|
Overview
Ribavirin was first synthesized in 1970 by ICN Pharmaceuticals (now “Valent International Pharmaceuticals”). In 1986, its first major use was the treatment of RSV (respiratory syncitial virus) infections in pediatric patients, but since its FDA approval in 1998, it has primarily been used as a component in treating Hepatitis C by inhibiting the synthesis of viral RNA. [2]
Structure and Function
While the main function of Ribavirin is to treat Hepatitis C and RSV, Ribavirin alone is not enough to treat these diseases and is commonly combined with interferon alpha2b[1]. Ribavirin contains antiviral activity which inhibits DNA/RNA synthesis. It is chemically classified as a nucleoside analog because the structure of Ribavirin resembles the structure of the nucleoside guanosine. Ribavirin is water soluble and is able to mimic other purines, such as adenosine. However, a key difference between the structure of Ribavirin and the purine nucleosides is that the cyclic attachment to the ribose in Ribavirin contains only one ring, as opposed to purines which are heterocyclic. Despite this, it is able to go through similar mechanisms as that of nucleosides, such as phosphorylating into a triphosphate. Its structural similarity to the common nucleoside guanosine may suggest how the drug can inhibit DNA/RNA synthesis through purine mimicry. [3]
4pb1
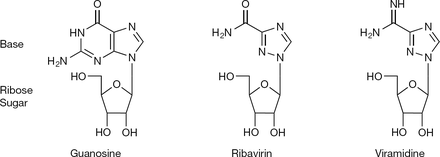
Comparison of the 2D structure of ribavirin to the structures of the nucleoside guanosine and a similiar anti-viral drug viramidine. [3]
Protein Interaction
Ribavirin with RNA-dependent RNA polymerase
Virally-encoded RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) is critical for successful viral replication. The incorporation of nucleoside analogs, such as Ribavirin, by RdRp have been shown to induce error in viral replication
Ribavirin attaches to the binding pocket, which is comprised of tyrosine at position 344 and aspartic acid at positions 250, 346, and 347. The incorporation of Ribavirin into the RNA results in base-pairing with uracil or cytosine, which increases the mutation rate and leads to viral death. [4]
3sfu
Ribavirin with CNT2
Nucleoside transporters facilitate the transport of nucleosides across cell membranes to be used in protein synthesis. Concentrated NTs (CNTs) use the energy of ion gradients for active transportation , while equilibrative NTs (ENTs) transport nucleosides passively down their concentration gradient. Ribavirin is a substrate of ENT1, ENT2, and CNT2. CNT2 binds to the ribose of the ribavirin via hydrogen bonding involving glutamic acid at position 332, asparagine at position 368, and serine at position 371[5].
4pb1
Disease
Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is an infectious disease that affects the liver due to the Hepatitis C virus (HCV). This disease can be acute or chronic and can even lead to death. By binding to the gC1qR receptor, HCV proteins are able to effectively inhibit the differentiation of helper T cells. In addition, HCV core proteins work by preventing the synthesis of the antiviral interferon IFN-γ. Thus, weakening the body’s immunity and making it susceptible to infection. Ribavirin is used in combination with peginterferon to treat Hepatitis C.[6] By adding pegylated interferon-alpha to ribavirin, the drug had a longer half-life, which required only single weekly dosing for Hepatitis C treatment. [7] There are two types of polyethylene glycol (PEG):1. P-INFa-2b and 2. P-INFa-2a. While P-INFa-2b is linear, covalently attached to histidine, and subject to hydrolysis upon injection, P-INFa-2a is branched, attached to lysine through amide bonds, and circulates as a whole molecule upon injection. The limited distribution of P-INFa-2a results in a longer half-life. [8]
Pneumonia
Respiratory syncytial virus is responsible for viral pneumonia. This infection causes the air sacs in one or both of the lungs to become inflamed and potentially filled with fluid or pus. In infants, children, and adults over the age of 65, pneumonia can be deadly. It has been shown that Ribavirin can treat viral pneumonia by preventing transcription of respiratory syncytial virus. [9]
Mechanism
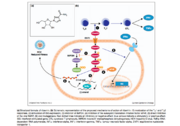
Ribavirin, when administered in combination with pegylated interferon alpha, induces an antiviral state in host cells, resulting in reduced virus replication rates and activation of the host immune system. It is thought that Ribavirin acts as an antiviral agent by disrupting viral RNA synthesis, which would impact both transcription and genome replication in the Hepatitis C virus. However, the exact mechanism by which the drug interferes with this process is unknown. Several theories have been proposed to explain the effect of Ribavirin in inhibiting the replication of the Hepatitis C virus [7].
