We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
UBC13 MMS2
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (15 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | <Structure load='1J7D' size='350 | + | <Structure load='1J7D' size='350' scene='69/695700/Ubc13_mms2_overall/1' caption='Human ubiquitin conjugating enzyme E2 13 complex with HMM2 (PDB code [[1j7d]])' > |
==Summary== | ==Summary== | ||
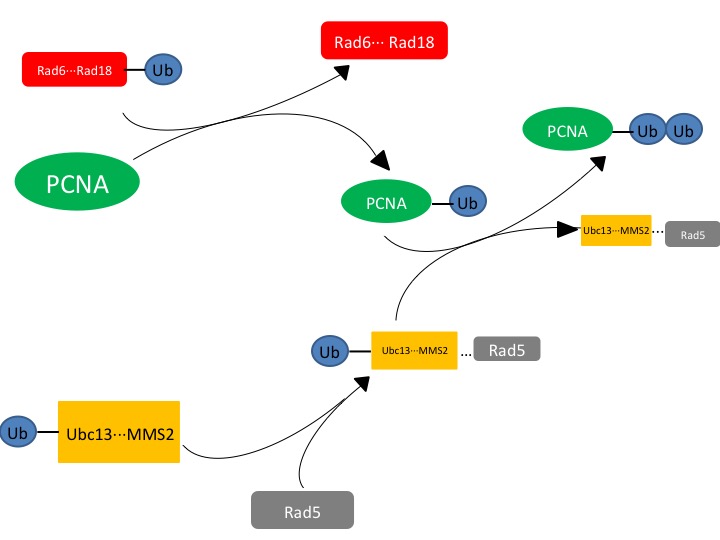
| - | Ubc13 is an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme that can form a heterodimer with Mms2 to function as a part of the translesion synthesis (TLS) pathway,<ref name=halas>3. Halas, A.; Podlaska, A. F.; Derkacz, J. F.; McIntyre, J. F.; Skoneczna, A. F.; Sledziewska-Gojska, E. The roles of PCNA SUMOylation, Mms2-Ubc13 and Rad5 in translesion DNA synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Molecular microbiology JID - 8712028 0809.</ref><ref name=anderson>1. Andersen, P. L.; Zhou, H. F.; Pastushok, L. F.; Moraes, T. F.; McKenna, S. F.; Ziola B FAU - Ellison, Michael,J.; FAU, E. M.; FAU, D. V.; Xiao, W. Distinct regulation of Ubc13 functions by the two ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme variants Mms2 and Uev1A. The Journal of cell biology JID - 0375356 1107.</ref>. When bound to Mms2, Ubc13 will polyubiquitinate proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), a sliding clamp protein at the DNA transcription fork<ref name=halas>3. Halas, A.; Podlaska, A. F.; Derkacz, J. F.; McIntyre, J. F.; Skoneczna, A. F.; Sledziewska-Gojska, E. The roles of PCNA SUMOylation, Mms2-Ubc13 and Rad5 in translesion DNA synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Molecular microbiology JID - 8712028 0809.</ref>. Ubc13-Mms2 functions to polyubiquitinate PCNA following the initial monoubiquitination by Rad6-Rad18 (another E2 complex)<ref name=anderson>1. Andersen, P. L.; Zhou, H. F.; Pastushok, L. F.; Moraes, T. F.; McKenna, S. F.; Ziola B FAU - Ellison, Michael,J.; FAU, E. M.; FAU, D. V.; Xiao, W. Distinct regulation of Ubc13 functions by the two ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme variants Mms2 and Uev1A. The Journal of cell biology JID - 0375356 1107.</ref>. | + | '''Ubc13''' is an '''E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme''' that can form a heterodimer with Mms2 to function as a part of the translesion synthesis (TLS) pathway,<ref name=halas>3. Halas, A.; Podlaska, A. F.; Derkacz, J. F.; McIntyre, J. F.; Skoneczna, A. F.; Sledziewska-Gojska, E. The roles of PCNA SUMOylation, Mms2-Ubc13 and Rad5 in translesion DNA synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Molecular microbiology JID - 8712028 0809.</ref><ref name=anderson>1. Andersen, P. L.; Zhou, H. F.; Pastushok, L. F.; Moraes, T. F.; McKenna, S. F.; Ziola B FAU - Ellison, Michael,J.; FAU, E. M.; FAU, D. V.; Xiao, W. Distinct regulation of Ubc13 functions by the two ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme variants Mms2 and Uev1A. The Journal of cell biology JID - 0375356 1107.</ref>. When bound to Mms2, Ubc13 will polyubiquitinate proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), a sliding clamp protein at the DNA transcription fork<ref name=halas>3. Halas, A.; Podlaska, A. F.; Derkacz, J. F.; McIntyre, J. F.; Skoneczna, A. F.; Sledziewska-Gojska, E. The roles of PCNA SUMOylation, Mms2-Ubc13 and Rad5 in translesion DNA synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Molecular microbiology JID - 8712028 0809.