Sarcosine oxidase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (3 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
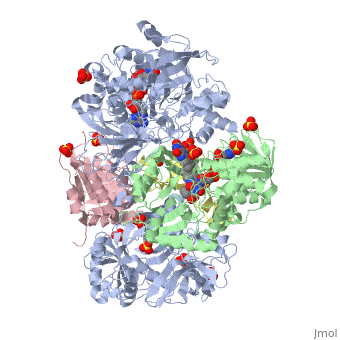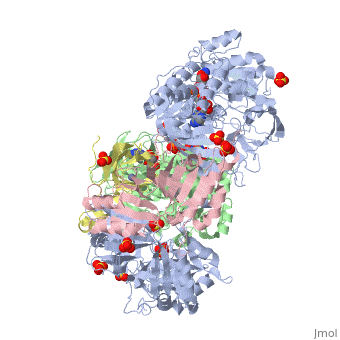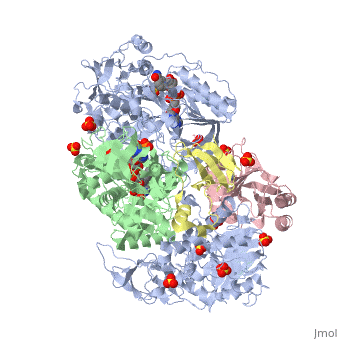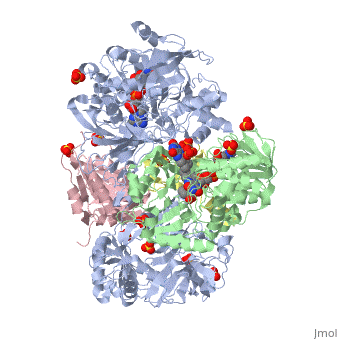
| - | + | <StructureSection load='3ad8' size='350' side='right' scene='' caption='Heterotetramer of sarcosine oxidase containing FAD, FMN and NAD showing α subunit (grey), β subunit (green), γ subunit (pink) and δ subunit (yellow). Complex with pyrrole-2-carboxylate, sulfate and Zn+2 ions (grey) [[3ad8]]'> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | '''Sarcosine oxidase''' (SOX) catalyzes the demethylation of sarcosine+O2+H4-tetrahydrofolate to produce glycine, hydrogen peroxide and 5, 10-methylene-tetrahydrofolate. Sarcosine metabolism can be the source of carbon and energy for many microorganisms. SOXs are found as monomers, heterodirmers and heterotetramers<ref>PMID:24185971</ref>. Monomeric SOX uses FAD as cofactor. Heterotetrameric SOX uses FAD and FMN as cofactors. | ||
| + | </StructureSection> | ||
==3D structures of sarcosine oxidase== | ==3D structures of sarcosine oxidase== | ||
| Line 12: | Line 8: | ||
{{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | {{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | ||
| - | * | + | *Monomeric sarcosine oxidase |
**[[1el5]], [[1el7]], [[1el8]], [[1el9]], [[1eli]], [[2gf3]] – BaSOX + inhibitor – ''Bacillus''<br /> | **[[1el5]], [[1el7]], [[1el8]], [[1el9]], [[1eli]], [[2gf3]] – BaSOX + inhibitor – ''Bacillus''<br /> | ||
| Line 19: | Line 15: | ||
**[[3qse]] – BaSOX + arcosine<br /> | **[[3qse]] – BaSOX + arcosine<br /> | ||
**[[1y56]] – SOX + protein – ''Pyrococcus horikoshii''<br /> | **[[1y56]] – SOX + protein – ''Pyrococcus horikoshii''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[7exs]] – SOX (mutant) – ''Thermomicrobium roseum''<br /> | ||
*Sarcosine oxidase heterotetramer | *Sarcosine oxidase heterotetramer | ||
| Line 29: | Line 26: | ||
**[[2gag]], [[2gah]] – SOX + furoic acid – ''Stenotrophomonas maltophilia'' | **[[2gag]], [[2gah]] – SOX + furoic acid – ''Stenotrophomonas maltophilia'' | ||
}} | }} | ||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
3D structures of sarcosine oxidase
Updated on 15-March-2022
References
- ↑ Suzuki H. Sarcosine oxidase: structure, function, and the application to creatinine determination. Amino Acids. 1994 Feb;7(1):27-43. doi: 10.1007/BF00808444. PMID:24185971 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF00808444