|
|
| (19 intermediate revisions not shown.) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
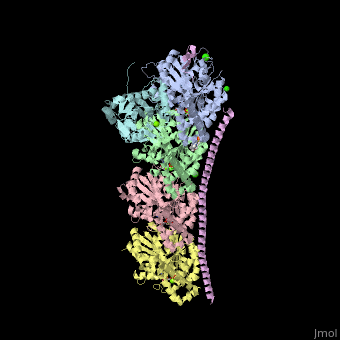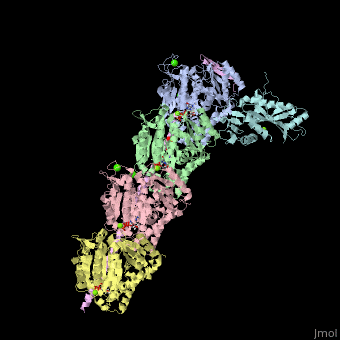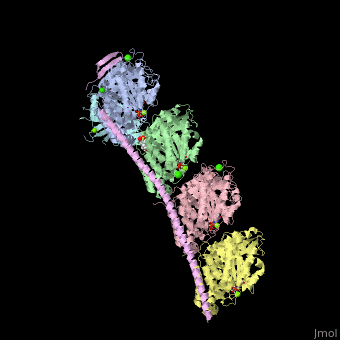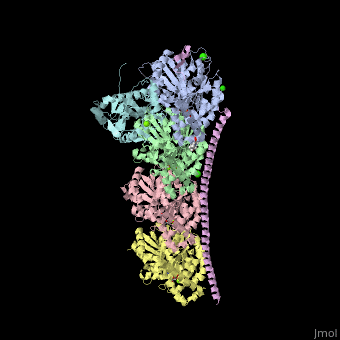
| - | <StructureSection load='4iij' size='340' side='right' caption='Tubulin tyrosine ligase (cyan) complex with α-tubulin (grey and pink), β-tubulin (green and yellow), stathmin (magenta), MES, GTP, Ca+2, Cl- and Mg+2 ions (PDB code [[4iij]])' scene=''> | + | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='Tubulin tyrosine ligase (cyan) complex with α-tubulin (grey and pink), β-tubulin (green and yellow), stathmin (magenta), MES, GTP, Ca+2, Cl- and Mg+2 ions (PDB code [[4iij]])' scene='70/707399/Cv/1' pspeed='8'> |
| | == Function == | | == Function == |
| - | '''Tubulin tyrosine ligase''' (TTL) adds tyrosine in an ATP-dependent reaction to the C-terminal of a detyrosinated a-tubulin. The detyrosination of α-tubulin is a posttranslational modification which exposes glutamate in the new tubulin C-terminal. The detyrosinated α-tubulin forms Glu-microtubules<ref>PMID:10842328</ref>. The complex of TTL and tubulin contains [[Stathmin]] (TM) - another tubulin-binding protein<ref>PMID:23624152</ref>. | + | '''Tubulin tyrosine ligase''' (TTL) adds tyrosine in an ATP-dependent reaction to the C-terminal of a detyrosinated a-tubulin. The detyrosination of α-tubulin is a posttranslational modification which exposes glutamate in the new tubulin C-terminal. The detyrosinated α-tubulin forms Glu-microtubules<ref>PMID:10842328</ref>. The complex of TTL and tubulin contains [[Stathmin]] (STM) - another tubulin-binding protein<ref>PMID:23624152</ref>. |
| | | | |
| | == Disease == | | == Disease == |
| Line 7: |
Line 7: |
| | | | |
| | == Structural highlights == | | == Structural highlights == |
| - | TTL structure is composed of N-terminal, central and C-terminal domains. TTL interacts with α- and β-tubulin via 3 loops and one helix terminal<ref>PMID:23358242</ref>. | + | <scene name='70/707399/Cv/5'>Tubulin tyrosine ligase complex with α-tubulin (2 chains), β-tubulin (2 chains), and stathmin</scene>. TTL structure is composed of <scene name='70/707399/Cv/6'>N-terminal, central and C-terminal domains</scene>. <scene name='70/707399/Cv/7'>TTL interacts with α- and β-tubulin</scene> via 3 loops and one helix terminal<ref>PMID:23358242</ref>. |
| - | </StructureSection>
| + | |
| | | | |
| | == 3D Structures of tubulin tyrosine ligase == | | == 3D Structures of tubulin tyrosine ligase == |
| | | | |
| - | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}}
| + | [[Tubulin tyrosine ligase 3D structures]] |
| - | | + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | [[3tig]] – fTTL - frog<br /> | + | |
| - | [[3tii]] – fTTL + phosphomethylphosphonic acid adenylate <br />
| + | |
| - | [[3tin]] – fTTL + ADP <br />
| + | |
| - | [[4iij]] – cTTL + rSTM + tubulin + GTP + GDP - chicken<br />
| + | |
