|
|
| (2 intermediate revisions not shown.) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| | | | |
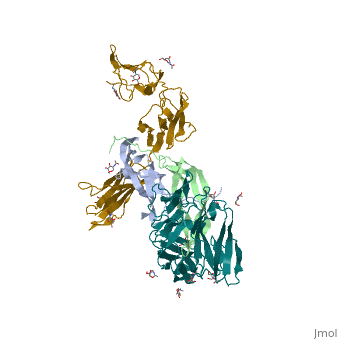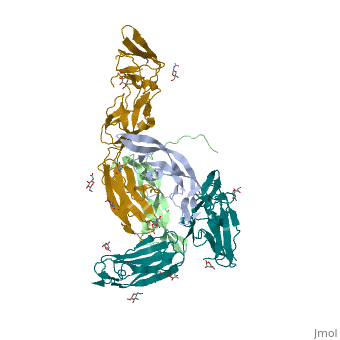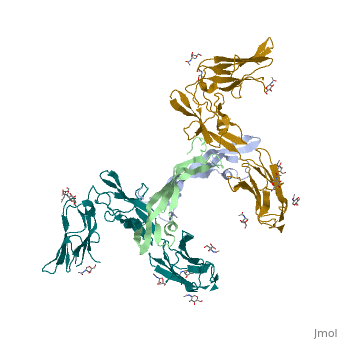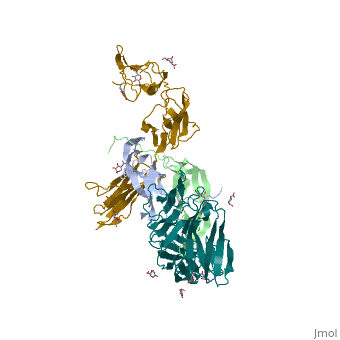
| | ==The structure of a platelet derived growth factor receptor complex== | | ==The structure of a platelet derived growth factor receptor complex== |
| - | <StructureSection load='3mjg' size='340' side='right' caption='[[3mjg]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.30Å' scene=''> | + | <StructureSection load='3mjg' size='340' side='right'caption='[[3mjg]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.30Å' scene=''> |
| | == Structural highlights == | | == Structural highlights == |
| - | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[3mjg]] is a 4 chain structure with sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human Human]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=3MJG OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=3MJG FirstGlance]. <br> | + | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[3mjg]] is a 4 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=3MJG OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=3MJG FirstGlance]. <br> |
| - | </td></tr><tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='pdbligand=NAG:N-ACETYL-D-GLUCOSAMINE'>NAG</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=NDG:2-(ACETYLAMINO)-2-DEOXY-A-D-GLUCOPYRANOSE'>NDG</scene></td></tr> | + | </td></tr><tr id='method'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Empirical_models|Method:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="methodDat">X-ray diffraction, [[Resolution|Resolution]] 2.3Å</td></tr> |
| - | <tr id='gene'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Gene|Gene:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">PDGF2, PDGFB, SIS ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&srchmode=5&id=9606 HUMAN]), PDGFRB ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&srchmode=5&id=9606 HUMAN])</td></tr> | + | <tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="ligandDat"><scene name='pdbligand=NAG:N-ACETYL-D-GLUCOSAMINE'>NAG</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=NDG:2-(ACETYLAMINO)-2-DEOXY-A-D-GLUCOPYRANOSE'>NDG</scene></td></tr> |
| - | <tr id='activity'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Activity:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Receptor_protein-tyrosine_kinase Receptor protein-tyrosine kinase], with EC number [http://www.brenda-enzymes.info/php/result_flat.php4?ecno=2.7.10.1 2.7.10.1] </span></td></tr>
| + | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=3mjg FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=3mjg OCA], [https://pdbe.org/3mjg PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=3mjg RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/3mjg PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=3mjg ProSAT]</span></td></tr> |
| - | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=3mjg FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=3mjg OCA], [http://pdbe.org/3mjg PDBe], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=3mjg RCSB], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/3mjg PDBsum], [http://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=3mjg ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | + | |
| | </table> | | </table> |
| | == Disease == | | == Disease == |
| - | [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/PDGFB_HUMAN PDGFB_HUMAN]] Note=A chromosomal aberration involving PDGFB is found in dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Translocation t(17;22)(q22;q13) with PDGFB.<ref>PMID:12660034</ref> [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/PGFRB_HUMAN PGFRB_HUMAN]] Note=A chromosomal aberration involving PDGFRB is found in a form of chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML). Translocation t(5;12)(q33;p13) with EVT6/TEL. It is characterized by abnormal clonal myeloid proliferation and by progression to acute myelogenous leukemia (AML). Note=A chromosomal aberration involving PDGFRB may be a cause of acute myelogenous leukemia. Translocation t(5;14)(q33;q32) with TRIP11. The fusion protein may be involved in clonal evolution of leukemia and eosinophilia. Note=A chromosomal aberration involving PDGFRB may be a cause of juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia. Translocation t(5;17)(q33;p11.2) with SPECC1. Defects in PDGFRB are a cause of myeloproliferative disorder chronic with eosinophilia (MPE) [MIM:[http://omim.org/entry/131440 131440]]. A hematologic disorder characterized by malignant eosinophils proliferation. Note=A chromosomal aberration involving PDGFRB is found in many instances of myeloproliferative disorder chronic with eosinophilia. Translocation t(5;12) with ETV6 on chromosome 12 creating an PDGFRB-ETV6 fusion protein. Translocation t(5;15)(q33;q22) with TP53BP1 creating a PDGFRB-TP53BP1 fusion