This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox Reserved 1137
From Proteopedia
| (5 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
==''Plasmodium falciparum'' Atg8 in complex with ''Plasmodium falciparum'' Atg3 peptide== | ==''Plasmodium falciparum'' Atg8 in complex with ''Plasmodium falciparum'' Atg3 peptide== | ||
<StructureSection load='4EOY' size='340' side='right' caption='Atg8/Atg3 complex' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='4EOY' size='340' side='right' caption='Atg8/Atg3 complex' scene=''> | ||
| - | + | 4eoy is the PDB code corresponding to a proteic complex composed of two structures : Atg8 and Atg3. These proteins belong to an organism named ''Plasmodium falciparum'', a parasite which is responsible for malaria. They play a part in autophagy, a process which consists in recycling a part of the cytoplasm in order to make the cell go from the sporozoite (growing) state to the erythrocytic infective state. | |
== Function == | == Function == | ||
=== Cellular effects === | === Cellular effects === | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| - | The autophagy related proteins (Atg) are proteins which purpose is to help the parasite to survive and develop. Atg8 and Atg3 are both involved in the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Autophagy autophagy] process, by creating an autophagosome and then making it grow. The autophagosome can be compared to a vacuole and absorbs the components of the cytoplasm (in a non specific way). When the growing phase (sporozoite) of the cell is over,in the case of ''Plasmodium falciparum'', the autophagy is launched by the cell in order to become erythrocytic-infective. This is the time when the cell starts its viral activity. Lysosomes then merge with the autophagosme to form the autolysosome. Once this process is done, the autolysosome can complete its purpose : recycle the its content. | + | The autophagy related proteins (Atg) are proteins which purpose is to help the parasite to survive and develop. Atg8 and Atg3 are both involved in the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Autophagy autophagy] process, by creating an [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Autophagosome autophagosome] and then making it grow. The autophagosome can be compared to a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vacuole vacuole] and absorbs the components of the cytoplasm (in a non specific way). When the growing phase ([https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Apicomplexan_life_cycle sporozoite]) of the cell is over,in the case of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Plasmodium_falciparum ''Plasmodium falciparum''], the autophagy is launched by the cell in order to become erythrocytic-infective. This is the time when the cell starts its viral activity. [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lysosome Lysosomes] then merge with the autophagosme to form the [https://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/autolysosome autolysosome]. Once this process is done, the autolysosome can complete its purpose : recycle the its content. In fact, all the molecules inside are degradated and their components (like aminoacids) are reused in order to synthetise viral proteins. |
=== Molecular effects === | === Molecular effects === | ||
---- | ---- | ||
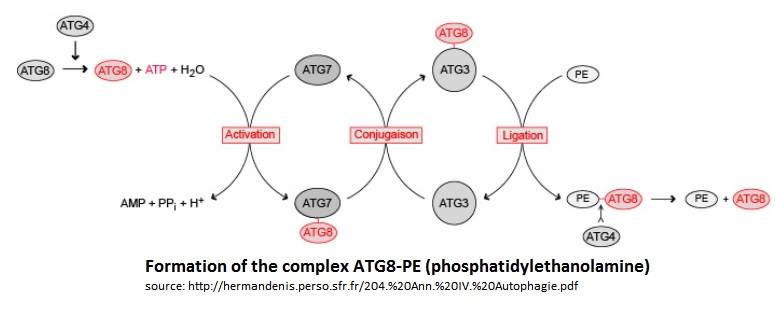
| - | In the Atg8 system, there are several steps until Atg8 is activated. Firstly, the cysteine protease Atg4 cleaves the last residue of the C-terminal domain of Atg8 by consuming 1 molecule of ATP and H20. Then, the Atg7 (E1-like enzyme) activates the C-terminal glycine exposed and therefore forms an intermediate Atg8-Atg7 by creating a thioester bond. Atg3 (E2-like enzyme) then replaces Atg7 in the complex to form an Atg8-Atg3 thioester intermediate. Phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) then links to the N-terminal domain of Atg8. This final complex (Atg8-Atg3-PE) serves as an intermediate for membrane tethering and hemifusion of the autophagosome. This complex is primordial for the elongation of the autophagosome. Notice that Atg8-Atg3-PE is the active complex, but Atg8-PE can also be sufficient to do this task (like this is showed on the scheme below). | + | In the Atg8 system, there are several steps until Atg8 is activated. Firstly, the cysteine protease Atg4 cleaves the last residue of the C-terminal domain of Atg8 by consuming 1 molecule of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adenosine_triphosphate ATP] and H20. Then, the Atg7 (E1-like enzyme) activates the C-terminal glycine exposed and therefore forms an intermediate Atg8-Atg7 by creating a thioester bond. Atg3 (E2-like enzyme) then replaces Atg7 in the complex to form an Atg8-Atg3 thioester intermediate. [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phosphatidylethanolamine Phosphatidylethanolamine] (PE) then links to the N-terminal domain of Atg8. This final complex (Atg8-Atg3-PE) serves as an intermediate for membrane [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tether_(cell_biology) tethering] and hemifusion of the autophagosome. This complex is primordial for the elongation of the autophagosome. Notice that Atg8-Atg3-PE is the active complex, but Atg8-PE can also be sufficient to do this task (like this is showed on the scheme below). |
