Cancidas
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (5 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
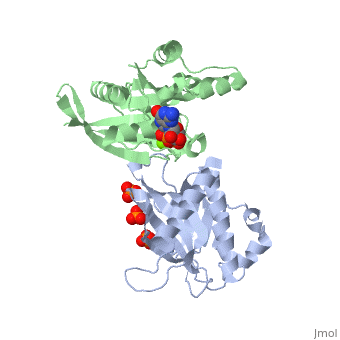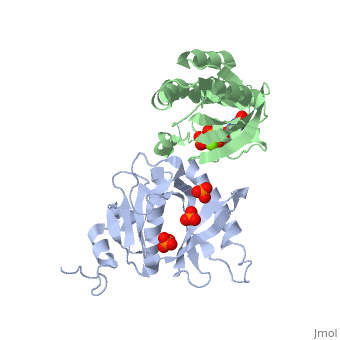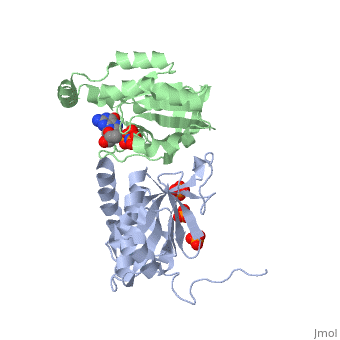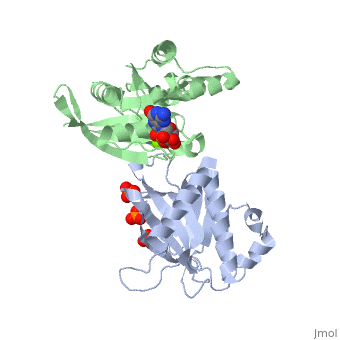
| - | <StructureSection load='3A58' size='340' side='right' caption='Rho1 p, a precursor of beta glucan synthase' scene=''> | + | <StructureSection load='3A58' size='340' side='right' caption='Yeast Rho1 p, a precursor of beta glucan synthase (green) complex with SEC3P (grey), cancidas, GNP, phosphate and Mg+2 ion (green (PDB code [[3a58]])' scene=''> |
==Function== | ==Function== | ||
| - | Caspofungin is a cyclic peptide, isolated from the fermentation products of the fungus ''G. lozoyensis'', that inhibits cell wall synthesis with inhibition of 1,3-β-glucan synthase. Inhibiting 1,3-β-glucan synthase leads to weakening of the cell wall and cell content leakage until death results. Caspofungin is unlike azole antifungal drugs as it triggers apoptosis of fungi and is not simply fungistatic <ref>DOI 10.1159/000447802</ref>. Members of the ''Aspergillus'' and ''Candida'' genera are most susceptible to the drug showing extreme susceptibility in hyphae extremities, sites of cell wall synthesis <ref> https://www.merck.com/product/usa/pi_circulars/c/cancidas/cancidas_pi.pdf</ref>. | + | '''Caspofungin''' is a cyclic peptide, isolated from the fermentation products of the fungus ''G. lozoyensis'', that inhibits cell wall synthesis with inhibition of 1,3-β-glucan synthase. Inhibiting 1,3-β-glucan synthase leads to weakening of the cell wall and cell content leakage until death results. Caspofungin is unlike azole antifungal drugs as it triggers apoptosis of fungi and is not simply fungistatic. Many fungistatic drugs target the cell membrane rather than the cell wall or inhibit DNA and protein synthesis <ref>DOI 10.1159/000447802</ref>. Members of the ''Aspergillus'' and ''Candida'' genera are most susceptible to the drug showing extreme susceptibility in hyphae extremities, sites of cell wall synthesis. Other pathogenic fungi that were previously believed to be saprophytic have also shown susceptibility <ref> https://www.merck.com/product/usa/pi_circulars/c/cancidas/cancidas_pi.pdf</ref>. |
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
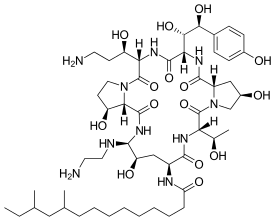
| - | Caspofungin is composed of a cyclic hexapeptide with an N-terminus acylated by a carboxylic acid chain. The chemical structure contains a 3-hydroxy-proline residue, 3,4-dihydroxy-homotyrosine residue, 3-hydroxy-ornithine residue, 4-hydroxy-5-ethylenediamino-ornithine residue, 4-hydroxy-proline residue, and a threonine residue <ref>https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Caspofungin#section=Top</ref>. | + | Caspofungin is composed of a cyclic hexapeptide with an N-terminus acylated by a carboxylic acid chain. The chemical structure contains a 3-hydroxy-proline residue, 3,4-dihydroxy-homotyrosine residue, 3-hydroxy-ornithine residue, 4-hydroxy-5-ethylenediamino-ornithine residue, 4-hydroxy-proline residue, and a threonine residue. It is a derivative of pneumoncandin B0 <ref>https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Caspofungin#section=Top</ref>. |
| - | [[Image:Caspofungin.png]] | + | [[Image:Caspofungin.png|thumb|400px|left|Fig 1. Organic structure of caspofungin]] |
