</scene> | ||
| + | |||
| + | - 15 <scene name='60/604483/Beta_sheets/2'>β sheets</scene> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The protein's '''active site''' is formed of <scene name='60/604483/Zinc_binding_site/2'>three histidines</scene> (residues 94,96 and 119) that can bind a zinc ion. The active site is located in an '''hydrophobic hole''' : | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Znnn.png|500px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | There are two binding sites for mercury : | ||
| + | |||
| + | - <scene name='60/604483/Hg_binding_site/1'>Hg binding site</scene>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | - <scene name='60/604483/Hgb_binding_site/1'>HgB binding site</scene>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | We can see here the conservation of the residues: <jmol> | ||
| + | <jmolCheckbox> | ||
| + | <scriptWhenChecked>select protein; define ~consurf_to_do selected; consurf_initial_scene = true; script "/wiki/ConSurf/f2/1f2w_consurf.spt"</scriptWhenChecked> | ||
| + | <scriptWhenUnchecked>script /wiki/extensions/Proteopedia/spt/initialview01.spt</scriptWhenUnchecked> | ||
| + | </jmolCheckbox> | ||
| + | </jmol> | ||
| + | [[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The most conserved residues are located in the active site's cavity. | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
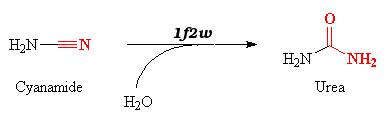
| - | + | In this complex, 1f2w catalyzes the hydration of cyanamide into urea according to the equation : | |
| - | + | [[Image:Cyanamide.png]] | |
| - | + | Cyanamide is a toxic compound, and is an analog of CO2. It can thereby bind the active site of the carbonic anhydrase II thanks to the zinc ion. | |
| - | == | + | The reaction is a '''suicide inhibition''': the enzyme binds an suicide substrate (here cyanamide), and this substrate is modified by the enzyme (here into urea) and produces a reactive group that forms a '''stable inhibitor-enzyme complex'''. |
| + | |||
| + | The inactivation of the carbonic anhydrase II leads to health issues. In fact, it can cause several diseases, such as osteopetrosis autosomal recessive type 3 (also known as Guibaud-Vainsel syndrome). This syndrome is associated with renal tubular acidosis, cerebral calcification (marble brain disease) and in some cases with mental retardation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Mechanism of Action== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The <scene name='60/604483/Cnn_binding_site/2'>Cyanamide</scene> can bind the metal ion and two threonine residues (THR 199 and 200), it is thereby adding to the coordination sphere. The cyanamid attacks the zinc ion (nucleophilic attack). Afertwards the water molecule performs a nucleophilic attack on the zinc-activated cyanamide substrate forming urea which remains bound to the zinc ion. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Urea is tightly linked to the carbonic anhydrase II, acting in this way as an inhibitor. | ||
| - | This is a sample scene created with SAT to <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/1">color</scene> by Group, and another to make <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/2">a transparent representation</scene> of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes. | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1. Briganti F, Mangani S, Scozzafava A, Vernaglione G, Supuran CT (1999) "Carbonic anhydrase catalyzes cyanamide hydration | ||
| + | |||
| + | to urea: is it mimicking the physiological reaction?" J. Biol. Chem 528-36. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | 2. Guerri A, Briganti F, Scozzafava A, Supuran CT, Mangani S (2000) "Mechanism of cyanamide hydration catalyzed by carbonic | ||
| + | |||
| + | anhydrase II suggested by cryogenic X-ray diffraction" Biochemistry 12391-7 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | 3. RCBS: http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1f2w consulted the 2/01/2015 [online] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | 4. PDJB: http://pdbj.org/mine/summary/1f2w consulted the 2/01/2014 [online] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | 5. Jennalib: http://jenalib.fli-leibniz.de/cgi-bin/ImgLib.pl?CODE=1f2w consulted the 3/01/2015 [online] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | 6. Wikipedia "Carbonic anhydrase" http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carbonic_anhydrase consulted the 27/12/2014 [online] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | 7. Wikipedia "Cyanamide" http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cyanamide consulted the 27/12/2014 [online] | ||
| + | |||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Editors== | ||
| + | Flinois Arielle | ||
| + | |||
| + | Hubschwerlin Jean | ||
Current revision
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 15/11/2014, through 15/05/2015 for use in the course "Biomolecule" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the Strasbourg University. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 951 through Sandbox Reserved 975. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
1f2w Cyanamide-Carbonic Anhydrase II EC 4.2.1.1
| |||||||||||
References
1. Briganti F, Mangani S, Scozzafava A, Vernaglione G, Supuran CT (1999) "Carbonic anhydrase catalyzes cyanamide hydration
to urea: is it mimicking the physiological reaction?" J. Biol. Chem 528-36.
2. Guerri A, Briganti F, Scozzafava A, Supuran CT, Mangani S (2000) "Mechanism of cyanamide hydration catalyzed by carbonic
anhydrase II suggested by cryogenic X-ray diffraction" Biochemistry 12391-7
3. RCBS: http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1f2w consulted the 2/01/2015 [online]
4. PDJB: http://pdbj.org/mine/summary/1f2w consulted the 2/01/2014 [online]
5. Jennalib: http://jenalib.fli-leibniz.de/cgi-bin/ImgLib.pl?CODE=1f2w consulted the 3/01/2015 [online]
6. Wikipedia "Carbonic anhydrase" http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carbonic_anhydrase consulted the 27/12/2014 [online]
7. Wikipedia "Cyanamide" http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cyanamide consulted the 27/12/2014 [online]
Editors
Flinois Arielle
Hubschwerlin Jean