protein. Note=A chromosomal aberration involving PDGFRB may be the cause of a myeloproliferative disorder (MBD) associated with eosinophilia. Translocation t(1;5)(q23;q33) that forms a PDE4DIP-PDGFRB fusion protein. Note=A chromosomal aberration involving PGFRB is found in a patient with T-lymphoblastic lymphoma (T-ALL) and an associated myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN) with eosinophilia. Translocation t(5;6)(q33-34;q23) with CEP85L. The translocation fuses the 5'-end of CEP85L (isoform 4) to the 3'-end of PDGFRB. | + | [https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/PDGFB_HUMAN PDGFB_HUMAN] Note=A chromosomal aberration involving PDGFB is found in dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Translocation t(17;22)(q22;q13) with PDGFB.<ref>PMID:12660034</ref> |
| | == Function == | | == Function == |
| - | [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/PDGFB_HUMAN PDGFB_HUMAN]] Growth factor that plays an essential role in the regulation of embryonic development, cell proliferation, cell migration, survival and chemotaxis. Potent mitogen for cells of mesenchymal origin. Required for normal proliferation and recruitment of pericytes and vascular smooth muscle cells in the central nervous system, skin, lung, heart and placenta. Required for normal blood vessel development, and for normal development of kidney glomeruli. Plays an important role in wound healing. Signaling is modulated by the formation of heterodimers with PDGFA (By similarity). [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/PGFRB_HUMAN PGFRB_HUMAN]] Tyrosine-protein kinase that acts as cell-surface receptor for homodimeric PDGFB and PDGFD and for heterodimers formed by PDGFA and PDGFB, and plays an essential role in the regulation of embryonic development, cell proliferation, survival, differentiation, chemotaxis and migration. Plays an essential role in blood vessel development by promoting proliferation, migration and recruitment of pericytes and smooth muscle cells to endothelial cells. Plays a role in the migration of vascular smooth muscle cells and the formation of neointima at vascular injury sites. Required for normal development of the cardiovascular system. Required for normal recruitment of pericytes (mesangial cells) in the kidney glomerulus, and for normal formation of a branched network of capillaries in kidney glomeruli. Promotes rearrangement of the actin cytoskeleton and the formation of membrane ruffles. Binding of its cognate ligands - homodimeric PDGFB, heterodimers formed by PDGFA and PDGFB or homodimeric PDGFD -leads to the activation of several signaling cascades; the response depends on the nature of the bound ligand and is modulated by the formation of heterodimers between PDGFRA and PDGFRB. Phosphorylates PLCG1, PIK3R1, PTPN11, RASA1/GAP, CBL, SHC1 and NCK1. Activation of PLCG1 leads to the production of the cellular signaling molecules diacylglycerol and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate, mobilization of cytosolic Ca(2+) and the activation of protein kinase C. Phosphorylation of PIK3R1, the regulatory subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, leads to the activation of the AKT1 signaling pathway. Phosphorylation of SHC1, or of the C-terminus of PTPN11, creates a binding site for GRB2, resulting in the activation of HRAS, RAF1 and down-stream MAP kinases, including MAPK1/ERK2 and/or MAPK3/ERK1. Promotes phosphorylation and activation of SRC family kinases. Promotes phosphorylation of PDCD6IP/ALIX and STAM. Receptor signaling is down-regulated by protein phosphatases that dephosphorylate the receptor and its down-stream effectors, and by rapid internalization of the activated receptor.<ref>PMID:2835772</ref> <ref>PMID:2850496</ref> <ref>PMID:2554309</ref> <ref>PMID:1653029</ref> <ref>PMID:1709159</ref> <ref>PMID:1846866</ref> <ref>PMID:1314164</ref> <ref>PMID:1396585</ref> <ref>PMID:7685273</ref> <ref>PMID:7691811</ref> <ref>PMID:7692233</ref> <ref>PMID:11297552</ref> <ref>PMID:11331881</ref> <ref>PMID:21098708</ref> <ref>PMID:20494825</ref> <ref>PMID:20529858</ref> <ref>PMID:21733313</ref> <ref>PMID:8195171</ref> <ref>PMID:21679854</ref> | + | [https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/PDGFB_HUMAN PDGFB_HUMAN] Growth factor that plays an essential role in the regulation of embryonic development, cell proliferation, cell migration, survival and chemotaxis. Potent mitogen for cells of mesenchymal origin. Required for normal proliferation and recruitment of pericytes and vascular smooth muscle cells in the central nervous system, skin, lung, heart and placenta. Required for normal blood vessel development, and for normal development of kidney glomeruli. Plays an important role in wound healing. Signaling is modulated by the formation of heterodimers with PDGFA (By similarity). |
| | == Evolutionary Conservation == | | == Evolutionary Conservation == |
| | [[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | | [[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] |