| + | {{Clear}} | ||
== Mechanism == | == Mechanism == | ||
| - | The mode of action of caspofungin is unclear | + | The mode of action of caspofungin is unclear but it is believed that 1,3-β-glucan synthase synthesis is blocked by non-competitive inhibition. Glucan biosynthesis absence in host cells ensures good selectivity for pathogenic fungi. 1,3-β-glucan synthase is formed from the subunits Fks p, which binds UDP, and Rho 1 p, which binds GTP<ref>https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkg117</ref>. |
== Medical Details/Additional Information == | == Medical Details/Additional Information == | ||
| - | ''Candida glabrata'' is one of the most common fungal human pathogens found primarily in immunocompromised patients with HIV | + | ''Candida glabrata'' is one of the most common fungal human pathogens that causes candidiasis, with symptoms such as thrush, and is found primarily in immunocompromised patients with HIV, undergoing chemotherapy, or have obtained an organ transplant<ref>https://www.cdc.gov/fungal/diseases/candidiasis/</ref>. Recently ''C. glabrata'' has become more resistant to azole drugs which target the fungal cell membrane so the use of cell wall synthesis inhibitors such as caspofungin has increased <ref>DOI 10.1534/g3.116.032490</ref>. |
Mutations in Fks p glucan synthase subunit have allowed pathogenic fungi to obtain resistance to caspofungin hindering its potency<ref>Balashov, S. V., Park, S., & Perlin, D. S. (2006). Assessing resistance to the echinocandin antifungal drug caspofungin in Candida albicans by profiling mutations in FKS1. Antimicrobial Agents And Chemotherapy, 50(6), 2058-2063.</ref>. Analysis of diversifying the structure of caspofungin showed the possibility of making the drug more potent to pathogenic fungi. By finding the optimal side chains and keeping the right lipopeptide as the hydrophobic core with the left lipopeptide as a hydrophilic structure, the compound becomes more active against ''Candida'' and ''Aspergillus'' <ref>http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2012.02.015</ref>. | Mutations in Fks p glucan synthase subunit have allowed pathogenic fungi to obtain resistance to caspofungin hindering its potency<ref>Balashov, S. V., Park, S., & Perlin, D. S. (2006). Assessing resistance to the echinocandin antifungal drug caspofungin in Candida albicans by profiling mutations in FKS1. Antimicrobial Agents And Chemotherapy, 50(6), 2058-2063.</ref>. Analysis of diversifying the structure of caspofungin showed the possibility of making the drug more potent to pathogenic fungi. By finding the optimal side chains and keeping the right lipopeptide as the hydrophobic core with the left lipopeptide as a hydrophilic structure, the compound becomes more active against ''Candida'' and ''Aspergillus'' <ref>http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2012.02.015</ref>. | ||
| + | Caspofungin and azole drugs alone have been ineffective against ''Cryptococcus neoformans'', a fungus that causes a form of meningitis pneumonia like symptoms in immunocompromised patients. Studies that used an azole drug along with caspofungin showed that the fungal wall is affected and growth is hindered, however<ref>https://www.cdc.gov/fungal/diseases/cryptococcosis-neoformans/</ref>. | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||