We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox1087
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
(New page: ==Your Heading Here (maybe something like 'Structure')== <StructureSection load='1ema' size='340' side='right' caption='Caption for this structure' scene=''> This is a default text for you...) |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
Green fluorescent protein (1ema) | Green fluorescent protein (1ema) | ||
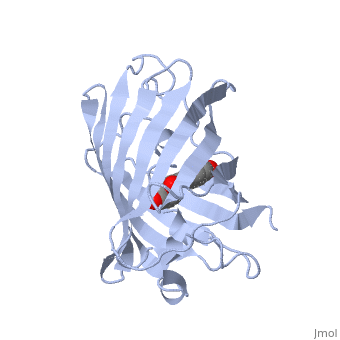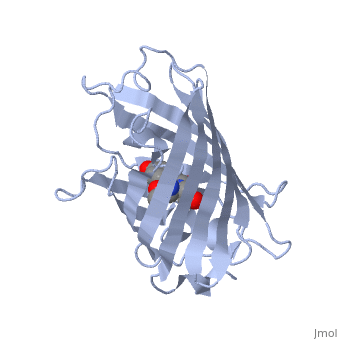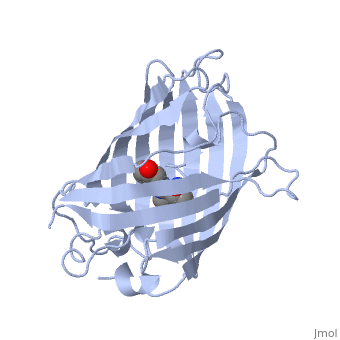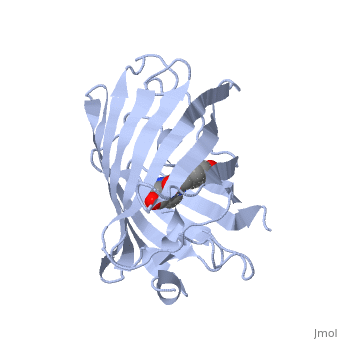
| - | Green fluorescent protein (GFP), originally isolated from the jellyfish Aequorea victoria (PDB entry 1ema), fluorsceses green (509nm) when exposed to blue light (395nm and 475nm). It is one of the most important proteins used in biological research because it can be used to tag otherwise invisible gene products of interest and thus observe their existence, location and movement. | + | <scene name='70/700359/1ema/1'>Green fluorescent protein</scene> (GFP), originally isolated from the jellyfish Aequorea victoria (PDB entry <scene name='70/700359/111/1'>1ema</scene>), fluorsceses green (509nm) when exposed to blue light (395nm and 475nm). It is one of the most important proteins used in biological research because it can be used to tag otherwise invisible gene products of interest and thus observe their existence, location and movement. |
Exploring the Structure | Exploring the Structure | ||
| - | GFP is a beta barrel protein with 11 beta sheets. It is a 26.9kDa protein made up of 238 amino acids. The chromophore, responsible for the fluorescent properties of the protein, is buried inside the beta barrel as part of the central alpha helix passing through the barrel. The chromophore forms via spontaneous cyclization and oxidation of three residues in the central alpha helix: -Thr65 (or Ser65)-Tyr66-Gly67. This cyclization and oxidation creates the chromophore's five-membered ring via a new bond between the threonine and the glycine residues.[1] | + | GFP is a beta barrel protein with 11 beta sheets. It is a 26.9kDa protein made up of (238 amino acids) <scene name='70/700359/999/1'>lema</scene>. The chromophore, responsible for the fluorescent properties of the protein, is buried inside the beta barrel as part of the central alpha helix passing through the barrel. The chromophore forms via spontaneous cyclization and oxidation of three residues in the central alpha helix: -Thr65 (or Ser65)-Tyr66-Gly67. This cyclization and oxidation creates the chromophore's five-membered ring via a new bond between the threonine and the glycine residues.[1] |
Current revision
Your Heading Here (maybe something like 'Structure')
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644