| | Check<jmol> | | Check<jmol> |
| | <jmolCheckbox> | | <jmolCheckbox> |
| - | <scriptWhenChecked>select protein; define ~consurf_to_do selected; consurf_initial_scene = true; script "/wiki/ConSurf/mj/3mjg_consurf.spt"</scriptWhenChecked> | + | <scriptWhenChecked>; select protein; define ~consurf_to_do selected; consurf_initial_scene = true; script "/wiki/ConSurf/mj/3mjg_consurf.spt"</scriptWhenChecked> |
| - | <scriptWhenUnchecked>script /wiki/extensions/Proteopedia/spt/initialview01.spt</scriptWhenUnchecked> | + | <scriptWhenUnchecked>script /wiki/extensions/Proteopedia/spt/initialview03.spt</scriptWhenUnchecked> |
| | <text>to colour the structure by Evolutionary Conservation</text> | | <text>to colour the structure by Evolutionary Conservation</text> |
| | </jmolCheckbox> | | </jmolCheckbox> |
| Line 32: |
Line 31: |
| | </div> | | </div> |
| | <div class="pdbe-citations 3mjg" style="background-color:#fffaf0;"></div> | | <div class="pdbe-citations 3mjg" style="background-color:#fffaf0;"></div> |
| - | | |
| - | ==See Also== | |
| - | *[[Hormone|Hormone]] | |
| | == References == | | == References == |
| | <references/> | | <references/> |
| | __TOC__ | | __TOC__ |
| | </StructureSection> | | </StructureSection> |
| - | [[Category: Human]] | + | [[Category: Homo sapiens]] |
| - | [[Category: Receptor protein-tyrosine kinase]] | + | [[Category: Large Structures]] |
| - | [[Category: He, X]] | + | [[Category: He X]] |
| - | [[Category: Shim, A H.R]] | + | [[Category: Shim AHR]] |
| - | [[Category: Growth factor-receptor complex]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Hormone-transferase complex]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Protein-protein complex]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Transferase-hormone complex]]
| + | |
| Structural highlights
Disease
PDGFB_HUMAN Note=A chromosomal aberration involving PDGFB is found in dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Translocation t(17;22)(q22;q13) with PDGFB.[1]
Function
PDGFB_HUMAN Growth factor that plays an essential role in the regulation of embryonic development, cell proliferation, cell migration, survival and chemotaxis. Potent mitogen for cells of mesenchymal origin. Required for normal proliferation and recruitment of pericytes and vascular smooth muscle cells in the central nervous system, skin, lung, heart and placenta. Required for normal blood vessel development, and for normal development of kidney glomeruli. Plays an important role in wound healing. Signaling is modulated by the formation of heterodimers with PDGFA (By similarity).
Evolutionary Conservation
Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf.
Publication Abstract from PubMed
Platelet-derived growth factors (PDGFs) and their receptors (PDGFRs) are prototypic growth factors and receptor tyrosine kinases which have critical functions in development. We show that PDGFs share a conserved region in their prodomain sequences which can remain noncovalently associated with the mature cystine-knot growth factor domain after processing. The structure of the PDGF-A/propeptide complex reveals this conserved, hydrophobic association mode. We also present the structure of the complex between PDGF-B and the first three Ig domains of PDGFRbeta, showing that two PDGF-B protomers clamp PDGFRbeta at their dimerization seam. The PDGF-B:PDGFRbeta interface is predominantly hydrophobic, and PDGFRs and the PDGF propeptides occupy overlapping positions on mature PDGFs, rationalizing the need of propeptides by PDGFs to cover functionally important hydrophobic surfaces during secretion. A large-scale structural organization and rearrangement is observed for PDGF-B upon receptor binding, in which the PDGF-B L1 loop, disordered in the structure of the free form, adopts a highly specific conformation to form hydrophobic interactions with the third Ig domain of PDGFRbeta. Calorimetric data also shows that the membrane-proximal homotypic PDGFRalpha interaction, albeit required for activation, contributes negatively to ligand binding. The structural and biochemical data together offer insights into PDGF-PDGFR signaling, as well as strategies for PDGF-antagonism.
Structures of a platelet-derived growth factor/propeptide complex and a platelet-derived growth factor/receptor complex.,Shim AH, Liu H, Focia PJ, Chen X, Lin PC, He X Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jun 22;107(25):11307-12. Epub 2010 Jun 2. PMID:20534510[2]
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
References
- ↑ Sandberg AA, Anderson WD, Fredenberg C, Hashimoto H. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans of breast. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2003 Apr 1;142(1):56-9. PMID:12660034
- ↑ Shim AH, Liu H, Focia PJ, Chen X, Lin PC, He X. Structures of a platelet-derived growth factor/propeptide complex and a platelet-derived growth factor/receptor complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jun 22;107(25):11307-12. Epub 2010 Jun 2. PMID:20534510
|