Ricin
From Proteopedia
| (9 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
'''Ricin''' is a potent cytotoxin that is synthesized in the endosperm cells of maturing seeds of the castor oil plant (''Ricinus communis'')<ref name="lord">PMID: 8119491</ref>. Ricin belongs to a small multi-gene family<ref name="montfort">PMID: 3558397</ref> that is composed of eight members. Ricin is classified as a type II heterodimeric Ribosome Inactivating Protein<ref name="lord" /> or RIPs. For toxins in Proteopedia see [[Toxins]]. | '''Ricin''' is a potent cytotoxin that is synthesized in the endosperm cells of maturing seeds of the castor oil plant (''Ricinus communis'')<ref name="lord">PMID: 8119491</ref>. Ricin belongs to a small multi-gene family<ref name="montfort">PMID: 3558397</ref> that is composed of eight members. Ricin is classified as a type II heterodimeric Ribosome Inactivating Protein<ref name="lord" /> or RIPs. For toxins in Proteopedia see [[Toxins]]. | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='3rtj' size=' | + | See also [[Ricin: A toxic protein]]; [[Ricin: Structure and function]]. |
| + | |||
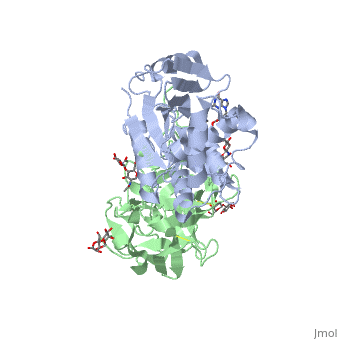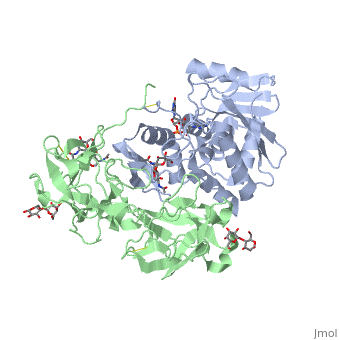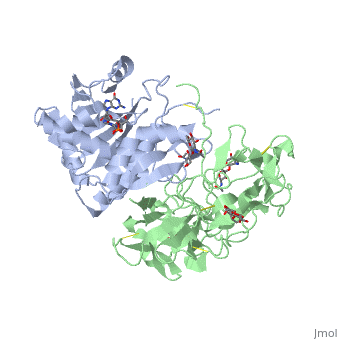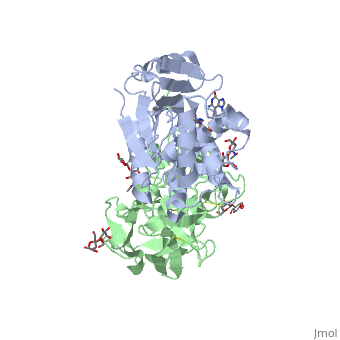
| + | <StructureSection load='3rtj' size='350' side='right' caption='Glycosylated ricin chain A (grey) and chain B (green) bound to dinucleotide APG (stick model) (PDB entry [[3rtj]])'> | ||
==Structure== | ==Structure== | ||
Ricin is a heterodimer that consists of a 32 kilodalton A chain glycoprotein (light blue) linked by a <scene name='38/382952/Disulfide_bond_between_subunit/3'>disulfide bond</scene> to a 32 kilodalton <scene name='Sandbox_BCMB402_Ricin/B_subunit/1'>B chain</scene> glycoprotein<ref name="montfort" /> (green). | Ricin is a heterodimer that consists of a 32 kilodalton A chain glycoprotein (light blue) linked by a <scene name='38/382952/Disulfide_bond_between_subunit/3'>disulfide bond</scene> to a 32 kilodalton <scene name='Sandbox_BCMB402_Ricin/B_subunit/1'>B chain</scene> glycoprotein<ref name="montfort" /> (green). | ||
| Line 12: | Line 14: | ||
The <scene name='Sandbox_BCMB402_Ricin/A_subunit_secondary_structure/2'> A chain</scene> is an alpha/beta protein which contains eight alpha helices (pink) and eight beta sheets (yellow). It has three domains<ref name="Weston">PMID: 7990130</ref>. <scene name='Sandbox_BCMB402_Ricin/Domain_1_of_a_subunit/2'>Domain 1 </scene> consists of a beta sheet containing both parallel and anti-parallel strands. The <scene name='Sandbox_BCMB402_Ricin/Domain2_of_a_subunit/1'> second alpha helical domain </scene> makes up the core of the protein, and includes the active site. The<scene name='Sandbox_BCMB402_Ricin/Domain3_of_a_subunit/1'> third domain</scene> interacts with the B chain, and contains a helix and two beta strands. | The <scene name='Sandbox_BCMB402_Ricin/A_subunit_secondary_structure/2'> A chain</scene> is an alpha/beta protein which contains eight alpha helices (pink) and eight beta sheets (yellow). It has three domains<ref name="Weston">PMID: 7990130</ref>. <scene name='Sandbox_BCMB402_Ricin/Domain_1_of_a_subunit/2'>Domain 1 </scene> consists of a beta sheet containing both parallel and anti-parallel strands. The <scene name='Sandbox_BCMB402_Ricin/Domain2_of_a_subunit/1'> second alpha helical domain </scene> makes up the core of the protein, and includes the active site. The<scene name='Sandbox_BCMB402_Ricin/Domain3_of_a_subunit/1'> third domain</scene> interacts with the B chain, and contains a helix and two beta strands. | ||
| - | The A chain contains the active site that is responsible for inactivating the [[Ribosome]] via depurination. RIPs have very diverse structures, containing only eight invariant residues<ref name = "lord"/>. These <scene name='Sandbox_BCMB402_Ricin/Conserved_residues/2'>conserved residues</scene> are clustered in the active site. | + | The '''A chain''' contains the active site that is responsible for inactivating the [[Ribosome]] via depurination. RIPs have very diverse structures, containing only eight invariant residues<ref name = "lord"/>. These <scene name='Sandbox_BCMB402_Ricin/Conserved_residues/2'>conserved residues</scene> are clustered in the active site. |
