Cytochrome c
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (30 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
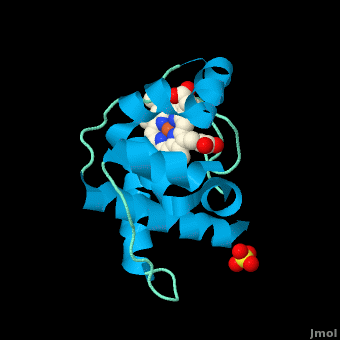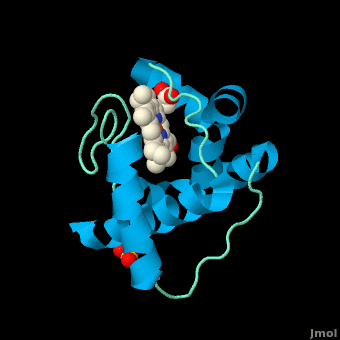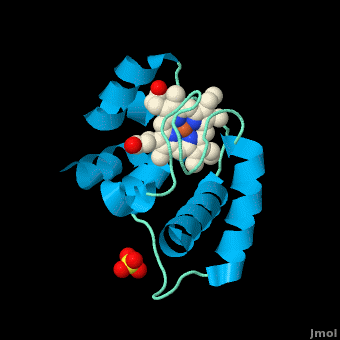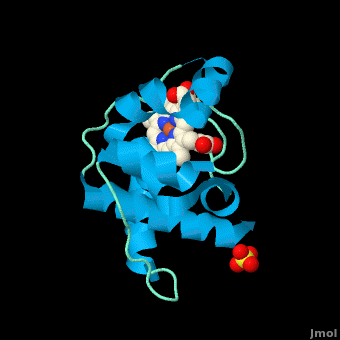
| - | <StructureSection load=' | + | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' scene='Cytochrome_c/Cyt_c/1' caption='Cytochrome c with heme complex with sulfate (PDB code [[3cp5]])'> |
| - | The '''cytochrome ''c''''' (cyt ''c'') proteins are a superfamily belonging to the class of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/All-α_proteins all-α proteins], which are denoted as such by having an α-helical core. Each protein in this superfamily also contains one or more covalently-bound [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heme heme prosthetic groups].<ref>PMID:11697912</ref><ref name=main /> The cyt ''c'' superfamily contains many different families, some of which are better characterized than others. These families include monodomain and multi-domain C-type cytochromes, such as [http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/1etp cyt c4], a diheme C-type cytochrome, and [http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/2ozy NrfB], a pentaheme C-type cytochrome. In particular, the monoheme cyt ''c'' from ''Rhodothermus marinus'' has been previously studied and provides an excellent example of how some protein characteristics and structures can be extremely diverse, yet conserved, through evolution. For details on decaheme cyt see [[MtrF]]. | + | The '''cytochrome ''c''''' (cyt ''c'') proteins are a superfamily belonging to the class of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/All-α_proteins all-α proteins], which are denoted as such by having an α-helical core. Each protein in this superfamily also contains one or more covalently-bound [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heme heme prosthetic groups].<ref>PMID:11697912</ref><ref name=main /> The cyt ''c'' superfamily contains many different families, some of which are better characterized than others. These families include monodomain and multi-domain C-type cytochromes, such as [http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/1etp cyt c4], a diheme C-type cytochrome, and [http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/2ozy NrfB], a pentaheme C-type cytochrome. In particular, the monoheme cyt ''c'' from ''Rhodothermus marinus'' has been previously studied and provides an excellent example of how some protein characteristics and structures can be extremely diverse, yet conserved, through evolution.<br /> For details on decaheme cyt see [[MtrF]].<br /> |
| + | |||
| + | Cytochromes c549, c550, c553, c554, c555, c556, c557, c558, c562 are named after their optical absorption band length. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''Cytochrome c2''' transfers electron from the reduced heme to the bacteriochlorophyl in the reaction centre<ref> PMID 15977062</ref>. | ||
| + | *'''Cytochrome c3''' is specific to anaerobic metabolism in sulphate-reducing bacteria<ref> PMID 12885397</ref>. | ||
| + | *'''Cytochrome c4''' is a dihaem cytochrome<ref> PMID 9032080</ref>. | ||
| + | *'''Cytochrome c7''' is a tri-haem cytochrome<ref> PMID 15133162</ref>. For details on Cyt c7 see [[Cytochrome c 7]]. | ||
| + | *'''Cytochrome c550''' is a component of the PSII complex of cyanobacteria<ref> PMID 22289879</ref>. | ||
| + | *'''Cytochrome c553''' is the primary electron donor of the heliobacteria reaction centre<ref> PMID 24557489</ref>. | ||
