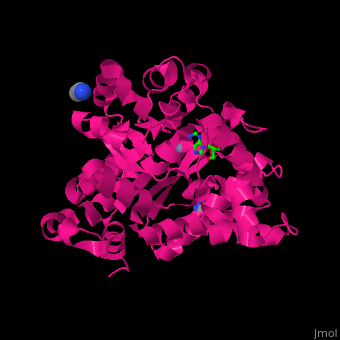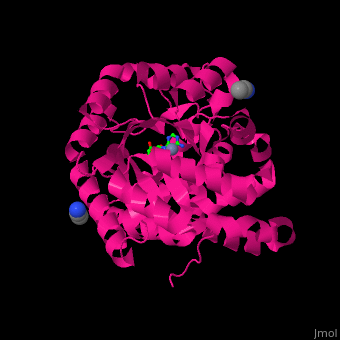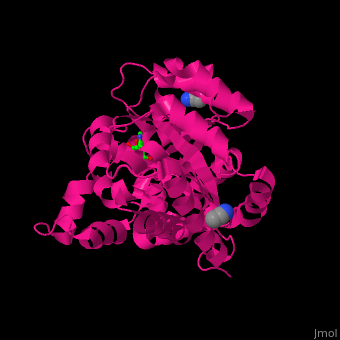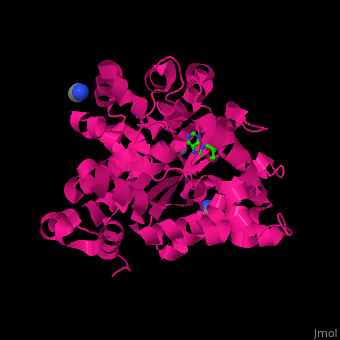Adenosine deaminase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (13 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | <StructureSection load=' | + | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of adenosine deaminase complex with Zn+2 (grey), acetonitrile and adenosine (stick figure) (PDB entry [[2pgf]])' scene='54/547081/Cv/1'> |
| - | + | == Function == | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | '''Adenosine deaminase''' (ADA) or '''double-stranded RNA-specific editase''' deaminates adenosine and deoxyadenosine into inosine or deoxyinosine. ADA is part of the purine metabolism. In humans ADA is involved in the development and maintenance of the immune system. ADA binds dipeptidyl peptidase IV. The complex acts as a positive regulator of T-cell coactivation and regulates lymphocytes-epithelial adhesion.<ref>PMID:1925539</ref> | |
| + | *'''Double-stranded RNA-specific adenosine deaminase''' catalyses the C-6 deamination of adenosine in viral RNAs and cellular pre-mRNA<ref>PMID:9735305</ref>. | ||
| + | *'''tRNA-specific adenosine deaminase''' catalyses the deamination of adenosine to inosine in tRNA<ref>PMID:10430867</ref>. | ||
| - | + | == Disease == | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ADA deficiency is the cause of severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID). SCID was the first disorder to be treated by gene therapy. | |
| - | + | == Relevance == | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ADA is used in testing for the presence of tuberculosis as its level is increased in TB patients. | |
| - | + | == Structural highlights == | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | There are 2 isoforms of ADA: ADA1 and ADA2. <scene name='54/547081/Cv/3'>ADA contains Zn+2 ion in its active site</scene> ([[2pgf]]).<ref>PMID:18602399</ref> Water mlecules are shown as red spheres. | |
| - | + | == 3D Structures of adenosine deaminase == | |
| - | + | [[Adenosine deaminase 3D structures]] | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | *tRNA-specific adenosine deaminase | ||
| - | + | ==References == | |
| - | + | <references/> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | }} | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Wilson DK, Rudolph FB, Quiocho FA. Atomic structure of adenosine deaminase complexed with a transition-state analog: understanding catalysis and immunodeficiency mutations. Science. 1991 May 31;252(5010):1278-84. PMID:1925539
- ↑ Liu Y, Herbert A, Rich A, Samuel CE. Double-stranded RNA-specific adenosine deaminase: nucleic acid binding properties. Methods. 1998 Jul;15(3):199-205. PMID:9735305 doi:10.1006/meth.1998.0624
- ↑ Maas S, Gerber AP, Rich A. Identification and characterization of a human tRNA-specific adenosine deaminase related to the ADAR family of pre-mRNA editing enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Aug 3;96(16):8895-900. PMID:10430867 doi:10.1073/pnas.96.16.8895
- ↑ Larson ET, Deng W, Krumm BE, Napuli A, Mueller N, Van Voorhis WC, Buckner FS, Fan E, Lauricella A, DeTitta G, Luft J, Zucker F, Hol WG, Verlinde CL, Merritt EA. Structures of substrate- and inhibitor-bound adenosine deaminase from a human malaria parasite show a dramatic conformational change and shed light on drug selectivity. J Mol Biol. 2008 Sep 12;381(4):975-88. Epub 2008 Jun 24. PMID:18602399 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2008.06.048