We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
NADH
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (2 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
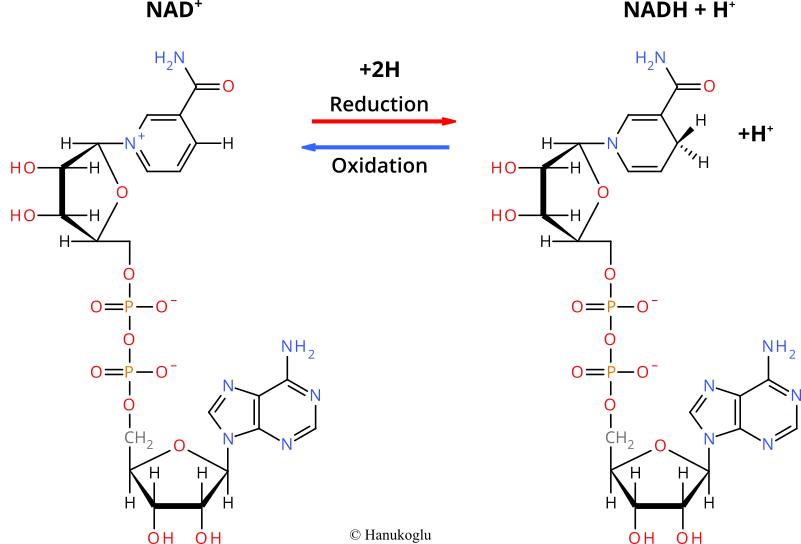
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme that participates in electron transfer reactions. The oxidized form of NAD is abbreviated as NAD<sup>+</sup> and it can accept two electrons. The reduced form of NAD is abbreviated as NADH. | Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme that participates in electron transfer reactions. The oxidized form of NAD is abbreviated as NAD<sup>+</sup> and it can accept two electrons. The reduced form of NAD is abbreviated as NADH. | ||
| - | Equation for the redox reaction for these two forms of NAD: | + | Equation for the redox reaction for these two forms of NAD: NAD<sup>+</sup> + 2H → NADH + H<sup>+</sup> |
| - | + | ||
| - | NAD<sup>+</sup> + 2H → NADH + H<sup>+</sup> | + | |
| - | + | ||
| + | [[Image:NAD-NADH-redox-reactions.png]] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Current revision
NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide)
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme that participates in electron transfer reactions. The oxidized form of NAD is abbreviated as NAD+ and it can accept two electrons. The reduced form of NAD is abbreviated as NADH.
Equation for the redox reaction for these two forms of NAD: NAD+ + 2H → NADH + H+