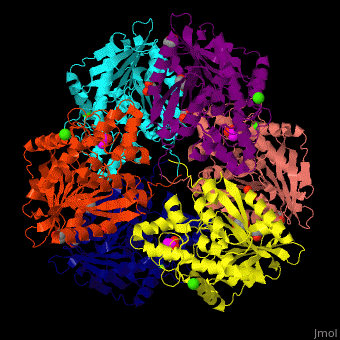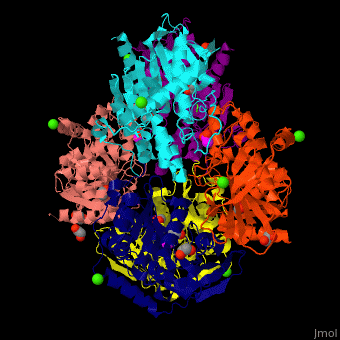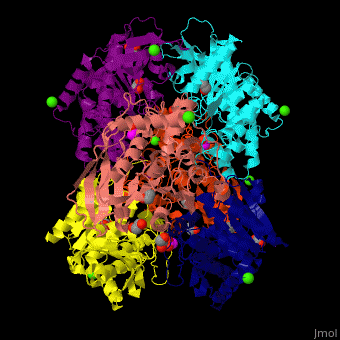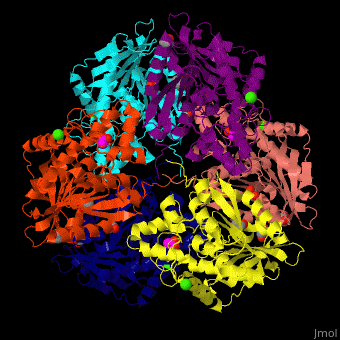
Acetylxylan esterase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (9 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | <StructureSection load=' | + | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' scene='48/489290/Cv/5' caption='Acetylxylan esterase hexamer complex with paraoxon inhibitor, ethylene glycol, acetate and Ca+2 ions, [[3m83]]'> |
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | '''Acetylxylan esterase''' (AXE) catalyzes the deacetylation of xylans and xylo-oligosaccharides. AXE is involved in the biodegradation of hemicellulose. AXE hydrolyzes the ester linkages of the acetyl groups in position 2 and/or 3 of xylose moiety of naturally acetylated xylan from hardwood. AXE is one of the accessory enzymes which are part of the xylanolytic system. Together with xylanase, β-xylosidase, α-arabinofuranosidase and methylglucoronidase, AXE is required for the complete degradation of xylan. | + | '''Acetylxylan esterase''' (AXE) catalyzes the deacetylation of xylans and xylo-oligosaccharides. AXE is involved in the biodegradation of hemicellulose. AXE hydrolyzes the ester linkages of the acetyl groups in position 2 and/or 3 of xylose moiety of naturally acetylated xylan from hardwood. AXE is one of the accessory enzymes which are part of the xylanolytic system. Together with xylanase, β-xylosidase, α-arabinofuranosidase and methylglucoronidase, AXE is required for the complete degradation of xylan.<ref>PMID:8647098</ref> |
== Relevance == | == Relevance == | ||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
== Structural Highlights == | == Structural Highlights == | ||
| - | *<scene name='48/489290/Cv/ | + | *<scene name='48/489290/Cv/6'>Acetylxylan esterase with paraoxon inhibitor, ethylene glycol, acetate and Ca+2 ions</scene>. |
| - | *<scene name='48/489290/Cv/ | + | *<scene name='48/489290/Cv/8'>Paraoxon inhibitor binding site</scene> ([[3m83]]). <ref>PMID:22411095</ref> |
| - | </ | + | *<scene name='48/489290/Cv/9'>Ca+2 coordination site</scene>. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. |
| + | |||
==3D structures of acetylxylan esterase== | ==3D structures of acetylxylan esterase== | ||
| + | [[Acetylxylan esterase 3D structures]] | ||
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | **[[2c71]], [[2c79]] – AXE + metal ion – ''Clostridium thermocellum''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3fyt]] – BpAXE (mutant) + β-D-xylopyranose<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3fyu]] – BpAXE + D-xylose<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2xlc]] – BpAXE + diethyl phosphonate<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3m83]] – TmAXE + paraoxon inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3m82]] – TmAXE + PMSF inhibitor | ||
| - | }} | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Margolles-Clark E, Tenkanen M, Soderlund H, Penttila M. Acetyl xylan esterase from Trichoderma reesei contains an active-site serine residue and a cellulose-binding domain. Eur J Biochem. 1996 May 1;237(3):553-60. PMID:8647098
- ↑ Levisson M, Han GW, Deller MC, Xu Q, Biely P, Hendriks S, Ten Eyck LF, Flensburg C, Roversi P, Miller MD, McMullan D, von Delft F, Kreusch A, Deacon AM, van der Oost J, Lesley SA, Elsliger MA, Kengen SW, Wilson IA. Functional and structural characterization of a thermostable acetyl esterase from Thermotoga maritima. Proteins. 2012 Jan 27. doi: 10.1002/prot.24041. PMID:22411095 doi:10.1002/prot.24041