Introduction
Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor 1 (commonly referred to as LPA1) is a G protein-coupled receptor and one of 6 different LPA receptors (LPA1-LPA6). These receptors bind the phospholipid derivative lysophosphatidic acid (LPA), a signaling molecule that acts as a potent mitogen upon binding to one of its six receptors.[1] LPA1 is part of the larger EDG receptor family, which includes the more widely studied sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors.[1] LPA1 is responsible for initiating several different signaling cascades with different molecules and G-proteins.[2] These cascades ultimately result in growth, survival, and movement of cells, as well as neural cell development.[3]
See also
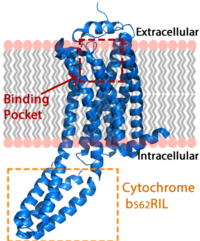
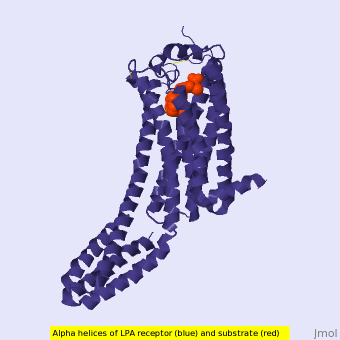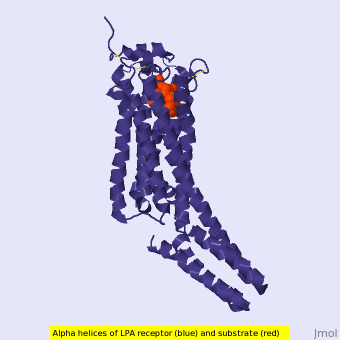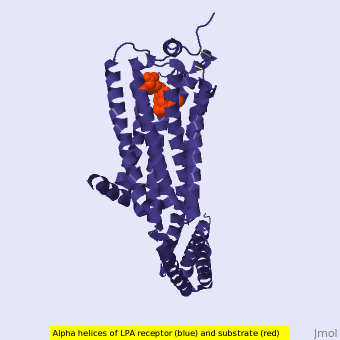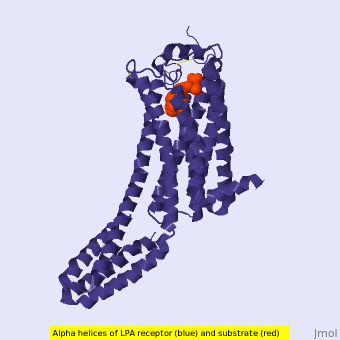
Figure 1: LPA receptor (blue) bound to the cell membrane. The binding pocket is highlighted in red. The added bRIL protein is highlighted in orange.
Lysophosphatidic Acid
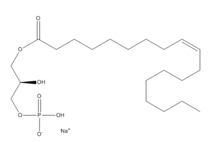
Figure 2: Chemical Structure of LPA (monoacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphate)
Lysophosphatidic Acid (LPA) consists of an unsaturated fatty acid chain, a glycerol backbone, and a free phosphate group (Figure 2). Lysophosphatidic acid is found in nearly all cells, tissues, and fluids of the body.
[1] LPA is present intracellularly as a precursor of phospholipid biosynthesis, and extracellularly as a signalling phospholipid.
Extracellularly, LPA is produced from lysophosphatidylcholine by the enzyme autotaxin.[1] Autotaxin was originally linked with metastasis, and this link was later discovered to be mediated through the production of LPA, which signals cell proliferation.[4] All of LPA’s activities are receptor mediated; the signalling lipid interacts with at least six G-protein coupled receptors LPA1-LPA6.
Structure
The LPA1 receptor protein is composed of 364 amino acids with a molecular weight of approximately 41 kDa. Common to all G-protein coupled receptors, LPA1 contains seven alpha helices which make up the seven transmembrane spanning domains with three intracellular loops and three extracellular loops.[5] Within these helices is an interior binding pocket that stabilizes the binding of LPA1's natural ligand, LPA (Figure 1). The opening to this binding pocket is larger than other LPA receptors, enabling this receptor to bind ligands other than its natural ligand, such as 2-AG.[1]
LPA1 lies in the membrane as shown in Figure 1, and as shown by the bound in the crystallization of LPA1 in orange. Most (red) reside on the intracellular and extracellular areas of the receptor, while most residues positioned on the trans membrane helices inside the membrane are hydrophobic (blue). A cytochrome b (b562RIL) protein was inserted into the third intracellular loop to facilitate crystallization (Figure 2).[1] The intracellular region of this membrane protein is coupled to a heterotrimeric G protein.