| - | The B chain is a lectin<ref name="lord" /> that <scene name='Sandbox_BCMB402_Ricin/Carbohydrate_binding/1'>binds</scene> to galactose-containing surface receptors. Originally it was thought that the mode of action of Ricin poisoning was due to hemagglutination due to a closely related, co-isolating lectin, RCA. | + | The '''B chain''' is a lectin<ref name="lord" /> that <scene name='Sandbox_BCMB402_Ricin/Carbohydrate_binding/1'>binds</scene> to galactose-containing surface receptors. Originally it was thought that the mode of action of Ricin poisoning was due to hemagglutination due to a closely related, co-isolating lectin, RCA. |
==Mechanism of action== | ==Mechanism of action== | ||
| Line 29: | Line 31: | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| - | ==3D structures of ricin | + | ==3D structures of ricin== |
| - | + | [[Ricin 3D structures]] | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | ** [[2aai]] - RTA + RTB<br /> | ||
| - | ** [[3px8]], [[3rti]] – RTA + RTB + formycin monophosphate<br /> | ||
| - | ** [[3rtj]] - RTA + RTB + dinucleotide | ||
| - | }} | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
* [[Ribosome]] | * [[Ribosome]] | ||
Current revision
This page, as it appeared on May 14, 2013, was featured in this article in the journal Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Education.
Ricin is a potent cytotoxin that is synthesized in the endosperm cells of maturing seeds of the castor oil plant (Ricinus communis)[1]. Ricin belongs to a small multi-gene family[2] that is composed of eight members. Ricin is classified as a type II heterodimeric Ribosome Inactivating Protein[1] or RIPs. For toxins in Proteopedia see Toxins.
See also Ricin: A toxic protein; Ricin: Structure and function.
| |||||||||||
3D structures of ricin
See Also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Lord JM, Roberts LM, Robertus JD. Ricin: structure, mode of action, and some current applications. FASEB J. 1994 Feb;8(2):201-8. PMID:8119491
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Montfort W, Villafranca JE, Monzingo AF, Ernst SR, Katzin B, Rutenber E, Xuong NH, Hamlin R, Robertus JD. The three-dimensional structure of ricin at 2.8 A. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5398-403. PMID:3558397
- ↑ Weston SA, Tucker AD, Thatcher DR, Derbyshire DJ, Pauptit RA. X-ray structure of recombinant ricin A-chain at 1.8 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1994 Dec 9;244(4):410-22. PMID:7990130 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1994.1739
- ↑ Rutenber E, Ready M, Robertus JD. Structure and evolution of ricin B chain. Nature. 1987 Apr 9-15;326(6113):624-6. PMID:3561502 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/326624a0
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Rapak A, Falnes PO, Olsnes S. Retrograde transport of mutant ricin to the endoplasmic reticulum with subsequent translocation to cytosol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Apr 15;94(8):3783-8. PMID:9108055
- ↑ Holmberg L, Nygard O. Depurination of A4256 in 28 S rRNA by the ribosome-inactivating proteins from barley and ricin results in different ribosome conformations. J Mol Biol. 1996 May 31;259(1):81-94. PMID:8648651 doi:10.1006/jmbi.1996.0303
- ↑ Chiou JC, Li XP, Remacha M, Ballesta JP, Tumer NE. The ribosomal stalk is required for ribosome binding, depurination of the rRNA and cytotoxicity of ricin A chain in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Microbiol. 2008 Dec;70(6):1441-52. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06492.x., Epub 2008 Oct 30. PMID:19019145 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06492.x
- ↑ Tesh VL. The induction of apoptosis by Shiga toxins and ricin. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2012;357:137-78. doi: 10.1007/82_2011_155. PMID:22130961 doi:10.1007/82_2011_155
- ↑ Yermakova A, Vance DJ, Mantis NJ. Sub-domains of ricin's B subunit as targets of toxin neutralizing and non-neutralizing monoclonal antibodies. PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e44317. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044317. Epub 2012 Sep 11. PMID:22984492 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0044317
- ↑ Jetzt AE, Cheng JS, Li XP, Tumer NE, Cohick WS. A relatively low level of ribosome depurination by mutant forms of ricin toxin A chain can trigger protein synthesis inhibition, cell signaling and apoptosis in mammalian cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2012 Dec;44(12):2204-11. doi:, 10.1016/j.biocel.2012.09.004. Epub 2012 Sep 12. PMID:22982239 doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2012.09.004
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Ann Taylor, Joel L. Sussman, Douglas Read, Wayne Decatur, David Canner, Angel Herraez, Jaime Prilusky, Alexander Berchansky, Andrea Gorrell