| - | [[4ihj]] – cTTL + rSTM + tubulin + GTP + GDP + ADP <br />
| + | |
| - | [[4wbn]] – cTTL + rSTM + tubulin + GTP + GDP + phosphomethylphosphonic acid adenylate <br />
| + | |
| - | [[4o2a]] – cTTL + rSTM + tubulin + GTP + GDP + ADP + inhibitor<br />
| + | |
| - | [[4i4t]] – cTTL + rSTM + tubulin + GTP + GDP + zampanolide <br />
| + | |
| - | [[4i50]] – cTTL + rSTM + tubulin + GTP + GDP + epothilone <br />
| + | |
| - | [[4o4l]], [[4tuy]], [[4tv8]], [[4yj2]], [[4yj3]] – cTTL + rSTM + tubulin + GTP + GDP + anti-cancer drugs<br />
| + | |
| - | [[4i55]] – cTTL + rSTM + tubulin + GTP + GDP + phosphomethylphosphonic acid adenylate <br />
| + | |
| - | [[4o2b]] – cTTL + rSTM + tubulin + GTP + GDP + phosphomethylphosphonic acid adenylate + anti-gout drug<br />
| + | |
| - | [[4o4h]], [[4o4j]], [[4o4i]] – cTTL + rSTM + tubulin + GTP + GDP + phosphomethylphosphonic acid adenylate + anti-cancer drug<br />
| + | |
| | | | |
| | == References == | | == References == |
| | <references/> | | <references/> |
| | + | </StructureSection> |
| | + | [[Category:Topic Page]] |
|
Function
Tubulin tyrosine ligase (TTL) adds tyrosine in an ATP-dependent reaction to the C-terminal of a detyrosinated a-tubulin. The detyrosination of α-tubulin is a posttranslational modification which exposes glutamate in the new tubulin C-terminal. The detyrosinated α-tubulin forms Glu-microtubules[1]. The complex of TTL and tubulin contains Stathmin (STM) - another tubulin-binding protein[2].
Disease
Mutated TTL causes morphogenic abnormalities and cancer. There is a loss of TTL activity during tumor growth[3].
Structural highlights
. TTL structure is composed of . via 3 loops and one helix terminal[4].
3D Structures of tubulin tyrosine ligase
Tubulin tyrosine ligase 3D structures
References
- ↑ Idriss HT. Phosphorylation of tubulin tyrosine ligase: a potential mechanism for regulation of alpha-tubulin tyrosination. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2000 May;46(1):1-5. PMID:10842328 doi:<1::AID-CM1>3.0.CO;2-6 http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0169(200005)46:1<1::AID-CM1>3.0.CO;2-6
- ↑ Szyk A, Piszczek G, Roll-Mecak A. Tubulin tyrosine ligase and stathmin compete for tubulin binding in vitro. J Mol Biol. 2013 Jul 24;425(14):2412-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2013.04.017. Epub 2013, Apr 25. PMID:23624152 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2013.04.017
- ↑ Lafanechere L, Courtay-Cahen C, Kawakami T, Jacrot M, Rudiger M, Wehland J, Job D, Margolis RL. Suppression of tubulin tyrosine ligase during tumor growth. J Cell Sci. 1998 Jan;111 ( Pt 2):171-81. PMID:9405300
- ↑ Prota AE, Magiera MM, Kuijpers M, Bargsten K, Frey D, Wieser M, Jaussi R, Hoogenraad CC, Kammerer RA, Janke C, Steinmetz MO. Structural basis of tubulin tyrosination by tubulin tyrosine ligase. J Cell Biol. 2013 Feb 4;200(3):259-70. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201211017. Epub 2013 Jan , 28. PMID:23358242 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201211017
|