|
|
| (17 intermediate revisions not shown.) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
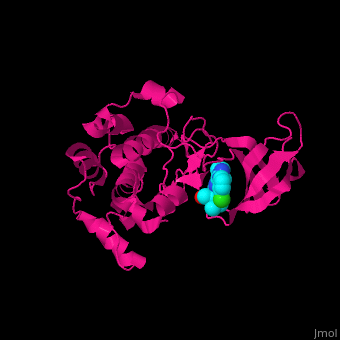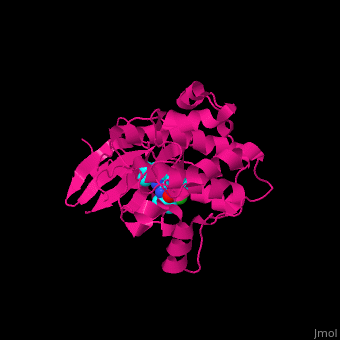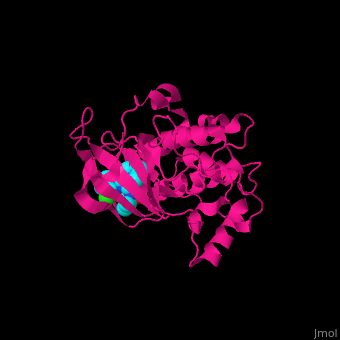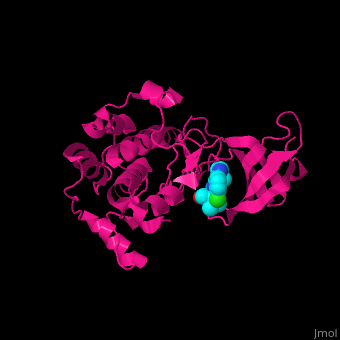
| - | {{STRUCTURE_2z7q| PDB=2z7q | SIZE=300| SCENE=Ribosomal_protein_S6_kinase/Cv/1 |right|CAPTION=Ribosomal protein S6 kinase complex with AMP-PCP and Mg+2 ion (green) [[2z7q]] }}
| + | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='Human ribosomal protein S6 kinase α−1 complex with the inhibitor purvalanol (PDB entry [[2z7s]])' scene='43/434545/Cv/2'> |
| | + | __TOC__ |
| | + | == Function == |
| | + | [[Ribosomal protein S6 kinase]] (RPS6K) regulates RPS6<ref>PMID:22168436</ref>. RPS6K activity controls the ribosome biogenesis transcriptional program. |
| | + | *'''Ribosomal protein S6 kinase alpha''' confers resistance towards therapy of acute myeloid leukaemia using venetoclax/azacitidine<ref>PMID:37414921</ref>. |
| | + | == Relevance == |
| | + | hRPS6K α is overexpressed in breast cancer and is associated with poor prognosis<ref>PMID:19085255</ref>. Inhibitors of RPS6S are studied as potential therapeutic agents for treatment of variety of diseases including diabetes and cancer<ref>PMID:24072592</ref>. |
| | | | |
| - | [[Ribosomal protein S6 kinase]] (RPS6K) regulates RPS6.
| + | == Structural highlights == |
| | + | The <scene name='43/434545/Cv/5'>inhibitor purvalanol binds hRPS6K in the ATP-binding pocket between the N- and C-terminal lobes</scene><ref>PMID:17965187</ref>. <scene name='43/434545/Cv/6'>Active site</scene>. Water molecule are shown as red sphere. |
| | | | |
| | == 3D Structures of Ribosomal protein S6 kinase == | | == 3D Structures of Ribosomal protein S6 kinase == |
| | + | [[Ribosomal protein S6 kinase 3D structures]] |
| | | | |
| - | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}}
| + | == References == |
| - | {{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0|
| + | <references/> |
| - | | + | </StructureSection> |
| - | *Ribosomal protein S6 kinase α
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | **[[2z7q]] - hRPS6K α−1 N-terminal kinase domain - human<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[3rny]], [[2wnt]] - hRPS6K α−1 C-terminal kinase domain<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[2qr7]], [[2qr8]] - mRPS6K α−3 C-terminal kinase domain (mutant) - mouse<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[3g51]] - mRPS6K α−3 N-terminal kinase domain<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[1vzo]] - hRPS6K α−5 N-terminal kinase domain (mutant) <br />
| + | |
| - | **[[3kn6]] - hRPS6K α−5 C-terminal kinase domain<br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | *Ribosomal protein S6 kinase α complex
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | **[[2z7s]], [[2z7r]] - hRPS6K α−1 N-terminal kinase domain+inhibitor<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[4nif]] - hRPS6K α−1 C-terminal kinase domain + mitogen-activated protein kinase 1<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[3ubd]] - hRPS6K α−3 N-terminal kinase domain + flavonol glycoside<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[4gue]] - mRPS6K α−3 N-terminal kinase domain + flavonol glycoside<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[4el9]] - mRPS6K α−3 N-terminal kinase domain + inhibitor<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[4nus]], [[4nw5]], [[4nw6]] - hRPS6K α−3 N-terminal kinase domain + inhibitor<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[4d9t]], [[4d9u]], [[4jg6]], [[4jg7]], [[4jg8]] - hRPS6K α−3 C-terminal kinase domain + inhibitor<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[4m8t]], [[4mao]] - mRPS6K α−3 C-terminal kinase domain (mutant) + inhibitor<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[3kn5]] - hRPS6K α−5 C-terminal kinase domain+AMPPNP<br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | *Ribosomal protein S6 kinase β