[[Image:atg8f.jpg]] | [[Image:atg8f.jpg]] | ||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
== Relevance == | == Relevance == | ||
Malaria is a strikening disease killing more than millions of people every years, primarily children. This is one of the most killing disease on earth at this time. That's why it is essential to focus the medical research on malaria's treatment. | Malaria is a strikening disease killing more than millions of people every years, primarily children. This is one of the most killing disease on earth at this time. That's why it is essential to focus the medical research on malaria's treatment. | ||
| - | Recent studies (2012) have shown a start point for drug researches. In fact 1,2,3-tihydroxybenzene have shown to prevent protein-protein interaction between Atg8 and Atg3, inhibiting autophagosome's elongation and leading to the no-infectiveness of the parasite. | + | Recent studies (2012) have shown a start point for drug researches. In fact [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pyrogallol 1,2,3-tihydroxybenzene] have shown to prevent protein-protein interaction between Atg8 and Atg3, inhibiting autophagosome's elongation and leading to the no-infectiveness of the parasite. |
Current revision
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 15/12/2015, through 15/06/2016 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1120 through Sandbox Reserved 1159. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Plasmodium falciparum Atg8 in complex with Plasmodium falciparum Atg3 peptide
| |||||||||||
References
1. Hain AU, Weltzer RR, Hammond H, Jayabalasingham B, Dinglasan RR, Graham DR, Colquhoun DR, Coppens I, Bosch J Structural characterization and inhibition of the plasmodium atg8-atg3 interaction. J.Struct.Biol. (2012) 180 p.551
2. Machiko Sakoh-Nakatogawa, Kazuaki Matoba, Eri Asai, Hiromi Kirisako, Junko Ishii, Nobuo N Noda, Fuyuhiko Inagaki, Hitoshi Nakatogawa & Yoshinori Ohsumi Atg12–Atg5 conjugate enhances E2 activity of Atg3 by rearranging its catalytic site Nature Structural & Molecular Biology 20, 433-439 (2013) doi :10.1083/nsmb.2527
3. Oliver H. Weiergräber, Jeannine Mohrlüder and Dieter Willbold Atg8 Family Proteins — Autophagy and Beyond, DOI: 10.5772/55647 Biochemistry, Genetics and Molecular Biology » "Autophagy - A Double-Edged Sword - Cell Survival or Death?", book edited by Yannick Bailly, ISBN 978-953-51-1062-0, Published: April 17, 2013 under CC BY 3.0 license.
4. Herman Denis, http://hermandenis.perso.sfr.fr/204.%20Ann.%20IV.%20Autophagie.pdf
5. Patrice Codogno Les gènes ATG et la macro-autophagie Med Sci (Paris). 2004 August; 20(8-9): 734–736. Published online 2004 August 15. doi: 10.1051/medsci/2004208-9734
6. Hain AU, Bartee D, Sanders NG, Miller AS, Sullivan DJ, Levitskaya J, Meyers CF, Bosch J. Identification of an Atg8-Atg3 protein-protein interaction inhibitor from the medicines for Malaria Venture Malaria Box active in blood and liver stage Plasmodium falciparum parasites. J Med Chem. 2014 Jun 12;57(11):4521-31. doi: 10.1021/jm401675a. Epub 2014 May 19
7. Masaya Yamaguchi, Nobuo N. Noda, Hitoshi Nakatogawa, Hiroyuki Kumeta, Yoshinori Ohsumi and Fuyuhiko Inagaki Autophagy-related Protein 8 (Atg8) Family Interacting Motif in Atg3 Mediates the Atg3-Atg8 Interaction and Is Crucial for the Cytoplasm-to-Vacuole Targeting Pathway. The Journal of Biological Chemistry vol.28. 2010, September 17. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.11367
8. Hain AU1, Weltzer RR, Hammond H, Jayabalasingham B, Dinglasan RR, Graham DR, Colquhoun DR, Coppens I, Bosch J. Structural characterization and inhibition of the Plasmodium Atg8-Atg3 interaction. J Struct Biol. 2012 Dec;180(3):551-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2012.09.001. Epub 2012 Sep 13.PMID:22982544
9. Machiko Sakoh-Nakatogawa, Kazuaki Matoba, Eri Asai, Hiromi Kirisako, Junko Ishii, Nobuo N Noda, Fuyuhiko Inagaki, Hitoshi Nakatogawa & Yoshinori Ohsumi. Atg12–Atg5 conjugate enhances E2 activity of Atg3 by rearranging its catalytic site. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology. 2013 February. doi:10.1038/nsmb.2527