</ref>. Ubc13-Mms2 functions to polyubiquitinate PCNA following the initial monoubiquitination by Rad6-Rad18 (another E2 complex)<ref name=anderson>1. Andersen, P. L.; Zhou, H. F.; Pastushok, L. F.; Moraes, T. F.; McKenna, S. F.; Ziola B FAU - Ellison, Michael,J.; FAU, E. M.; FAU, D. V.; Xiao, W. Distinct regulation of Ubc13 functions by the two ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme variants Mms2 and Uev1A. The Journal of cell biology JID - 0375356 1107.</ref>. It is important to note that Ubc13 lacks the ability to be catalytically active without Mms2, hinting at inaccuracies within the statement "structure determines function." |
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
* Another E2 complex, Rad6-Rad18, starts the process of DNA repair by monoubiquitinating PCNA near the replication fork of DNA. This DNA repair will arrest cell cycle progression until DNA repair is complete<ref name=anderson>1. Andersen, P. L.; Zhou, H. F.; Pastushok, L. F.; Moraes, T. F.; McKenna, S. F.; Ziola B FAU - Ellison, Michael,J.; FAU, E. M.; FAU, D. V.; Xiao, W. Distinct regulation of Ubc13 functions by the two ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme variants Mms2 and Uev1A. The Journal of cell biology JID - 0375356 1107.</ref>. | * Another E2 complex, Rad6-Rad18, starts the process of DNA repair by monoubiquitinating PCNA near the replication fork of DNA. This DNA repair will arrest cell cycle progression until DNA repair is complete<ref name=anderson>1. Andersen, P. L.; Zhou, H. F.; Pastushok, L. F.; Moraes, T. F.; McKenna, S. F.; Ziola B FAU - Ellison, Michael,J.; FAU, E. M.; FAU, D. V.; Xiao, W. Distinct regulation of Ubc13 functions by the two ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme variants Mms2 and Uev1A. The Journal of cell biology JID - 0375356 1107.</ref>. | ||
* UEV1A, another cofactor enzyme that binds to Ubc13, is thought to compete with Mms2 for binding to Ubc13. This is thought to be a regulatory mechanism for Ubc13 activity in the nucleus of cells<ref name=anderson>1. Andersen, P. L.; Zhou, H. F.; Pastushok, L. F.; Moraes, T. F.; McKenna, S. F.; Ziola B FAU - Ellison, Michael,J.; FAU, E. M.; FAU, D. V.; Xiao, W. Distinct regulation of Ubc13 functions by the two ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme variants Mms2 and Uev1A. The Journal of cell biology JID - 0375356 1107.</ref>. | * UEV1A, another cofactor enzyme that binds to Ubc13, is thought to compete with Mms2 for binding to Ubc13. This is thought to be a regulatory mechanism for Ubc13 activity in the nucleus of cells<ref name=anderson>1. Andersen, P. L.; Zhou, H. F.; Pastushok, L. F.; Moraes, T. F.; McKenna, S. F.; Ziola B FAU - Ellison, Michael,J.; FAU, E. M.; FAU, D. V.; Xiao, W. Distinct regulation of Ubc13 functions by the two ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme variants Mms2 and Uev1A. The Journal of cell biology JID - 0375356 1107.</ref>. | ||