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | **[[3a60]], [[3a61]], [[3a62]], [[4l3j]], [[4l3l]] - hRPS6K β−1 kinase domain<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[4l42]], [[4l43]], [[4l44]], [[4l45]], [[4l46]], [[3we4]], [[3wf5]], [[3wf6]], [[4rlo]], [[4rlp]] - hRPS6K β−1 kinase domain + pyrimidine derivative<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[3wf7]] - hRPS6K β−1 kinase domain + purine derivative<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[3wf8]], [[3wf9]] - hRPS6K β−1 kinase domain + quinoline derivative<br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | }}
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| | [[Category:Topic Page]] | | [[Category:Topic Page]] |
|
Function
Ribosomal protein S6 kinase (RPS6K) regulates RPS6[1]. RPS6K activity controls the ribosome biogenesis transcriptional program.
- Ribosomal protein S6 kinase alpha confers resistance towards therapy of acute myeloid leukaemia using venetoclax/azacitidine[2].
Relevance
hRPS6K α is overexpressed in breast cancer and is associated with poor prognosis[3]. Inhibitors of RPS6S are studied as potential therapeutic agents for treatment of variety of diseases including diabetes and cancer[4].
Structural highlights
The [5]. . Water molecule are shown as red sphere.
3D Structures of Ribosomal protein S6 kinase
Ribosomal protein S6 kinase 3D structures
References
- ↑ Magnuson B, Ekim B, Fingar DC. Regulation and function of ribosomal protein S6 kinase (S6K) within mTOR signalling networks. Biochem J. 2012 Jan 1;441(1):1-21. doi: 10.1042/BJ20110892. PMID:22168436 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1042/BJ20110892
- ↑ Weidenauer K, Schmidt C, Rohde C, Pauli C, Blank MF, Heid D, Waclawiczek A, Corbacioglu A, Göllner S, Lotze M, Vierbaum L, Renders S, Krijgsveld J, Raffel S, Sauer T, Trumpp A, Pabst C, Müller-Tidow C, Janssen M. The ribosomal protein S6 kinase alpha-1 (RPS6KA1) induces resistance to venetoclax/azacitidine in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2023 Aug;37(8):1611-1625. PMID:37414921 doi:10.1038/s41375-023-01951-8
- ↑ Kim D, Akcakanat A, Singh G, Sharma C, Meric-Bernstam F. Regulation and localization of ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1 isoforms. Growth Factors. 2009 Feb;27(1):12-21. doi: 10.1080/08977190802556986. PMID:19085255 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/08977190802556986
- ↑ Couty S, Westwood IM, Kalusa A, Cano C, Travers J, Boxall K, Chow CL, Burns S, Schmitt J, Pickard L, Barillari C, McAndrew PC, Clarke PA, Linardopoulos S, Griffin RJ, Aherne GW, Raynaud FI, Workman P, Jones K, van Montfort RL. The discovery of potent ribosomal S6 kinase inhibitors by high-throughput screening and structure-guided drug design. Oncotarget. 2013 Aug 25. PMID:24072592
- ↑ Ikuta M, Kornienko M, Byrne N, Reid JC, Mizuarai S, Kotani H, Munshi SK. Crystal structures of the N-terminal kinase domain of human RSK1 bound to three different ligands: Implications for the design of RSK1 specific inhibitors. Protein Sci. 2007 Dec;16(12):2626-35. Epub 2007 Oct 26. PMID:17965187 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1110/ps.073123707
|