We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Cytochrome f
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (9 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | <StructureSection load=' | + | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='Turnip heme-containing cytochrome f (PDB entry [[1ctm]])' scene='48/484838/Cv/8'> |
| - | + | ||
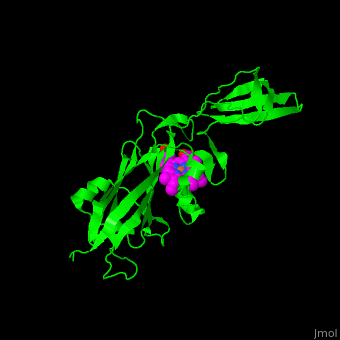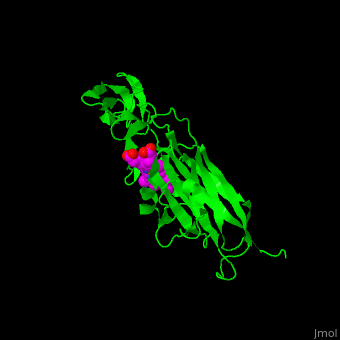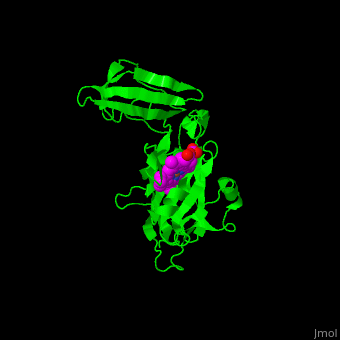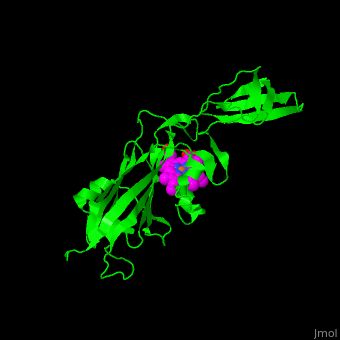
| - | + | '''Cytochrome f''' (Cytf) is the largest subunit of the cytochrome b6f complex. This complex transfers electrons from plastocyanin to the two reaction center complexes of oxygenic photosynthetic membranes.<ref>PMID:7631417</ref> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | See also [[Hemeproteins]]. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | '''Cytochrome f''' (Cytf) is the largest subunit of the cytochrome b6f complex. This complex transfers electrons from plastocyanin to the two reaction center complexes of oxygenic photosynthetic membranes.<ref>PMID:7631417</ref> | + | |
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
The cytochrome b6f complex contains 4 subunits: Cytf, Cytb6, Rieske iron-sulfur protein and subunit IV. Cytf has an internal chain of water molecules conserved in all its 3D structures. The water chain is assumed to be a proton wire. | The cytochrome b6f complex contains 4 subunits: Cytf, Cytb6, Rieske iron-sulfur protein and subunit IV. Cytf has an internal chain of water molecules conserved in all its 3D structures. The water chain is assumed to be a proton wire. | ||
| - | </StructureSection> | ||
| - | ==3D structures of cytochrome f== | ||
| - | + | <scene name='48/484838/Cv/12'>Heme binding site</scene> in Turnip cytochrome f | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | <scene name='48/484838/Cv/13'>Covalent binding of heme to 2 Cys residues</scene> | |
| - | + | <scene name='48/484838/Cv/14'>Fe coordination site</scene> (PDB entry [[1ctm]]). | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ==3D structures of cytochrome f== | |
| + | [[Cytochrome f 3D structures]] | ||
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | **[[1q90]] – CrCytf <br /> | ||
| - | **[[1vf5]], [[2e7r]] - MlCytf – ''Mastigocladus laminosus''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2d2c]] - MlCytf + dibromo-methyl-isopropylbenzoquinone<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2e75]] - MlCytf + nonyl-hydroxyquinoline oxide<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2e76]] - MlCytf + tridecyl-stigmatellin<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2zt9]] - Cytf - Nostoc | ||
| - | }} | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
[[Category: Topic Page]] | [[Category: Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Prince RC, George GN. Cytochrome f revealed. Trends Biochem Sci. 1995 Jun;20(6):217-8. PMID:7631417