We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Pheromone binding protein
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (3 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | ==Introduction== | ||
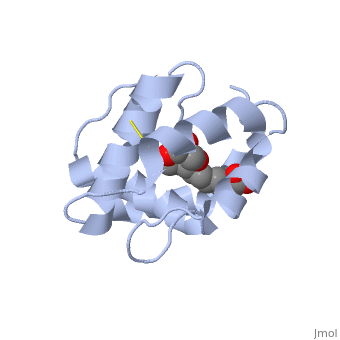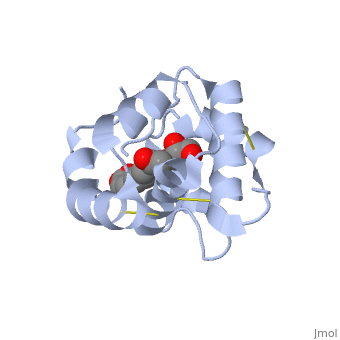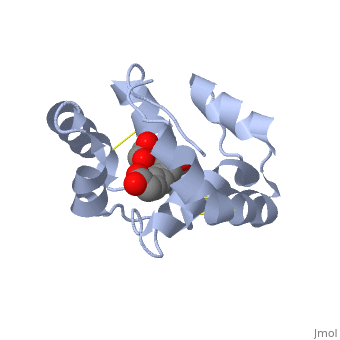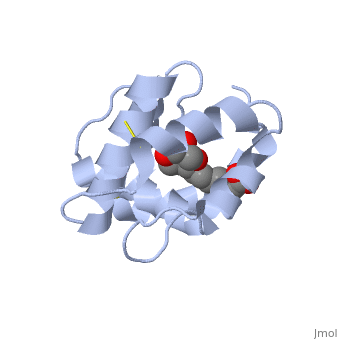
<StructureSection load='3bfa' size='340' side='right' caption='Pheromone binding protein of honey bee complex with pheromone (PDB code [[3bfa]]).' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='3bfa' size='340' side='right' caption='Pheromone binding protein of honey bee complex with pheromone (PDB code [[3bfa]]).' scene=''> | ||
| - | Pheromone binding proteins [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pheromone_binding_protein (PBP)] are type of Odorant binding proteins [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Odorant-binding_protein (OBP)] - soluble proteins mediating the early stages of volatiles detection in both insects and vertebrates<ref>DOI:10.3389/fphys.2014.00320</ref>. The volatiles (pheromones and other small hydrophobic molecules) are solubilized by the OBPs and activate the chemoreceptors. | + | __TOC__ |
| + | ==Introduction== | ||
| + | '''Pheromone binding proteins''' [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pheromone_binding_protein (PBP)] are type of Odorant binding proteins [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Odorant-binding_protein (OBP)] - soluble proteins mediating the early stages of volatiles detection in both insects and vertebrates<ref>DOI:10.3389/fphys.2014.00320</ref>. The volatiles (pheromones and other small hydrophobic molecules) are solubilized by the OBPs and activate the chemoreceptors. | ||
As a model protein of this family we will further describe the well investigated Pheromone binding protein of the honey bee, ASP1. | As a model protein of this family we will further describe the well investigated Pheromone binding protein of the honey bee, ASP1. | ||
| Line 29: | Line 30: | ||
**[[1xfr]] – sPBP – NMR<br /> | **[[1xfr]] – sPBP – NMR<br /> | ||
**[[1gm0]] – sPBP (mutant) – NMR<br /> | **[[1gm0]] – sPBP (mutant) – NMR<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1qwv]], [[1two]], [[2jpo]] – | + | **[[1qwv]], [[1two]], [[2jpo]], [[6um9]] – mPBP – moth - NMR<br /> |
| + | **[[6vq5]] – mPBP <br /> | ||
| + | **[[7uo6]] – PBP2 – corn borer - NMR<br /> | ||
| + | **[[7vw8]], [[7vw9]] – bwPBP1 - bollworm<br /> | ||
* Pheromone binding protein complex | * Pheromone binding protein complex | ||
| - | |||
**[[3bfa]], [[3bfb]], [[3bfh]], [[3cyz]] – bPBP residues 26-144 + pheromone<br /> | **[[3bfa]], [[3bfb]], [[3bfh]], [[3cyz]] – bPBP residues 26-144 + pheromone<br /> | ||
| Line 39: | Line 42: | ||
**[[2p70]] – sPBP + odorant<br /> | **[[2p70]] – sPBP + odorant<br /> | ||
**[[2p71]] – sPBP + iodohexadecane<br /> | **[[2p71]] – sPBP + iodohexadecane<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4inw]], [[4inx]] – PBP + hexadecadienal – Amyelois transitella<br /> | + | **[[4inw]], [[4inx]] – PBP + hexadecadienal – ''Amyelois transitella''<br /> |
| + | **[[7vwa]] – bwPBP1 + odorant <br /> | ||
}} | }} | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
3D structures of pheromone-binding protein
Updated on 23-August-2023
References
- ↑ Pelosi P, Iovinella I, Felicioli A, Dani FR. Soluble proteins of chemical communication: an overview across arthropods. Front Physiol. 2014 Aug 27;5:320. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2014.00320. eCollection, 2014. PMID:25221516 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2014.00320
- ↑ Winston, M.L., 1987. The Biology of the Honey Bee. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA.
- ↑ Pesenti ME, Spinelli S, Bezirard V, Briand L, Pernollet JC, Tegoni M, Cambillau C. Structural basis of the honey bee PBP pheromone and pH-induced conformational change. J Mol Biol. 2008 Jun 27;380(1):158-69. Epub 2008 Apr 27. PMID:18508083 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2008.04.048