Structural Stabilization
Three native in the extracellular region of this receptor provide fold stability.[1] The first disulfide bond constrains the N terminal helix to extracellular loop (ECL) 2. The second disulfide bond shapes ECL2, and the third binds ECL3 to one of the transmembrane alpha helices. These disulfide bonds provide intramolecular stabilization along the extracellular region of the LPA1 receptor, where the substrate enters into the binding pocket. The is a six turn alpha helix and functions like a cap on the extracellular side of the protein, packing tightly against ECL1 and ECL2.[1] The N-terminus helix also provides that interact with the ligand when bound. The extracellular region of this receptor plays a role in substrate specificity.
Key Ligand Interactions
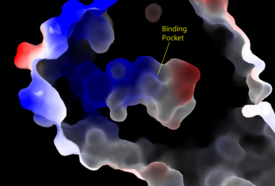
Figure 3: Electrostatic illustration of the amphipathic binding pocket of the LPA
1 receptor. This binding pocket was revealed by cutting away the exterior or the protein. This binding pocket, located in the interior of the protein, has both polar and nonpolar regions. The blue and red coloration highlight the positively and negatively charged regions, respectively, and the white color shows the nonpolar region of the binding pocket.
The biological ligand of the LPA
1 receptor receptor is
lysophosphatidic acid (LPA), a phospholipid that contains a long, nonpolar tail, a phosphate head, a chiral hydroxyl group, and an ester group (Figure 2). This receptor provides specificity for its ligand by the amphipathic binding pocket; the positive region on the left hand side of the pocket stabilizes the LPA's phosphate group, the nonpolar region at the bottom of the binding pocket stabilizes the hydrophobic tail of LPA, and the polar region at the top of the pocket stabilize binding of the ester and hydroxyl group (Figure 3). The for LPA consists of both polar and nonpolar residues. residues are located on the N terminus and within the binding pocket. A also interacts with the long acyl chain of LPA. The shape and polarity of the binding pocket makes it specific for molecules with a polar head and long hydrophobic tail shaped like LPA.
ONO-9780307 (ON7) is an antagonist for LPA due to its large nonpolar region, chiral hydroxyl group, ester, and carboxylic acid which all resemble portions of the LPA molecule (Figure 4). Four separate interactions with this antagonist of LPA1 help demonstrate the key interactions that stabilize the binding of the LPA phospholipid to this receptor. In the nonpolar region of the binding pocket, of LPA1 stabilize the large nonpolar group of ON7. At the polar region, the ligand binding is stabilized by forming ionic and polar interactions with the carboxylic acid and the hydroxyl group of ON7.[1] In addition, interplay between causes another stabilizing component with the ON7 antagonist. Glu293 forms polar interactions with Lys39, positioning it in close proximity to to the carboxylic acid of ON7, which then interactions with Lys39 via ionic bonding.[1] While Lys39 is highly conserved among all six LPA receptors, a neighboring histidine residue is specific to the LPA1 receptor. forms both ionic and polar interactions with the carboxylic acid of ON7. Protonation of this residue greatly affects the binding affinity of LPA, leading to an increase in the pathways associated with cell proliferation and migration. Because cancerous tumors create acidic environments where His40 is protonated, this residue is an important link to tumor growth and cancer cell movement.[1]
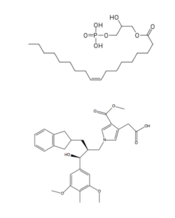
Figure 4: Structures of LPA and its antagonist, ON7.