| + | *'''Cytochrome c554''' is a tetra-haem cytochrome involved in the oxidation of ammonia<ref> PMID 11372197</ref>. | ||
| + | *'''Cytochrome c555''' is a cytochrome from a primitive anaerobic green sulphur bacteria<ref> PMID 202947</ref>. | ||
| + | *'''Cytochrome c557''' and '''cytochrome c558''' are mitochondrial and contain atypical harm-binding sitei<ref> PMID 242319</ref>. | ||
| + | *'''Cytochrome cL''' is found in methylotrops. It receives an electron from PQQ cofactor of methanol dehydrogenase to produce formaldehyde<ref> PMID 32627749</ref>. | ||
| + | *'''Cytochrome cd1''' icatalyzes the reduction of NO2 to NO and water. | ||
| + | *'''Cytochrome cH''' is the electron donor to the oxidase in methylotrophs<ref> PMID 10386873</ref>. | ||
| + | *'''Cytochrome c XoxG''' is a cytochrome from the lanthanide-dependent methanol dehydrogenase system of methylothrophic bacteria<ref> PMID 31017712</ref>. | ||
| + | See also [[Cytochrome C -Adis]], [[Hemeproteins]], [[Cytochrome C (Hebrew)]], [[Cytochrome C (arabic)]]. | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
| Line 14: | Line 31: | ||
<scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_335/Heme/1'>'Figure 1. The heme group of monoheme cytochrome ''c'' purified from ''Rhodothermus marinus''</scene> | <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_335/Heme/1'>'Figure 1. The heme group of monoheme cytochrome ''c'' purified from ''Rhodothermus marinus''</scene> | ||
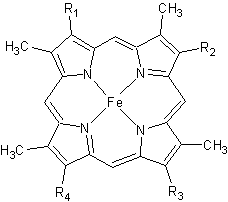
| - | All members in the C-type cytochrome superfamily contain a heme prosthetic group that is covalently attached to the protein via two thioether bonds to cysteine residues. Most cytochromes ''c'' occur in a | + | All members in the C-type cytochrome superfamily contain a heme prosthetic group that is covalently attached to the protein via two thioether bonds to cysteine residues. Most cytochromes ''c'' occur in a where the histidine residue is one of the two axial ligands of the heme iron.<ref name=main>PMID:18855424</ref><ref name=heme /> In monoheme cytochromes ''c'', the other axial position may be left vacant or be occupied by histidine or methionine residues; however, it can sometimes be occupied by cysteine or lysine residues.<ref name=main />. In ''Rm''cyt''c'', XX represents a threonine (Thr46) and an alanine residue (Ala47) that help form the loop 2 structure. |
[[Image:heme.gif |frame|left| Figure 2. The tetrapyrrolic heme prosthetic group that can either be covalently attached to or closely associated with various proteins, such as cytochromes and other globin proteins. In ''Rm''cyt''c'', R2 is an ethyl group covalently attached to Cys 45, and R3 is a methyl group covalently attached to Cys48.]] | [[Image:heme.gif |frame|left| Figure 2. The tetrapyrrolic heme prosthetic group that can either be covalently attached to or closely associated with various proteins, such as cytochromes and other globin proteins. In ''Rm''cyt''c'', R2 is an ethyl group covalently attached to Cys 45, and R3 is a methyl group covalently attached to Cys48.]] | ||
| Line 53: | Line 70: | ||
==Structural model of the [Fe]-hydrogenase/cytochrome C553 complex combining NMR and soft-docking<ref>PMID:10748163</ref>== | ==Structural model of the [Fe]-hydrogenase/cytochrome C553 complex combining NMR and soft-docking<ref>PMID:10748163</ref>== | ||
