This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Fibrinogen binding protein
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (One intermediate revision not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
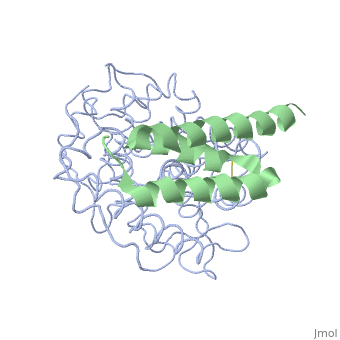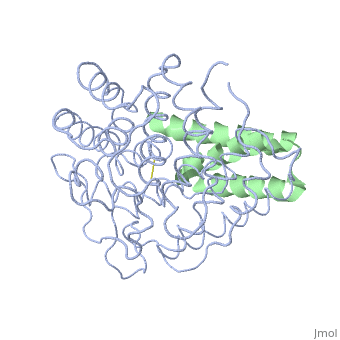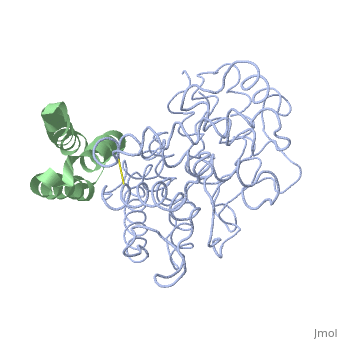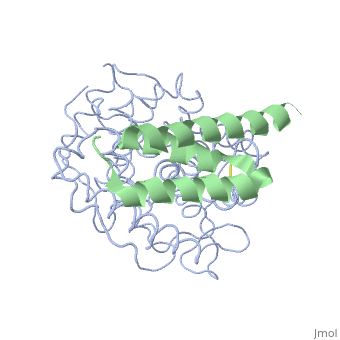
| + | <StructureSection load='2gox' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of Efb (green) complex with complement C3 α chain fragment (grey) (PDB entry [[2gox]])' scene=''> | ||
== Extra cellular fibrinogen binding protein- Efb == | == Extra cellular fibrinogen binding protein- Efb == | ||
'''''Staphylococcous Aureus''''' is a bacterium that is commonly found on human skin and respiratory tracts; however, when it becomes pathogenic it can cause many diseases: skin infections, respiratory diseases(pneumonia), food poisoning. It is a Gram +, cluster forming coccus, non-motile, facultative Anaerobe and a leading cause of nosocomial infection. [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Staphylococcus_aureus More about Staph Aureus] | '''''Staphylococcous Aureus''''' is a bacterium that is commonly found on human skin and respiratory tracts; however, when it becomes pathogenic it can cause many diseases: skin infections, respiratory diseases(pneumonia), food poisoning. It is a Gram +, cluster forming coccus, non-motile, facultative Anaerobe and a leading cause of nosocomial infection. [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Staphylococcus_aureus More about Staph Aureus] | ||
| Line 9: | Line 10: | ||
'''Efb function''' is a protein that is secreted by Staphylococcous Aureus which mimics the natural proteins in the body that inhibit the complement system. These proteins are called regulator of complement activation(RCA). In general, RCA proteins suppress the activation of C3 and C4 by dissociating the subunits of C3 and/or C5 convertases or by acting as cofactors for factor I–dependent cleavage of C3b and/or C4b. <ref name="Ad">PMID:17351618</ref> Efb has been shown to bind to the C3d domain of C3 and C3B, inhibiting its function. | '''Efb function''' is a protein that is secreted by Staphylococcous Aureus which mimics the natural proteins in the body that inhibit the complement system. These proteins are called regulator of complement activation(RCA). In general, RCA proteins suppress the activation of C3 and C4 by dissociating the subunits of C3 and/or C5 convertases or by acting as cofactors for factor I–dependent cleavage of C3b and/or C4b. <ref name="Ad">PMID:17351618</ref> Efb has been shown to bind to the C3d domain of C3 and C3B, inhibiting its function. | ||
| - | + | ||
==Structural motifs== | ==Structural motifs== | ||
The overall dimensions of Efb-C were approximately 40x25x20 A° and 15.6 kDa, with the N-terminal a1 helix (K106–H125) connected | The overall dimensions of Efb-C were approximately 40x25x20 A° and 15.6 kDa, with the N-terminal a1 helix (K106–H125) connected | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
3D structures of fibrinogen binding protein
Updated on 19-October-2017
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Hammel M, Sfyroera G, Ricklin D, Magotti P, Lambris JD, Geisbrecht BV. A structural basis for complement inhibition by Staphylococcus aureus. Nat Immunol. 2007 Apr;8(4):430-7. Epub 2007 Mar 11. PMID:17351618 doi:10.1038/ni1450
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Rahul Gunasekera, Alexander Berchansky, Jaime Prilusky