Function
The LPA1 receptor is present in nearly all cells and tissues, and deletion of the LPA1 receptor has physiological effects on every organ system, indicating its wide range of functions. Specifically, this receptor initiates downstream signaling cascades with three Gα proteins: Gi/o, Gq/11, and G12/13. Specifically, Gα proteins begin signaling cascades that activate phospholipase C and MAPKs that signal for cell proliferation, survival, and migration. [2] Despite this receptor being expressed ubiquitously, LPA1 is highly expressed in neural tissue, aiding in several different neurodevelopmental processes including growth and folding of the cerebral cortex and the growth, survival, and migration of neural progenitor cells.[3] Finally, LPA1 receptors expressed in neural tissue act through a signaling pathway with the Rac1 G-protein to aid in Schwann cell migration and myelination.[6]
Receptor Comparison
Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Receptor
Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptors (LPA) are part of a larger family known as lysophospholipid receptor family (
EDG family), including the archetype sphingosine-1-phosphate receptors (S1P
1). The only structure previously reported in this GPCR family was of S1P
1, and it provides a comparison for the differential structure and function to LPA
1.
[1] A major difference was observed in ligand access between these two receptors. The binding path in LPA
1 is located in the extracellular milieu, while in S1P
1 the ligand accesses the binding pocket through the membrane (Figure 1). The overall shape of each binding pocket is also different, as the S1P
1 binding pocket has more of an oval shape, whereas
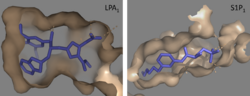
Figure 5: Comparison of the binding pockets of LPA
1 and S1P
1 receptors. The electron density (tan) of the binding pocket is shown around the ligand (purple). The limited binding sites of the receptors are shown in tan.
the LPA
1 binding pocket has a more spherical shape (Figure 5). The more spherical binding pocket for LPA
1 also gives it the ability to recognize a larger group of chemical species. In particular, LPA
1 has the ability to bind with ligands that have acyl chains of varying lengths.
[1] Since LPA
1 binds with a variety of acyl chains, it is used in multiple pathways.
Structural evidence for this altered ligand binding pathway includes global changes in the positioning of the extracellular loops (ECL) and transmembrane helices (TM). Specifically, a slight divergence of , which is positioned 3 Å closer to TMVII compared to S1P1, and a repositioning of , resulting in a divergence of 8 Å from S1P1 result in ligand access via the extracellular space. [1] This narrowing of the gap between TMI and TMVII blocks membrane ligand access in LPA1, while the greater distance between ECL3 and the other extracellular loops promotes extracellular access for LPA1. Additionally, ECL0 is helical in S1P1, but in LPA1. This increased flexibility that results from ECL0 lack of secondary structure in LPA1 further promotes favorable LPA access to the binding pocket from the extracellular space. [1]
Endocannabinoid Receptor 1
LPA1 is also closely related to the first of the six cannabinoid receptors. This close relation gives CB1 (Cannabinoid Receptor 1) the ability to bind to analogs of LPA and LPA1 the ability to bind to analogs of CB1 ligands. [1] This crossing over of ligand binding opens the possibility of metabolic crosstalk between the two signaling systems. [1] Complementary access to the LPA1 binding pocket can be achieved by phosphorylated CB1 ligand analogs, while complementary access to the CB1 binding site requires dephosphorylation of LPA1 ligand analogs. In both cases, a ligand could serve as a primary receptor modulator and a simultaneous prodrug for a different receptor. [1]
A major cannabinoid signaling molecule, 2-arachidonyl glycerol (2-AG, Figure 6), can be phosphorylated into 2-arachidonyl phosphatidic acid (2-ALPA). 2-ALPA has a similar structure to LPA, and is able to bind in the LPA
1 receptor binding pocket. 2-ALPA binding to LPA
1 causes the same downstream signaling that the LPA molecule does, effectively connecting these two systems. Promiscuous ligand binding between these two pathways has potential functional and therapeutic implications.