The <scene name='1e08/1e08-cofactors/1'>complex</scene> shows the specific interaction of the hydrogenase (light blue) with the cytochrome (pink), revealing the path of electron transport from the <scene name='1e08/1e08-activecluster/3'>active site metal cluster</scene>, through three iron-sulfur clusters, and ending in the cytochrome heme (colored red). Two <scene name='1e08/1e08-cys/2'>cysteine amino acids at the interface</scene>, CYS 38 in the hydrogenase and CYS10 in the cytochrome, are thought to provide the electron transfer pathway between the two proteins (these scenes were created by Jaime Prilusky, David S. Goodsell, and Eran Hodis). | The <scene name='1e08/1e08-cofactors/1'>complex</scene> shows the specific interaction of the hydrogenase (light blue) with the cytochrome (pink), revealing the path of electron transport from the <scene name='1e08/1e08-activecluster/3'>active site metal cluster</scene>, through three iron-sulfur clusters, and ending in the cytochrome heme (colored red). Two <scene name='1e08/1e08-cys/2'>cysteine amino acids at the interface</scene>, CYS 38 in the hydrogenase and CYS10 in the cytochrome, are thought to provide the electron transfer pathway between the two proteins (these scenes were created by Jaime Prilusky, David S. Goodsell, and Eran Hodis). | ||
| - | </StructureSection> | ||
| - | == | + | == Conformational control of the binding of diatomic gases to cytochrome c’ <ref>PMID 25792378 </ref>== |
| - | + | The cytochromes c′ (CYTcp) are found in denitrifying, methanotrophic and photosynthetic bacteria. These proteins are able to form stable adducts with CO and NO but not with O2. The binding of NO to CYTcp currently provides the best structural model for the NO activation mechanism of soluble guanylate cyclase. Ligand binding in CYTcps has been shown to be highly dependent on residues in both the proximal and distal heme pockets. Group 1 CYTcps typically have a phenylalanine residue positioned close to the distal face of heme, while for group 2, this residue is typically leucine. We have structurally, spectroscopically and kinetically characterised the CYTcp from ''Shewanella frigidimarina'' <scene name='69/696899/Cv/2'>(SFCP)</scene>, a protein that has a distal phenylalanine residue and a lysine in the proximal pocket in place of the more common arginine (<font color='red'><b>monomer A is colored in red</b></font>, <span style="color:lime;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">monomer B in green</span>, and <span style="color:yellow;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">heme group in yellow</span>). <scene name='69/696899/Cv/3'>Each monomer of the SFCP dimer folds as a 4-alpha-helical bundle</scene> in a similar manner to CYTcps previously characterised. | |
| - | + | * <scene name='69/696899/Cv/4'>Heme group and its environment in as-isolated SFCP</scene>. | |
| + | * <scene name='69/696899/Cv/5'>Proximal NO complex of SFCP (monomer A)</scene>. | ||
| + | * <scene name='69/696899/Cv/8'>Click here to see the difference between these structures</scene>. | ||
| + | SFCP exhibits biphasic binding kinetics for both NO and CO as a result of the high level of steric hindrance from the aromatic side chain of residue Phe 16. The binding of distal ligands is thus controlled by the conformation of the phenylalanine ring. | ||
| + | * <scene name='69/696899/Cv/12'>A superposition of the heme environments</scene> of <span style="color:lime;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">SFCP (in green</span>;[[4ulv]]), <font color='magenta'><b>RCCP (''R. capsulatus''; in magenta</b></font>; [[1cpq]]), <font color='red'><b>RSCP (''R. sphaeroides''; in red</b></font>; [[1gqa]]) and <span style="color:cyan;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">RGCP (''R. gelatinosus''; in cya)</span>; [[2j8w]]). | ||