Immunomodulation by Ribavirin may be responsible for the drug’s antiviral properties. It has been suggested that the natural CD4+ helper T cell response may be altered in the presence of Ribavirin. It is thought that ribavirin may enhance the T helper 1 response, resulting in greater clearance of virus [10]. However, there is conflicting evidence suggesting that the T helper 2 response may be implicated in this process instead [11]. Another possible mechanism involves the enhancement of interferon-stimulated gene (ISG) expression by Ribavirin. When a cell becomes infected with a virus, it may release interferons. Interferons are signaling molecules that function in a paracrine fashion to induce an antiviral state in neighboring cells, protecting them from infection. Ribavirin is thought to enhance the interferon signaling pathway [12], resulting in a wider antiviral response. This theory has been supported in studies using cell culture models [13]. It has also been suggested that the relationship between Ribavirin and inosine 5’-monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH) may impact the virus RNA synthesis. IMPDH plays a significant role in the guanine nucleotide synthesis pathway. It results in the conversion of inosine 5’-monophosphate to xanthine 5’-monophosphate, which is an intermediate for the nucleotide guanosine [14]. Therefore, modulation of IMPDH activity affects a cell’s reservoir of guanosine. Ribavirin has been shown to function as a competitive inhibitor for IMPDH [15]. Because guanosine triphosphate (GTP) plays a critical role in the viral genome replication process, inhibition of IMPDH would result in the prevention of viral replication.
Ribavirin has also been shown to act as an inhibitor for eIF4E, a protein of the translation initiation complex [16]. Because of its structural similarity to guanosine, it mimics the 7-methyl guanosine mRNA cap, preventing translation of viral mRNA. This would result in reduced capacity for viral replication within an infected cell. The Hepatitis C viral genome is replicated by RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). A modified form of Ribavirin, Ribavirin 5’-triphosphate (RTP) is also believed to directly inhibit RdRp activity [17], resulting in lower rates of genome replication. If Ribavirin is converted to the monophosphate form, RMP, it is believed to be incorporated into the viral genome, functioning as a mutagen.
References
- Gish, R. G. Treating HCV with ribavirin analogue and ribavirin-like molecules. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. 2005, November 17;1-6. doi:10.1093/jac/dki405
- Thomas, E., Ghany, M., Liang, J., The application and mechanism of action of ribavirin in therapy of hepatitis C. Antiviral Chemistry & Chemotherapy 23:1-12 (2012)doi: 10.3851/IMP2125
- Chung, R.T., Gale, M.J., Polyak, S.J., Lemon, S.M., Liang, T.J., & Hoofnagle, J.H. Mechanisms of action of interferon and ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C: Summary of a workshop. Hepatology. 2008;47 (1), 306-320. doi: 10.1002/hep.22070
- Alam, I., Lee, J., Cho, K. J., Han, K.R., Yang, J.M., Chung, M.S., & Kim, K. H. Crystal structures of murine norovirus-1 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase in complex with 2-thiouridine or ribavirin. Virology. 2012, 426: 143-151. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2012.01.016
- Johnson, ZL, Lee, JH, Lee, M, Kwon, DY, Hong, J, Lee, SY. Structural basis of nucleoside and nucleoside drug selectivity by concentrative nucleoside transporters. eLife. 2014, 3:e03604. doi: 10.7554/eLife.03604.
- Paeshuyse, J, Dallmeier, K, Neyts, J. Ribavirin for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus infection: a review of the proposed mechanisms of action. Current Opinion in Virology. 2011;1(6) 590-598. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2011.10.030
- National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. Pneumonia. 2016, September 26; Retrieved from https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/pnu
- Foster, G. Pegylated interferons for the treatment of chronic Hepatitis C. Drugs. 2010;70(2):147-165. doi:10.2165/11531990-000000000-00000
- Hofmann WP, Herrmann E, Sarrazin C, Zeuzem S. Ribavirin mode of action in chronic hepatitis C: from clinical use back to molecular mechanisms. Liver Int. 2008, 28:1332-1343. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2008.01896.x
- Fujimoto T, Tomimatsu M, Iga D, Endo H, Otsuka K. Changes in the Th1/Th2 ratio during a 24-week course of an interferon alpha-2b plus ribavirin combination therapy for patients with chronic hepatitis C. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 23:E432- E437. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2008.05320.x
- Feld, JJ, Nanda, S, Huang, Y, Chen, W, Cam, M, Pusek, SN, Schwigler, LM, Theodore, D, Zacks, SL, Liang, TJ, Fried, MW. Hepatic gene expression during treatment with peginterferon and ribavirin: Identifying molecule pathways for treatment response. Hepatol. 2007, 46(5): 1548-1563. doi: 10.1002/hep.21853
- Thomas E, Feld JJ, Li QS, Hu ZY, Fried MW, Liang TJ. Ribavirin potentiates interferon action by augmenting interferon stimulated gene induction in hepatitis C virus cell culture models. Hepatology 2011, 53:32-41. doi: 10.1002/hep.23985
- Shu QN, Nair V. Inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH) as a target in drug discovery. Med. Res. Rev. 2008, 28:219-232. doi: 10.1002/chin.200823265
- Streeter, DG, Witkowski, JT, Khare, GP, Sidwell, RW, Bauer, RJ, Robins, RK, Simon, LN. Mechanisms of action of 1-β-D-ribofuranosyl-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide (virazole) a new broad spectrum antiviral agent. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1973, 70:1174-1178. PMID: 4197928
- Kentsis, A, Topisirovic, I, Culjkovic, B, Shao, L, Borden, KLB. Ribavirin suppresses eIF4E-mediated oncogenic transformation by physical mimicry of the guanosine mRNA cap. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2004, 101:18105-18110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0406927102
- Graci, JD, Cameron, CE. Mechanisms of action of ribavirin against distinct viruses. Rev. Med. Virol. 2006, 16: 37-48. doi: 10.1002/rmv.483
.
Molecules
|