Cyclin-dependent kinase regulatory subunit
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (5 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
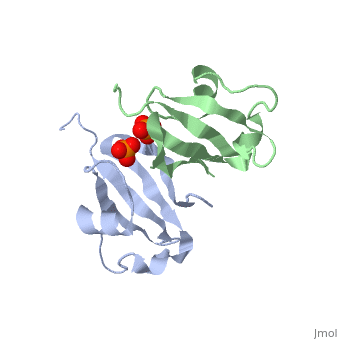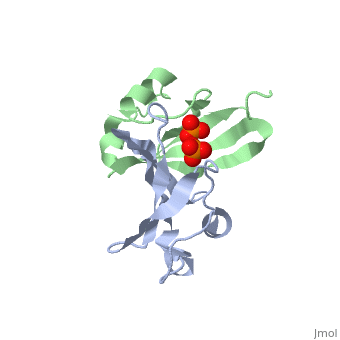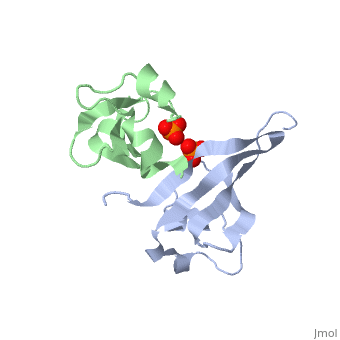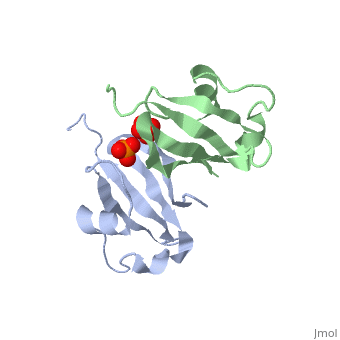
| - | '''Cyclin-dependent kinase regulatory subunit''' (CKS) is a small protein which is essential for the functioning of CDK-cyclin complex. CKS binds to the catalytic subunit of CDK see complex structure in <scene name='71/715441/Pdb4yc6/1'>pdb 4yc6</scene> where CDK1 is in grey, pink, magenta and gold and CKS1 i in green, yellow, cyan and red. CKS1 is essential for CDK5 functioning in neuronal differentiation.<ref>PMID:8491379</ref> | + | '''Cyclin-dependent kinase regulatory subunit''' (CKS) is a small protein which is essential for the functioning of CDK-cyclin complex. CKS binds to the catalytic subunit of CDK see complex structure in <scene name='71/715441/Pdb4yc6/1'>pdb 4yc6</scene> where CDK1 is in grey, pink, magenta and gold and CKS1 i in green, yellow, cyan and red. |
| - | + | *'''CKS1''' is essential for CDK5 functioning in neuronal differentiation.<ref>PMID:8491379</ref> | |
| - | + | *'''CKS2''' is implicated as an oncogene in various malignancies.<ref>PMID:31781310</ref> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| Line 12: | Line 10: | ||
CKS exists as hexamer of homodimers and can bind six kinase molecules. | CKS exists as hexamer of homodimers and can bind six kinase molecules. | ||
| - | </StructureSection> | ||
== 3D Structures of cyclin-dependent kinase regulatory subunit == | == 3D Structures of cyclin-dependent kinase regulatory subunit == | ||
| + | [[Cyclin-dependent kinase regulatory subunit 3D structures]] | ||
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | **[[4yc6]] – hCKS 1 + CDK1 <br /> | ||
| - | **[[1buh]] – hCKS 1 + CDK2<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1h4l]], [[1ung]] – hCKS 1 + CDK5<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1unh]], [[1unl]] – hCKS 1 + CDK5 + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3o0g]] – hCKS 1 + CDK5 + ATP analog<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2ass]] – hCKS 1 + Skp1 + Skp2<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2ast]] – hCKS 1 + Skp1 + Skp2 + CDK inhibitor peptide<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4y72]] – hCKS 2 + cyclin B1 + CDK1<br /> | ||
| - | }} | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| + | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Tang Y, Reed SI. The Cdk-associated protein Cks1 functions both in G1 and G2 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes Dev. 1993 May;7(5):822-32. PMID:8491379
- ↑ Zhang J, Song Q, Liu J, Lu L, Xu Y, Zheng W. Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Regulatory Subunit 2 Indicated Poor Prognosis and Facilitated Aggressive Phenotype of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Dis Markers. 2019 Oct 22;2019:8964015. PMID:31781310 doi:10.1155/2019/8964015