| + | * <scene name='69/696899/Cv/14'>Click here to see morph of this scene</scene>. | ||
| + | Only a proximal 5-coordinate NO adduct, confirmed by structural data, is observed with no detectable hexacoordinate distal NO adduct. | ||
| - | + | ==3D structures of cytochrome C== | |
| + | [[Cytochrome C 3D structures]] | ||
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | **[[3qvy]], [[3qw0]], [[3qw1]] – EcCyt + Zn<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3c62]], [[3c63]], [[3iq5]], [[3iq6]], [[3l1m]], [[3m15]], [[3nmi]], [[3nmk]] - EcCyt (mutant) + Zn<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3de8]], [[3m79]] - EcCyt (mutant) + Zn + Cu<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3de9]], [[3nmj]] - EcCyt (mutant) + Zn + Ni | ||
| - | }} | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Gough J, Karplus K, Hughey R, Chothia C. Assignment of homology to genome sequences using a library of hidden Markov models that represent all proteins of known structure. J Mol Biol. 2001 Nov 2;313(4):903-19. PMID:11697912 doi:10.1006/jmbi.2001.5080
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 2.11 2.12 2.13 2.14 2.15 Stelter M, Melo AM, Pereira MM, Gomes CM, Hreggvidsson GO, Hjorleifsdottir S, Saraiva LM, Teixeira M, Archer M. A Novel Type of Monoheme Cytochrome c: Biochemical and Structural Characterization at 1.23 A Resolution of Rhodothermus marinus Cytochrome c. Biochemistry. 2008 Oct 15. PMID:18855424 doi:10.1021/bi800999g
- ↑ Axelrod HL, Okamura MY. The structure and function of the cytochrome c2: reaction center electron transfer complex from Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Photosynth Res. 2005;85(1):101-14. PMID:15977062 doi:10.1007/s11120-005-1368-8
- ↑ ElAntak L, Morelli X, Bornet O, Hatchikian C, Czjzek M, Dolla A, Guerlesquin F. The cytochrome c3-[Fe]-hydrogenase electron-transfer complex: structural model by NMR restrained docking. FEBS Lett. 2003 Jul 31;548(1-3):1-4. PMID:12885397
- ↑ Kadziola A, Larsen S. Crystal structure of the dihaem cytochrome c4 from Pseudomonas stutzeri determined at 2.2A resolution. Structure. 1997 Feb 15;5(2):203-16. PMID:9032080
- ↑ Pokkuluri PR, Londer YY, Duke NE, Erickson J, Pessanha M, Salgueiro CA, Schiffer M. Structure of a novel c7-type three-heme cytochrome domain from a multidomain cytochrome c polymer. Protein Sci. 2004 Jun;13(6):1684-92. Epub 2004 May 7. PMID:15133162 doi:10.1110/ps.04626204
- ↑ Roncel M, Kirilovsky D, Guerrero F, Serrano A, Ortega JM. Photosynthetic cytochrome c550. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Aug;1817(8):1152-63. PMID:22289879 doi:10.1016/j.bbabio.2012.01.008
- ↑ Kashey TS, Cowgill JB, McConnell MD, Flores M, Redding KE. Expression and characterization of cytochrome c553 from Heliobacterium modesticaldum. Photosynth Res. 2014 Jun;120(3):291-9. PMID:24557489 doi:10.1007/s11120-014-9982-y
- ↑ Iverson TM, Arciero DM, Hooper AB, Rees DC. High-resolution structures of the oxidized and reduced states of cytochrome c554 from Nitrosomonas europaea. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2001 Apr;6(4):390-7. PMID:11372197
- ↑ Korszun ZR, Salemme FR. Structure of cytochrome c555 of Chlorobium thiosulfatophilum: primitive low-potential cytochrome c. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5244-7. PMID:202947 doi:10.1073/pnas.74.12.5244
- ↑ Pettigrew GW, Aviram I, Schejter A. Physicochemical properties of two atypical cytochromes c, Crithidia cytochrome c-557 and Euglena cytochrome c-558. Biochem J. 1975 Jul;149(1):155-67. PMID:242319 doi:10.1042/bj1490155