| - | *Several DNA polymerases such as rev1, pol eta, and pol zeta contain Ubiquitin-binding domains that recognize K164 polyubiquitination of PCNA<ref name=halas>3. Halas, A.; Podlaska, A. F.; Derkacz, J. F.; McIntyre, J. F.; Skoneczna, A. F.; Sledziewska-Gojska, E. The roles of PCNA SUMOylation, Mms2-Ubc13 and Rad5 in translesion DNA synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Molecular microbiology JID - 8712028 0809.</ref>. | + | *Several DNA polymerases such as rev1, pol eta, and pol zeta contain Ubiquitin-binding domains that recognize <scene name='69/695700/Pcna/1'>K164</scene> polyubiquitination of PCNA<ref name=halas>3. Halas, A.; Podlaska, A. F.; Derkacz, J. F.; McIntyre, J. F.; Skoneczna, A. F.; Sledziewska-Gojska, E. The roles of PCNA SUMOylation, Mms2-Ubc13 and Rad5 in translesion DNA synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Molecular microbiology JID - 8712028 0809.</ref>. |
*Rad5, an E3 RING (Really Interesting New Gene) protein, interacts with the Ubc13-Mms2 heterodimer in order to ligate the ubiquitin on the PCNA. Rad5, as well as Rad18 (RING proteins) are involved in the recruitment of Ubc13-Mms2 heterodimer formation<ref name=anderson>1. Andersen, P. L.; Zhou, H. F.; Pastushok, L. F.; Moraes, T. F.; McKenna, S. F.; Ziola B FAU - Ellison, Michael,J.; FAU, E. M.; FAU, D. V.; Xiao, W. Distinct regulation of Ubc13 functions by the two ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme variants Mms2 and Uev1A. The Journal of cell biology JID - 0375356 1107.</ref>. | *Rad5, an E3 RING (Really Interesting New Gene) protein, interacts with the Ubc13-Mms2 heterodimer in order to ligate the ubiquitin on the PCNA. Rad5, as well as Rad18 (RING proteins) are involved in the recruitment of Ubc13-Mms2 heterodimer formation<ref name=anderson>1. Andersen, P. L.; Zhou, H. F.; Pastushok, L. F.; Moraes, T. F.; McKenna, S. F.; Ziola B FAU - Ellison, Michael,J.; FAU, E. M.; FAU, D. V.; Xiao, W. Distinct regulation of Ubc13 functions by the two ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme variants Mms2 and Uev1A. The Journal of cell biology JID - 0375356 1107.</ref>. | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
Ubc13 weights 17.6 kDA, and Mms2 is 16.8 kDA<ref name=Pastushok> Pastushok, L.; FAU, M. T.; FAU, E. M.; Xiao, W. A single Mms2 "key" residue insertion into a Ubc13 pocket determines the interface specificity of a human Lys63 ubiquitin conjugation complex. The Journal of biological chemistry JID - 2985121R 0902.</ref>. The heterodimer is stable at high stalt concentrations (1 M), suggesting strong interactions between the two. Kd between the Ubc13 and Mms2 is 2 uM. | Ubc13 weights 17.6 kDA, and Mms2 is 16.8 kDA<ref name=Pastushok> Pastushok, L.; FAU, M. T.; FAU, E. M.; Xiao, W. A single Mms2 "key" residue insertion into a Ubc13 pocket determines the interface specificity of a human Lys63 ubiquitin conjugation complex. The Journal of biological chemistry JID - 2985121R 0902.</ref>. The heterodimer is stable at high stalt concentrations (1 M), suggesting strong interactions between the two. Kd between the Ubc13 and Mms2 is 2 uM. | ||
| - | <scene name='69/695700/Ubc13_mms2_phe57/1'>Phe57</scene> and Glu55 of Ubc13 interact with the N-terminal domain of Mms2 to ensure stable docking<ref name=Pastushok> Pastushok, L.; FAU, M. T.; FAU, E. M.; Xiao, W. A single Mms2 "key" residue insertion into a Ubc13 pocket determines the interface specificity of a human Lys63 ubiquitin conjugation complex. The Journal of biological chemistry JID - 2985121R 0902.</ref>. Additionally, Arg70 hydrophobically interacts with an alpha helix of Mms2 in two places<ref name=Pastushok> 7. Pastushok, L.; FAU, M. T.; FAU, E. M.; Xiao, W. A single Mms2 "key" residue insertion into a Ubc13 pocket determines the interface specificity of a human Lys63 ubiquitin conjugation complex. The Journal of biological chemistry JID - 2985121R 0902.