Rebetol
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (4 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<StructureSection load='' size='340' side='right' caption='Ribavirin PDB [[4pb1]]' scene='74/746008/Ribavirin_atalla2/1'> | <StructureSection load='' size='340' side='right' caption='Ribavirin PDB [[4pb1]]' scene='74/746008/Ribavirin_atalla2/1'> | ||
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
| - | Ribavirin was first synthesized in 1970 by ICN Pharmaceuticals (now “Valent International Pharmaceuticals”). In 1986, its first major use was the treatment of RSV (respiratory syncitial virus) infections in pediatric patients, but since its FDA approval in 1998, it has primarily been used as a component in treating Hepatitis C by inhibiting the synthesis of viral RNA. <ref>https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/37542<ref> The treatment was modified and approved in 2002 by the FDA by combining | + | Ribavirin was first synthesized in 1970 by ICN Pharmaceuticals (now “Valent International Pharmaceuticals”). In 1986, its first major use was the treatment of RSV (respiratory syncitial virus) infections in pediatric patients, but since its FDA approval in 1998, it has primarily been used as a component in treating Hepatitis C by inhibiting the synthesis of viral RNA. <ref>https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/37542<ref> The treatment for these infections was modified and approved in 2002 by the FDA by combining Ribavirin with interferon alfa2b. <ref name="gish"/> |
== Structure and Function == | == Structure and Function == | ||
| - | Sentence | + | Sentence |
== Structure and Function == | == Structure and Function == | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
== Structure and Function == | == Structure and Function == | ||
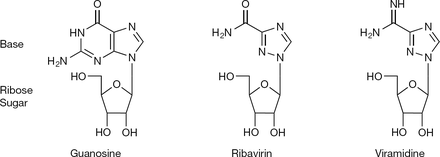
| - | While the main function of Ribavirin is to treat Hepatitis C and RSV, Ribavirin alone is not enough to treat these diseases and is commonly combined with interferon alpha2b<ref name="gish"/>. Ribavirin contains antiviral activity which inhibits DNA/RNA synthesis. It is chemically classified as a nucleoside analog because the structure of Ribavirin resembles the structure of the nucleoside guanosine. Ribavirin is water soluble and is able to mimic other purines, | + | While the main function of Ribavirin is to treat Hepatitis C and RSV, Ribavirin alone is not enough to treat these diseases and is commonly combined with interferon alpha2b<ref name="gish"/>. Ribavirin contains antiviral activity which inhibits DNA/RNA synthesis. It is chemically classified as a nucleoside analog because the structure of Ribavirin resembles the structure of the nucleoside guanosine. Ribavirin is water soluble and is able to mimic other purines, such as adenosine. However, a key difference between the structure of Ribavirin and the purine nucleosides is that the cyclic attachment to the ribose in Ribavirin contains only one ring, as opposed to purines which are heterocyclic. Despite this, it is able to go through similar mechanisms as that of nucleosides, such as phosphorylating into a triphosphate. Its structural similarity to the common nucleoside guanosine may suggest how the drug can inhibit DNA/RNA synthesis through purine mimicry. <ref name="structure"> doi: 10.3851/IMP2125 </ref> |
<scene name='74/746008/Ribavirin_atalla2/1'>Ribavirin</scene> [[4pb1]] | <scene name='74/746008/Ribavirin_atalla2/1'>Ribavirin</scene> [[4pb1]] | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
[[Image:Ribavirin Structure1.gif]] | [[Image:Ribavirin Structure1.gif]] | ||
| + | |||
Comparison of the 2D structure of ribavirin to the structures of the nucleoside guanosine and a similiar anti-viral drug viramidine. <ref name= "structure"/> | Comparison of the 2D structure of ribavirin to the structures of the nucleoside guanosine and a similiar anti-viral drug viramidine. <ref name= "structure"/> | ||
| Line 59: | Line 60: | ||
# Thomas, E., Ghany, M., Liang, J., The application and mechanism of action of ribavirin in therapy of hepatitis C. Antiviral Chemistry & Chemotherapy 23:1-12 (2012)doi: 10.3851/IMP2125 | # Thomas, E., Ghany, M., Liang, J., The application and mechanism of action of ribavirin in therapy of hepatitis C. Antiviral Chemistry & Chemotherapy 23:1-12 (2012)doi: 10.3851/IMP2125 | ||
# Chung, R.T., Gale, M.J., Polyak, S.J., Lemon, S.M., Liang, T.J., & Hoofnagle, J.H. Mechanisms of action of interferon and ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C: Summary of a workshop. Hepatology. 2008;47 (1), 306-320. doi: 10.1002/hep.22070 | # Chung, R.T., Gale, M.J., Polyak, S.J., Lemon, S.M., Liang, T.J., & Hoofnagle, J.H. Mechanisms of action of interferon and ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C: Summary of a workshop. Hepatology. 2008;47 (1), 306-320. doi: 10.1002/hep.22070 | ||
| - | # Paeshuyse, J, Dallmeier, K, Neyts, J. Ribavirin for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus infection: a review of the proposed mechanisms of action. Current Opinion in Virology. 2011;1(6) 590-598. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2011.10.030 | ||
#Alam, I., Lee, J., Cho, K. J., Han, K.R., Yang, J.M., Chung, M.S., & Kim, K. H. Crystal structures of murine norovirus-1 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase in complex with 2-thiouridine or ribavirin. Virology. 2012, 426: 143-151. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2012.01.016 | #Alam, I., Lee, J., Cho, K. J., Han, K.R., Yang, J.M., Chung, M.S., & Kim, K. H. Crystal structures of murine norovirus-1 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase in complex with 2-thiouridine or ribavirin. Virology. 2012, 426: 143-151. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2012.01.016 | ||
#Johnson, ZL, Lee, JH, Lee, M, Kwon, DY, Hong, J, Lee, SY. Structural basis of nucleoside and nucleoside drug selectivity by concentrative nucleoside transporters. eLife. 2014, 3:e03604. doi: 10.7554/eLife.03604. | #Johnson, ZL, Lee, JH, Lee, M, Kwon, DY, Hong, J, Lee, SY. Structural basis of nucleoside and nucleoside drug selectivity by concentrative nucleoside transporters. eLife. 2014, 3:e03604. doi: 10.7554/eLife.03604. | ||
| + | # Paeshuyse, J, Dallmeier, K, Neyts, J. Ribavirin for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus infection: a review of the proposed mechanisms of action. Current Opinion in Virology. 2011;1(6) 590-598. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2011.10.030 | ||
# National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. Pneumonia. 2016, September 26; Retrieved from https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/pnu | # National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. Pneumonia. 2016, September 26; Retrieved from https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/pnu | ||
# Foster, G. Pegylated interferons for the treatment of chronic Hepatitis C. Drugs. 2010;70(2):147-165. doi:10.2165/11531990-000000000-00000 | # Foster, G. Pegylated interferons for the treatment of chronic Hepatitis C. Drugs. 2010;70(2):147-165. doi:10.2165/11531990-000000000-00000 | ||
Current revision
(Ribavirin) 1-β-D-ribofuranosyl-1H-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide [1]
| |||||||||||
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Taylor H. Derby, Jamie Costa, Shannon Shaughnessy, Edmond R Atalla, Katherine Reynolds