Elongation factor
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (17 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
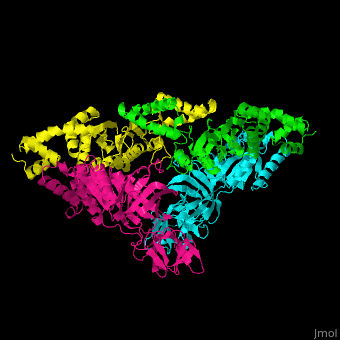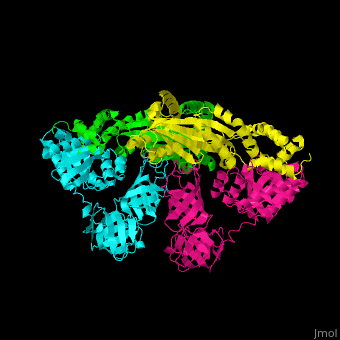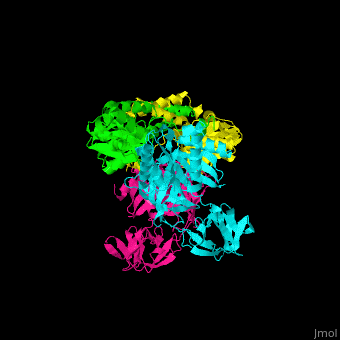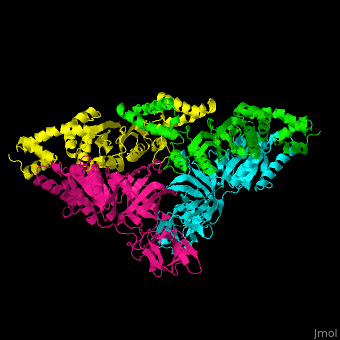
| - | <StructureSection load=' | + | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of EF-Tu (cyan and magenta) with EF-Ts (green and yellow) (PDB entry [[1efu]])' scene='51/517376/Cv/1'> |
| + | __FORCETOC__ | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Function == | ||
'''Elongation factors''' (EF) facilitate translational elongation during the formation of peptide bonds in the ribosome.<br /> | '''Elongation factors''' (EF) facilitate translational elongation during the formation of peptide bonds in the ribosome.<br /> | ||
| - | * '''EF-selB''' is selenocysteine-specific EF.<br /> | + | * '''EF-selB''' is selenocysteine-specific EF. See [[SelB]]<br /> |
* '''EF-Tu or EF 1-α''' (elongation factor thermo unstable) is a prokaryotic EF. EF-Tu contributes to translational accuracy. It catalyzes the addition of aminoacyl tRNA<ref>PMID:20798060</ref>. <br /> | * '''EF-Tu or EF 1-α''' (elongation factor thermo unstable) is a prokaryotic EF. EF-Tu contributes to translational accuracy. It catalyzes the addition of aminoacyl tRNA<ref>PMID:20798060</ref>. <br /> | ||
*'''EF-Ts or EF 1-β''' (elongation factor thermo stable) catalyzes the release of GDP from EF-Tu.<br /> | *'''EF-Ts or EF 1-β''' (elongation factor thermo stable) catalyzes the release of GDP from EF-Tu.<br /> | ||
| Line 13: | Line 16: | ||
* '''EF-1 γ''' acts during the delivery of aminoacyl tRNA to the ribosome.<br /> | * '''EF-1 γ''' acts during the delivery of aminoacyl tRNA to the ribosome.<br /> | ||
* '''EF-2''' promotes the translocation of the nascent protein chain from the A site to the P site on the ribosome<ref>PMID:16246167</ref>.<br /> | * '''EF-2''' promotes the translocation of the nascent protein chain from the A site to the P site on the ribosome<ref>PMID:16246167</ref>.<br /> | ||
| - | * '''EF-3''' is a unique EF in fungi hence it provides an anti-fungal drug target.<br /> | + | * '''EF-3''' is a unique EF in fungi hence it provides an anti-fungal drug target. See [[HEAT Repeat]]<br /> |
* '''EF Spt4, Spt5, Spt6''' are conserved among eukaryotes. They modulate the chromatin structure.<br /> | * '''EF Spt4, Spt5, Spt6''' are conserved among eukaryotes. They modulate the chromatin structure.<br /> | ||
* '''EF-CA150''' is believed to play a role in coupling transcription and splicing.<br /> | * '''EF-CA150''' is believed to play a role in coupling transcription and splicing.<br /> | ||
| - | * '''Elongin B and C | + | * '''Elongin complex''' or '''SIII''' activates elongation by RNA polymerase II by suppressing transient pausing of the enzyme<ref>PMID:7660129</ref>. The complex is composed of elongin A, B and C. '''Elongin A''' (EloA) is the active component of the complex. '''Elongin B and C''' (EloBC) are the regulatory subunits of it. '''Von Hippel-Landau tumor suppressor protein''' (VHL) binds to EloBC and inhibits transcriptional elongation.<br /> |
| - | + | * '''Negative EF''' (NELF) are involved in regulating the pausing of RNA Pol II polymerase transcripton<ref>PMID:38401543</ref>.<br /> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | </ | + | <scene name='51/517376/Cv/4'>Complex EF-Tu with EF-Ts is heterotetramer</scene>, or, more exactly <scene name='51/517376/Cv/5'>heterodimer of homodimers</scene> (PDB entry [[1efu]]).<ref>PMID:8596629</ref> |
==3D structures of elongation factor== | ==3D structures of elongation factor== | ||
| + | [[Elongation factor 3D structures]] | ||
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | **[[1lqb]], [[1lm8]] – hEloBC + von-Hippel Lindau disease tumor suppressor + hypoxia inducible factor 1 α<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3zrc]], [[3ztc]], [[3ztd]], [[3zun]] - hEloBC + von-Hippel Lindau disease tumor suppressor + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3zrf]] - hEloBC + von-Hippel Lindau disease tumor suppressor<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2c9w]], [[2izv]], [[2jz3]] – hEloBC + suppressor of cytokine signaling<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3dcg]] – hEloBC + virion infectivity factor<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2xai]] - hEloBC + ankyrin rep<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1vcb]] – hEloBC + VHL<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2fnj]] - mEloBC + GUSTAVUS | ||
| - | }} | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Takeshita D, Tomita K. Assembly of Q{beta} viral RNA polymerase with host translational elongation factors EF-Tu and -Ts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Sep 7;107(36):15733-8. Epub 2010 Aug 23. PMID:20798060 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1006559107
- ↑ Jorgensen R, Merrill AR, Andersen GR. The life and death of translation elongation factor 2. Biochem Soc Trans. 2006 Feb;34(Pt 1):1-6. PMID:16246167 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1042/BST20060001
- ↑ Aso T, Lane WS, Conaway JW, Conaway RC. Elongin (SIII): a multisubunit regulator of elongation by RNA polymerase II. Science. 1995 Sep 8;269(5229):1439-43. PMID:7660129
- ↑ Su BG, Vos SM. Distinct negative elongation factor conformations regulate RNA polymerase II promoter-proximal pausing. Mol Cell. 2024 Apr 4;84(7):1243-1256.e5. PMID:38401543 doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2024.01.023
- ↑ Kawashima T, Berthet-Colominas C, Wulff M, Cusack S, Leberman R. The structure of the Escherichia coli EF-Tu.EF-Ts complex at 2.5 A resolution. Nature. 1996 Feb 8;379(6565):511-8. PMID:8596629 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/379511a0