[1]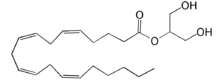
Figure 6: 2-arachidonylglycerol (2-AG)
located within the hydrophobic binding pocket of LPA1 may share responsibility for the preference for long unsaturated acyl chains, including the ligand LPA. The polarity of these residues provide favorable interactions between the ligand and the binding pocket.[1] Additionally, Asp129 and Trp210 may serve as a trigger for agonist induced conformational changes. These residues are also interesting in regard to GPCR phylogenic evolution. [1] in the binding pocket of LPA1 is unique to the lysophospholipid and cannabinoid receptors, suggesting that they are related. A model for lipid agonist binding generated through molecular modeling was used to dock two of the cannabinoid receptor CB1's most abundant endogenous ligands into the LPA1 binding pocket. [1] Rotameric shifts of Trp210 and Trp271 lead to the expansion of the binding pocket and the exposure of the π clouds of their indole rings. These shifts and expansion provided favorable interactions with the double bonds of the phosphorylated cannabinoid ligands. This favorable binding provided evidence that the hydrophobic binding pockets of LPA1 and CB1 are able to favorably bind the same poly-unsaturated acyl chains with metabolically interconvertible head groups.[1]
Disease Relevance
Because LPA1 is expressed in so many tissues throughout the body, LPA1 has been linked to the symptoms and progression of several different diseases and disorders.[7][8]
Cancer
Many of the functions of LPA1, i.e. cell proliferation, survival, and morphology, are implicated in cancers. LPA acts as a tumor mitogen and an inducer of tumor-derived cytokine to support the metastasis (spreading) of breast and ovarian cancer to bones. Inhibition of LPA1 can significantly reduce this progression, and therefore may be a promising treatment for patients with bone metastasis. [9] LPA does not have an effect on primary tumor size. [10] Part of this tumorigenesis can be explained by the action of on LPA1 where, when protonated His40 increases LPA binding affinity by up to 1kcal/mol.[1] Consequently, in the acidic environment produced by hypoxic tumors, LPA1 activity is increased, allowing these tumors to continue to proliferate, migrate, and survive.[8]
Pain
When an injury occurs, LPA is released in the body. LPA will then activate G-protein-coupled receptors. Within the nervous system, LPA plays a role in the nociceptive process (nociceptive pain is a sharp pain that can come from a mild burn or twisted ankle). The LPA signaling will activate GTPase RhoA [11]. Once activated Rho translocates to the plasma membrane. Rho will activate Rho kinase (ROCK) [11]. The activation of ROCK is a required step in the pathway in the stimulation of neurotic pain. When ROCK was inhibited the remaining pathway no longer functioned normally. Mice with the deletion of LPA1 receptors had lower levels of pain [11].
Fibrosis
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) has high rates of mortality [12]. Understanding how LPA can effect fibrosis, is an important factor to finding medication and a cure for this disease. The pathway of LPA-LPA1 is important in mediating fibroblast migration and Wound Healing. Once fibrosis has been contracted LPA levels increase in the bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid. The study showed that mice lacking LPA1 had protection from mortality and were able to survive fibrosis. LPA1 plays an active role between lung injury and contracting pulmonary fibrosis. The absence of LPA results in a vascular leak after an initial injury, leading to fibrosis. LPA1 is a link between lung injury and pulmonary fibrosis [12].
3D structures of lysophosphatidic acid receptor
Updated on 29-October-2025
4z34, 4z35, 4z36 - hLPA1 + antagonist - human
2lq4 – hLPA1 second extracellular loop 1-80 – NMR
7td0, 7td1, 7td2 – hLPAR1 + GI complex + LPA – Cryo EM
7yu5 – hLPAR1 + GI complex + scFv + agonist – Cryo EM
7yu3, 7yu6, 7yu7, 7yu8, 9ize, 9izf, 9izg, 9izh, 9j5v – hLPAR1 + GI complex + scFv + LPA derivative – Cryo EM
9itb – hLPAR6 + GI complex + scFv + LPA derivative – Cryo EM
7yu4 – hLPAR1 + LPA derivative – Cryo EM
4p0c – hLPAR2/NHERF2
9itb – hLPAR6 + minigaq + guanine nucleotice-binding protein subunit beta + nanobody + LPA – Cryo EM
9ite – hLPAR6 + minigaq + guanine nucleotice-binding protein subunit beta + scFv + LPA – Cryo EM
7yu3, 7yu6, 7yu7, 7yu8 – hLPAR1 + GI complex + scFv + LPA derivative – Cryo EM
7yu4 – hLPAR1 + LPA derivative – Cryo EM
5xsz – LPA6A (mutant) – zebra fish
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.16 1.17 1.18 1.19 1.20 1.21 1.22 1.23 Chrencik JE, Roth CB, Terakado M, Kurata H, Omi R, Kihara Y, Warshaviak D, Nakade S, Asmar-Rovira G, Mileni M, Mizuno H, Griffith MT, Rodgers C, Han GW, Velasquez J, Chun J, Stevens RC, Hanson MA. Crystal Structure of Antagonist Bound Human Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor 1. Cell. 2015 Jun 18;161(7):1633-43. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.06.002. PMID:26091040 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.06.002
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Yung, Y. C., N. C. Stoddard, and J. Chun. "LPA Receptor Signaling: Pharmacology, Physiology, and Pathophysiology." The Journal of Lipid Research 55.7 (2014): 1192-214. Web. 17 Feb. 2016.'