- ↑ Ghosh S, Dhanasingh I, Ryu J, Kim SW, Lee SH. Crystal structure of Cytochrome cL from the aquatic methylotrophic bacterium Methylophaga aminisulfidivorans MP(T). J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020 Jul 3. pii: jmb.2006.06029. doi:, 10.4014/jmb.2006.06029. PMID:32627749 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.4014/jmb.2006.06029
- ↑ Read J, Gill R, Dales SL, Cooper JB, Wood SP, Anthony C. The molecular structure of an unusual cytochrome c2 determined at 2.0 A; the cytochrome cH from Methylobacterium extorquens. Protein Sci. 1999 Jun;8(6):1232-40. PMID:10386873
- ↑ Featherston ER, Rose HR, McBride MJ, Taylor E, Boal AK, Cotruvo J Jr. Biochemical and structural characterization of XoxG and XoxJ and their roles in activity of the lanthanide-dependent methanol dehydrogenase, XoxF. Chembiochem. 2019 Apr 24. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201900184. PMID:31017712 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/cbic.201900184
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 Reedy CJ, Gibney BR. Heme protein assemblies. Chem Rev. 2004 Feb;104(2):617-49. PMID:14871137 doi:10.1021/cr0206115
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 Ambler RP. Sequence variability in bacterial cytochromes c. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 May 23;1058(1):42-7. PMID:1646017
- ↑ Cookson DJ, Moore GR, Pitt RC, Williams RJP, Campbell ID, Ambler RP, Bruschi M, Le Gall J. Structural homology of cytochromes c. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Feb;83(1):261-75.
- ↑ Than ME, Hof P, Huber R, Bourenkov GP, Bartunik HD, Buse G, Soulimane T. Thermus thermophilus cytochrome-c552: A new highly thermostable cytochrome-c structure obtained by MAD phasing. J Mol Biol. 1997 Aug 29;271(4):629-44. PMID:9281430 doi:10.1006/jmbi.1997.1181
- ↑ Soares CM, Baptista AM, Pereira MM, Teixeira M. Investigation of protonatable residues in Rhodothermus marinus caa3 haem-copper oxygen reductase: comparison with Paracoccus denitrificans aa3 haem-copper oxygen reductase. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2004 Mar;9(2):124-34. Epub 2003 Dec 23. PMID:14691678 doi:10.1007/s00775-003-0509-9
- ↑ Pereira MM, Santana M, Teixeira M. A novel scenario for the evolution of haem-copper oxygen reductases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001 Jun 1;1505(2-3):185-208. PMID:11334784
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 21.2 21.3 21.4 21.5 Karp, Gerald (2008). Cell and Molecular Biology (5th edition). Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-0470042175.
- ↑ Rajagopal BS, Wilson MT, Bendall DS, Howe CJ, Worrall JA. Structural and kinetic studies of imidazole binding to two members of the cytochrome c (6) family reveal an important role for a conserved heme pocket residue. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2011 Jan 26. PMID:21267610 doi:10.1007/s00775-011-0758-y
- ↑ Morelli X, Czjzek M, Hatchikian CE, Bornet O, Fontecilla-Camps JC, Palma NP, Moura JJ, Guerlesquin F. Structural model of the Fe-hydrogenase/cytochrome c553 complex combining transverse relaxation-optimized spectroscopy experiments and soft docking calculations. J Biol Chem. 2000 Jul 28;275(30):23204-10. PMID:10748163 doi:10.1074/jbc.M909835199
- ↑ Manole A, Kekilli D, Svistunenko DA, Wilson MT, Dobbin PS, Hough MA. Conformational control of the binding of diatomic gases to cytochrome c'. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2015 Mar 20. PMID:25792378 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00775-015-1253-7
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, David Canner, Joel L. Sussman, Melissa Morrison, Adis Hasic