Sandbox Reserved 1054
From Proteopedia
| (8 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | + | == 1CPX - Carboxypeptidase A from Bovine Pancreas == | |
| - | =Trehalose-''O''-mycolyltransferase Ag85C= | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| - | + | <scene name='69/694222/3cpaoverview/1'>Carboxypeptidase A (peptidyl-L-amino acid hydrolase, EC 3.4.17.1, often abbreviated CPA)</scene> is a metallo[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/exopeptidase exopeptidase] that hydrolytically cleaves peptides at the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/C-terminus C-terminal] peptide bond containing hydrophobic side chains. <ref name="CPA1">Bukrinsky JT, Bjerrum MJ, Kadziola A. 1998. Native carboxypeptidase A in a new crystal environment reveals a different conformation of the important tyrosine 248. ''Biochemistry''. 37(47):16555-16564. [http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/bi981678i DOI: 10.1021/bi981678i]</ref> Specifically, CPA is a Zn<sup>2+</sup> [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Metalloprotein#Metalloenzymes metalloenzyme] that carries out the hydrolysis of C-terminal polypeptide residues through the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Deprotonation deprotonation] of a water molecule that is coordinated to the Zn<sup>2+</sup> ion in the enzyme's [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Active_site active site].<ref name="CPA2">Christianson DW, Lipscomb WN. 1989. Carboxypeptidase A. ''Acc. Chem. Res.'' 22:62-69.</ref> From bovine pancreas, 1CPX has been crystallized in a new environment alongside two Zn<sup>2+</sup> ions, one catalytic, the other inhibitory. The inhibitory Zn<sup>2+</sup> ion in this more recent crystal structure not only prevents 1CPX from undergoing its [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/hydrolysis hydrolysis] mechanism; but also, this crystallographic data reveals a different conformation of the Tyr248 (GREEN LINK) residue suggesting alternative mechanistic behavior. <ref name="CPA1">Bukrinsky JT, Bjerrum MJ, Kadziola A. 1998. Native carboxypeptidase A in a new crystal environment reveals a different conformation of the important tyrosine 248. ''Biochemistry''. 37(47):16555-16564. [http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/bi981678i DOI: 10.1021/bi981678i]</ref> 1CPX consists of a single polypeptide chain that contains 307 amino acids. CPA proteins must first be activated by either [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trypsin trypsin] or [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chymotrypsin chymotrypsin] in order to achieve an active form that serves its biological function.<ref name="CPA1" /> This crystallographic data presents 1CPX activated by trypsin in its β-form and orthorhombic crystal form. | |
| - | <StructureSection load='1dqz' size='400' side='right' caption='Antigen 85C in ''Mycobacterium Tuberculosis''' scene=''> | ||
| - | ==Biological Role== | ||
| - | ===Cell Wall of Mycobacteria=== | ||
| - | The unusually thick and waxy cell wall of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mycobacterium mycobacteria] is primarily composed of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Peptidoglycan peptidoglycans], [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arabinogalactan arbinogalactans], and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mycolic_acid mycolic acids]. The mycolic acids, which have very long carbon chains and exhibit extreme hydrophobicity, are responsible for forming the outermost layer of the cell wall, thus creating a hydrophobic envelope surrounding the mycobacterium. Much of the mycolic acid content of the cell wall is in the form of esters (trehalose-6-monomycolate, TMM) and bis-esters (trehalose-6,6'-dimycolate, TDM, [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cord_factor cord factor]) of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trehalose trehalose]. | ||
| - | ===Enzymatic Activity=== | ||
| - | The antigen 85 (Ag85) complex in [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mycobacterium_tuberculosis ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis''] is composed of three homologous proteins: Ag85A, Ag85B, and Ag85C, encoded by the ''fbpA'', ''fbpB'', and ''fbpC'' genes, respectively. Each of these Ag85 components (A, B, and C) is an acyltransferase enzyme (EC 2.3.1.122) that can catalyze mycolyl transfer from TMM to another alcoholic substrate, including TMM itself (Figure 1). | ||
| - | [[Image:MycolylTransferReaction.jpg|700 px|center|thumb|'''Figure 1:''' A mycolyl transfer reaction catalyzed by Ag85C]] | ||
| - | + | This is about 1CPX. This is a carboxypeptidase from bovine pancreas with two Zinc binding sites.This is about 1CPX. This is a carboxypeptidase from bovine pancreas with two Zinc binding sites.This is about 1CPX. This is a carboxypeptidase from bovine pancreas with two Zinc binding sites.This is about 1CPX. This is a carboxypeptidase from bovine pancreas with two Zinc binding sites.This is about 1CPX. | |
| - | + | <scene name='75/752350/Tyr_248_zoom/1'>active site</scene> | |
| - | + | This is a carboxypeptidase from bovine pancreas with two Zinc binding sites. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | <Structure load='1CPX' size='350' frame='true' align='left' caption='This is a caption about 1CPX' scene='75/752350/Tyr_248_zoom/1' /> | ||
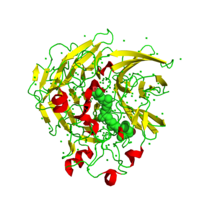
| - | + | [[Image:1CPX Cartoon.png|200 px|right|thumb|Figure Legend]] | |
| - | + | ||
| - | [[Image: | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
Current revision
1CPX - Carboxypeptidase A from Bovine Pancreas
Introduction
is a metalloexopeptidase that hydrolytically cleaves peptides at the C-terminal peptide bond containing hydrophobic side chains. [1] Specifically, CPA is a Zn2+ metalloenzyme that carries out the hydrolysis of C-terminal polypeptide residues through the deprotonation of a water molecule that is coordinated to the Zn2+ ion in the enzyme's active site.[2] From bovine pancreas, 1CPX has been crystallized in a new environment alongside two Zn2+ ions, one catalytic, the other inhibitory. The inhibitory Zn2+ ion in this more recent crystal structure not only prevents 1CPX from undergoing its hydrolysis mechanism; but also, this crystallographic data reveals a different conformation of the Tyr248 (GREEN LINK) residue suggesting alternative mechanistic behavior. [1] 1CPX consists of a single polypeptide chain that contains 307 amino acids. CPA proteins must first be activated by either trypsin or chymotrypsin in order to achieve an active form that serves its biological function.[1] This crystallographic data presents 1CPX activated by trypsin in its β-form and orthorhombic crystal form.
This is about 1CPX. This is a carboxypeptidase from bovine pancreas with two Zinc binding sites.This is about 1CPX. This is a carboxypeptidase from bovine pancreas with two Zinc binding sites.This is about 1CPX. This is a carboxypeptidase from bovine pancreas with two Zinc binding sites.This is about 1CPX. This is a carboxypeptidase from bovine pancreas with two Zinc binding sites.This is about 1CPX.
This is a carboxypeptidase from bovine pancreas with two Zinc binding sites.
|