</ref>. Mms2’s Phe13 is inserted between Glu55, Phe57, and Arg70 of Ubc13 to create a hydrophobic pocket<ref name=Pastushok> 7. Pastushok, L.; FAU, M. T.; FAU, E. M.; Xiao, W. A single Mms2 "key" residue insertion into a Ubc13 pocket determines the interface specificity of a human Lys63 ubiquitin conjugation complex. The Journal of biological chemistry JID - 2985121R 0902.</ref>. It is therorized that Glu55 and Arg70 of Ubc13 are more important for recognition instead of stability<ref name=Pastushok> 7. Pastushok, L.; FAU, M. T.; FAU, E. M.; Xiao, W. A single Mms2 "key" residue insertion into a Ubc13 pocket determines the interface specificity of a human Lys63 ubiquitin conjugation complex. The Journal of biological chemistry JID - 2985121R 0902.</ref>. | + | <scene name='69/695700/Ubc13_mms2_phe57/1'>Phe57</scene> and <scene name='69/695700/Ubc13_mms2_glu55/1'>Glu55</scene> of Ubc13 interact with the N-terminal domain of Mms2 to ensure stable docking<ref name=Pastushok> Pastushok, L.; FAU, M. T.; FAU, E. M.; Xiao, W. A single Mms2 "key" residue insertion into a Ubc13 pocket determines the interface specificity of a human Lys63 ubiquitin conjugation complex. The Journal of biological chemistry JID - 2985121R 0902.</ref>. Additionally, <scene name='69/695700/Ubc13_mms2_arg70/1'>Arg70</scene> hydrophobically interacts with an alpha helix of Mms2 in two places<ref name=Pastushok> 7. Pastushok, L.; FAU, M. T.; FAU, E. M.; Xiao, W. A single Mms2 "key" residue insertion into a Ubc13 pocket determines the interface specificity of a human Lys63 ubiquitin conjugation complex. The Journal of biological chemistry JID - 2985121R 0902.</ref>. Mms2’s <scene name='69/695700/Ubc13_mms2_phe13/1'>Phe13</scene> is inserted between Glu55, Phe57, and Arg70 of Ubc13 to create a <scene name='69/695700/Ubc13_mms2_hydrophobic/1'>hydrophobic pocket</scene><ref name=Pastushok> 7. Pastushok, L.; FAU, M. T.; FAU, E. M.; Xiao, W. A single Mms2 "key" residue insertion into a Ubc13 pocket determines the interface specificity of a human Lys63 ubiquitin conjugation complex. The Journal of biological chemistry JID - 2985121R 0902.</ref>. It is therorized that <scene name='69/695700/Ubc13_mms2_glu55_and_arg70/1'>Glu55 and Arg70</scene> of Ubc13 are more important for recognition instead of stability<ref name=Pastushok> 7. Pastushok, L.; FAU, M. T.; FAU, E. M.; Xiao, W. A single Mms2 "key" residue insertion into a Ubc13 pocket determines the interface specificity of a human Lys63 ubiquitin conjugation complex. The Journal of biological chemistry JID - 2985121R 0902.</ref>. |
==Mechanism== | ==Mechanism== | ||
| - | The exact mechanism for how Ubc13 transfers ubiquitin is not known, however the mechanism occurs in either a step-wise or concerted reaction. | + | The exact mechanism for how Ubc13 transfers ubiquitin is not known, however the mechanism occurs in either a step-wise or concerted reaction. Ubc13, as an E2, froms a covalent bond with ubiquitin and then transfers the ubiquitin to the target protein via a thioester intermediate. Ubiquitin is removed from Ubc13 and Mms2 complex and placed onto PCNA. |
| + | ==3D structure of Ubc13== | ||
| + | [[Ubiquitin conjugating enzyme]] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
David A Taves, Michal Harel, Christopher Alexander Hudson, Nicholas R. Dunham