User:Pierre Rossignol/Sandbox
From Proteopedia
< User:Pierre Rossignol(Difference between revisions)
| (One intermediate revision not shown.) | |||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
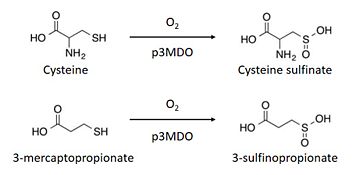
The thiol dioxygenase catalyses the dioxygenation of 3-mercaptopropionate to 3-sulfinopropionate. <ref>https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26272617</ref> | The thiol dioxygenase catalyses the dioxygenation of 3-mercaptopropionate to 3-sulfinopropionate. <ref>https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26272617</ref> | ||
| - | + | The substrate naturally binds itself to the ferrous iron through the thiol. However, spectroscopy indicates that each substrate can bind themselves to other parts of the enzyme as well. <ref>https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4591825/figure/F1/</ref> | |
It also oxidizes cysteine to cysteine sulfinate. <ref>https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26272617</ref> | It also oxidizes cysteine to cysteine sulfinate. <ref>https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26272617</ref> | ||
| - | This enzyme has a marked preference for 3-mercaptopronionate, | + | This enzyme has a marked preference for 3-mercaptopronionate, which explains why it is also referred to as a 3-mercaptopropionate dioxygenase.<ref>https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26272617</ref> |
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| - | Thiol dioxygenases | + | Thiol dioxygenases share a common structure described as a 6-stranded β-barrel core, and a canonical cupin or “jelly roll” β-barrel that is formed with cupin motif 1, an intermotif region, and cupin motif 2 each forming two of the core six β-strands in the folded protein structure.<ref>https://www-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.scd-rproxy.u-strasbg.fr/pmc/articles/PMC3136866/</ref> |
| - | The Thiol dioxygenase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa is made of 4 chains (named <scene name='75/751223/A/1'>A</scene>, <scene name='75/751223/B/1'>B</scene>, <scene name='75/751223/C/1'>C</scene>, <scene name='75/751223/D/1'>D</scene>)<ref>https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/mmdb/mmdbsrv.cgi?uid=130072&dps=1</ref>. Each chain is made of 211 amino acids and has a molecular | + | The Thiol dioxygenase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa is made up of 4 chains (named <scene name='75/751223/A/1'>A</scene>, <scene name='75/751223/B/1'>B</scene>, <scene name='75/751223/C/1'>C</scene>, <scene name='75/751223/D/1'>D</scene>)<ref>https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/mmdb/mmdbsrv.cgi?uid=130072&dps=1</ref>. Each chain is made up of 211 amino acids and has a molecular mass of 23 kDa. For its secondary structures, it has <scene name='75/751223/Alpha_helixes/2'>5 alpha helixes</scene> and <scene name='75/751223/Beta_sheets/1'>14 beta sheets</scene><ref>http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q9I0N5</ref>. Three Histidines, especially,<scene name='75/751223/Histidine_89/1'>Histidine 89</scene>, <scene name='75/751223/His_91/1'>Histidine 91</scene> and <scene name='75/751223/His_142/1'>Histidine 142</scene> constitute the binding sites of iron atom. |
| - | Furthermore, this | + | Furthermore, this protein has two different domains, namely a RmlC-like jelly roll fold and a RmlC-like cupin domain<ref>http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/protein/Q9I0N5</ref>. |
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
| - | A mammalian cysteine dioxygenase also exists and its active site is slightly different, because of the | + | A mammalian cysteine dioxygenase also exists and its active site is slightly different, because of the presence of a glutamine instead of an arginine. <ref> https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26272617 </ref> |
In humans, patients with a high level of cysteine and glutathione-cysteine mixed with disulphide are most likely to suffer from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pantothenate_kinase-associated_neurodegeneration Hallervorden-Spatz (HS) syndrome] which is essentially characterised by neurochemical abnormalities since it affects the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Globus_pallidus globus pallidus]. | In humans, patients with a high level of cysteine and glutathione-cysteine mixed with disulphide are most likely to suffer from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pantothenate_kinase-associated_neurodegeneration Hallervorden-Spatz (HS) syndrome] which is essentially characterised by neurochemical abnormalities since it affects the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Globus_pallidus globus pallidus]. | ||
Current revision
Thiol dioxygenase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21450006
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26272617
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26272617
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26272617
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26272617
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26272617
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4591825/figure/F1/
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26272617
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26272617
- ↑ https://www-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.scd-rproxy.u-strasbg.fr/pmc/articles/PMC3136866/
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/mmdb/mmdbsrv.cgi?uid=130072&dps=1
- ↑ http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q9I0N5
- ↑ http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/protein/Q9I0N5
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26272617
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/4073841