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Chun, J., Hla, T., Spiegel, S., and Moolenaar, W.H. “Lysophospholipid Receptors: Signaling and Biochemistry.” John Wiley & Sons, Inc. (2013) pp.i-xviii. 5 Feb. 2016.'
- ↑ Boutin JA, Ferry G. Autotaxin. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009 Sep;66(18):3009-21. doi: 10.1007/s00018-009-0056-9. Epub , 2009 Jun 9. PMID:19506801 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00018-009-0056-9
- ↑ Hernández-Méndez, Aurelio, Rocío Alcántara-Hernández, and J. Adolfo García-Sáinz. "Lysophosphatidic Acid LPA1-3 Receptors: Signaling, Regulation and in Silico Analysis of Their Putative Phosphorylation Sites." Receptors & Clinical Investigation Receptor Clin Invest 1.3 (2014). Web. 15 Feb. 2016.'
- ↑ Anliker B, Choi JW, Lin ME, Gardell SE, Rivera RR, Kennedy G, Chun J. Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) and its receptor, LPA1 , influence embryonic schwann cell migration, myelination, and cell-to-axon segregation. Glia. 2013 Dec;61(12):2009-22. doi: 10.1002/glia.22572. Epub 2013 Sep 24. PMID:24115248 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/glia.22572
- ↑ Lin ME, Herr DR, Chun J. Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) receptors: signaling properties and disease relevance. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2010 Apr;91(3-4):130-8. doi:, 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2009.02.002. Epub 2009 Mar 4. PMID:20331961 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2009.02.002
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Justus CR, Dong L, Yang LV. Acidic tumor microenvironment and pH-sensing G protein-coupled receptors. Front Physiol. 2013 Dec 5;4:354. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2013.00354. PMID:24367336 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2013.00354
- ↑ Boucharaba A, Serre CM, Guglielmi J, Bordet JC, Clezardin P, Peyruchaud O. The type 1 lysophosphatidic acid receptor is a target for therapy in bone metastases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Jun 20;103(25):9643-8. Epub 2006 Jun 12. PMID:16769891 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0600979103
- ↑ Marshall JC, Collins JW, Nakayama J, Horak CE, Liewehr DJ, Steinberg SM, Albaugh M, Vidal-Vanaclocha F, Palmieri D, Barbier M, Murone M, Steeg PS. Effect of inhibition of the lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 on metastasis and metastatic dormancy in breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012 Sep 5;104(17):1306-19. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djs319. Epub, 2012 Aug 21. PMID:22911670 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djs319
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 Inoue M, Rashid MH, Fujita R, Contos JJ, Chun J, Ueda H. Initiation of neuropathic pain requires lysophosphatidic acid receptor signaling. Nat Med. 2004 Jul;10(7):712-8. Epub 2004 Jun 13. PMID:15195086 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nm1060
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Tager AM, LaCamera P, Shea BS, Campanella GS, Selman M, Zhao Z, Polosukhin V, Wain J, Karimi-Shah BA, Kim ND, Hart WK, Pardo A, Blackwell TS, Xu Y, Chun J, Luster AD. The lysophosphatidic acid receptor LPA1 links pulmonary fibrosis to lung injury by mediating fibroblast recruitment and vascular leak. Nat Med. 2008 Jan;14(1):45-54. Epub 2007 Dec 9. PMID:18066075 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nm1685
Proteopedia Resources
Category:Lysophosphatidic acid binding
Category:Lysophosphatidic acid
Butler University Proteopedia Pages
See also: