We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 976
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (One intermediate revision not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | ==Tissue Plasminogen Activator (t-PA)== | + | ==Tissue-type Plasminogen Activator (t-PA)== |
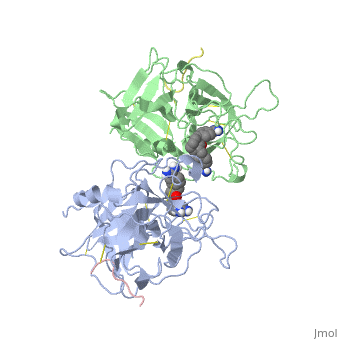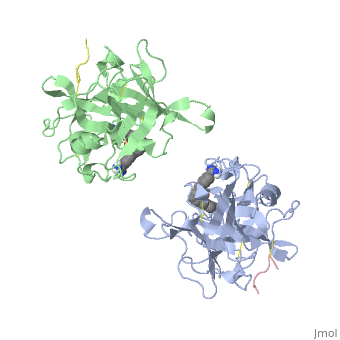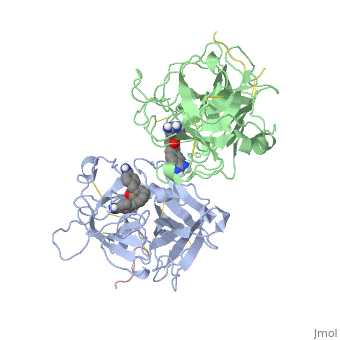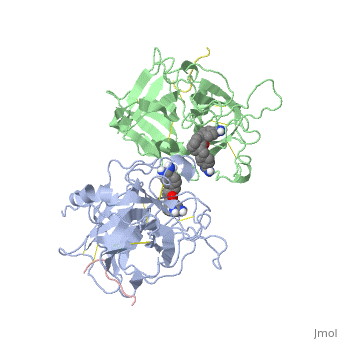
<StructureSection load='1a5h' size='340' side='right' caption='Stereo ribbon plot of the catalytic domain of t-PA in complex with the bis-benzamidine inhibitor' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='1a5h' size='340' side='right' caption='Stereo ribbon plot of the catalytic domain of t-PA in complex with the bis-benzamidine inhibitor' scene=''> | ||
'''Tissue-type Plasminogen Activator''' – usually called '''t-PA''' – is a trypsin-like serine protease that catalyses the conversion of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zymogen zymogen] plasminogen into [[plasmin]]. Once present in the blood, plasmin – which is an active enzyme – degrades [[fibrin]] clots, the product of a coagulation. tPA is clinically used as a treatment for acute [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stroke#Ischemic ischemic strokes], myocardial infarction and pulmonary embolism. | '''Tissue-type Plasminogen Activator''' – usually called '''t-PA''' – is a trypsin-like serine protease that catalyses the conversion of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zymogen zymogen] plasminogen into [[plasmin]]. Once present in the blood, plasmin – which is an active enzyme – degrades [[fibrin]] clots, the product of a coagulation. tPA is clinically used as a treatment for acute [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stroke#Ischemic ischemic strokes], myocardial infarction and pulmonary embolism. | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
The tissue-type Plasminogen Activator is a 69-kDa multidomain glycoprotein, which consists in a single polypeptide chain of 527-530 amino acids <ref name=vivien/>. There is three types of domain: F1 (homologous to fibronectin type I), G (epidermal growth-factor like) and kringle.<ref name=smith>Smith BO, Downing AK, Driscoll PC, Dudgeon TJ, Campbell ID (1995) The solution structure ans backbone dynamics of the fibronectin type I and epidermal growth factor-like pair of modules of tissue-type plasminogen activator. Structure, 3 : 823-833</ref> | The tissue-type Plasminogen Activator is a 69-kDa multidomain glycoprotein, which consists in a single polypeptide chain of 527-530 amino acids <ref name=vivien/>. There is three types of domain: F1 (homologous to fibronectin type I), G (epidermal growth-factor like) and kringle.<ref name=smith>Smith BO, Downing AK, Driscoll PC, Dudgeon TJ, Campbell ID (1995) The solution structure ans backbone dynamics of the fibronectin type I and epidermal growth factor-like pair of modules of tissue-type plasminogen activator. Structure, 3 : 823-833</ref> | ||
| - | The structures described below correspond to the structure of the catalytic domain of humain tPA in complex with a Bis-Benzamidine. The catalytic domain of a protein is the part of the enzyme that reacts with the substrate to induce the enzymatic reaction and benzamidine is an organic compound often used as an inhibitor | + | The structures described below correspond to the structure of the catalytic domain of humain tPA in complex with a Bis-Benzamidine. <scene name='68/686810/Newscene/1'>The catalytic domain of a protein is the part of the enzyme that reacts with the substrate to induce the enzymatic reaction and benzamidine</scene> is an organic compound often used as an inhibitor. Thus, the complexation of t-PA with bis-benzamidine revealed a strong structural similarities to other trypsin-like serine proteases, as alpha-chymotrypsine. tPA is known for its high specificity : tPA recognizes complexes or multiple elements on the surface of plasminogen, even distant form its cleavage site. In vivo, the tPA cleavage site is a single bond of plasminogen formed by the residues Arg560-Val561 <ref name=renatus >Renatus M, Bode W, Huber R, Stürzebecher J, Prasa D, Fisher S, Kohnert U, Stubbs MT (1997) Structural Mapping of the Active Site Specificity Determinants of Human Tissue-type Plasminogen Activator. The Journal of Biological Chemestry, 272 : 21712-21719</ref>. |
Few t-PA-specific inhibitors are known. Synthetic inhibitors for t-PA-like proteins has been based on Arginin and Lysin residues derivatives and the structurally related benzamidines. | Few t-PA-specific inhibitors are known. Synthetic inhibitors for t-PA-like proteins has been based on Arginin and Lysin residues derivatives and the structurally related benzamidines. | ||
Current revision
Tissue-type Plasminogen Activator (t-PA)
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Vivien D, Gauberti M, Montagne A, Defer G and Touzé E (2011) Impact of tissue plaminogen activator on the neurovascular unit : from clinical data to experimental evidence. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism, 31 : 2119-2134.
- ↑ Maithili Sashindranath,1 Eunice Sales,1 Maria Daglas,1 Roxann Freeman, (2012) The tissue-type plasminogen activator–plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 complex promotes neurovascular injury in brain trauma: evidence from mice and humans. Brain 2012: 135; 3251–3264
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Role of Tissue-Type Plasminogen Activator in Ischemic Stroke, Yasuhiro Suzuki 1, (2010) J Pharmacol Sci 113, 203 – 207 (2010)
- ↑ Thrombolytic Therapy for the Treatment of Prosthetic Heart Valve Thrombosis in Pregnancy With Low-Dose, Slow Infusion of Tissue-Type Plasminogen Activator (2013). Mehmet Özkan, Beytullah Çakal, Süleyman Karakoyun, Ozan Mustafa Gürsoy, doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.001145 Circulation. 2013;128:532-540; originally published online June 28, 2013
- ↑ Smith BO, Downing AK, Driscoll PC, Dudgeon TJ, Campbell ID (1995) The solution structure ans backbone dynamics of the fibronectin type I and epidermal growth factor-like pair of modules of tissue-type plasminogen activator. Structure, 3 : 823-833
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Renatus M, Bode W, Huber R, Stürzebecher J, Prasa D, Fisher S, Kohnert U, Stubbs MT (1997) Structural Mapping of the Active Site Specificity Determinants of Human Tissue-type Plasminogen Activator. The Journal of Biological Chemestry, 272 : 21712-21719