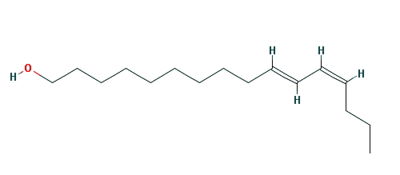
Bombykol, a sex pheromone of
Bombyx mori, from
PubChem Introduction
Odorant-binding protein (OBP) are soluble proteins which are involved in the processes of odorant detection in the olfactory sensilla [1]. Though functionally the same, vertebrates and insects OBP have different origin and structure.
OBPs are important for insect olfaction. For instance, OBP76a (LUSH) in the fly Drosophila melanogaster is required for the detection of the pheromone vaccenyl acetate [2] and has been proven to adopt a conformation that activates the odorant receptor [3].
For more details see Chemical communication in arthropods.
OBP Function
Despite five decades of intensive research, the exact roles of OBP and the mechanism by which the odorant receptor (OR) is activated are still in dispute [4][5].
A few functions have been suggested for OBP:
1. Solubilizing the odorant molecule and its transportation in the sensillar lymph.
2. Protecting the odorant molecule from the odorant degrading enzymes, in the sensillar lymph.
3. Activating the odorant receptor on the dendrite membrane, by the odorant-OBP complex.
4. Mediating the deactivation of the odorant molecule after the activation of the receptor.
5. An organic anion (the protein has 9 negative charges).
Of all, the first role of OBP as an odorant solubilizer and carrier is generally accepted.
In order to explain the structure and function of these fascinating proteins, this page will further focus on a particular OBP - the well investigated Bombyx mori pheromone binding protein: BmorPBP.
Bombyx mori BmorPBP (lets talk about sex..)
Pheromone binding proteins (PBPs) are specialized members of the insect odorant-binding protein (OBP) super-family.
The main purpose in the adult moth's short life is reproduction. In fact, the male and female moth invest all of their energy and resources hoping to reach to the ultimate goal- mating. This long journey begins when the female moth releases a sex pheromone, usually during specific hours in the night [6].
BmorPBP was first identified in the B. mori male antennae by Krieger et al. in 1996 [7], as the PBP of the first sex pheromone discovered ((E,Z)-10,12-hexadecadienol, or Bombykol). The male moth needs to detect minute amount of the pheromone in the air, while following a turbulent wind-born pheromone trail and response fast (experimental evidence shows a response time of 0.5 seconds[8]).
BmorPBP structure and function
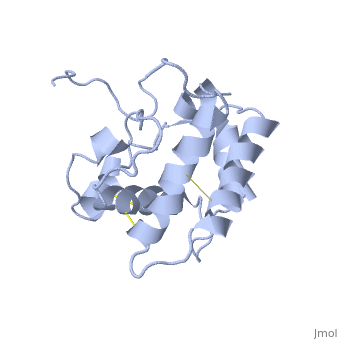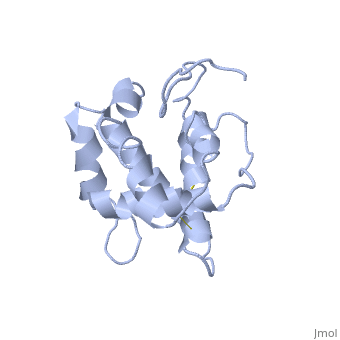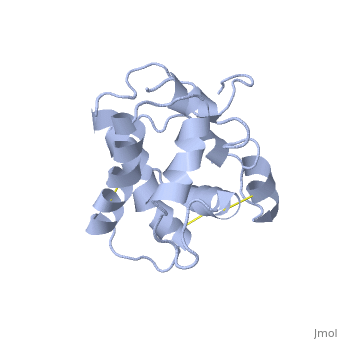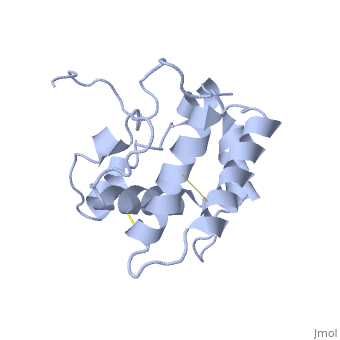
The protein has 164 amino acids that forms 6-7 alpha helices (depends on the protein conformation). Three disulfide bonds formed by residues tied four helices, and form the compact and robust structure of the protein. As expected from a soluble protein, its surface is covered with , which allows it to interact with the water molecule and solubilize in the sensillar lymph.
BmorPBP - ligand binding
The protein natural ligand is the moth pheromone . However, it was demonstrated that other molecules can also bind to the protein cavity [9]. The interaction with the ligand is through 4 alpha helices 1, 4, 5 and 6 in the core of the protein, which form the binding cavity [10].
Inside the binding cavity, interact with the pheromone, mainly by Van der Waals bonds. Out of those residues, some are conserved across OBP of lepidopteran (in green), and the rest are conserved in lepidopteran PBP only (in light blue).
In addition, the hydroxyl group of the pheromone bombykol forms a , Ser56 in red, oxygens are in purple (O–O distance of 2.8 Å).
Protein conformations
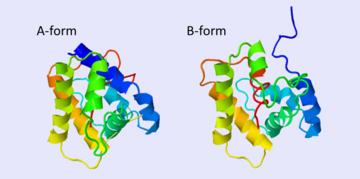
The A and B forms without ligand (PDB IDs:
1gm0 and
1ls8).
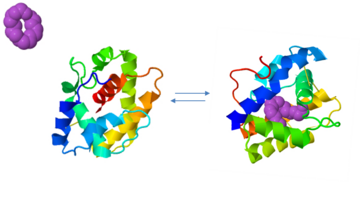
The A and B forms with ligand (PDB IDs:
1gm0 and
1ls8).
BmorPBP has two conformations: The "closed form" (A) and the "open form" (B)[11]. The bombykol and the alpha-helix located in the c-terminus of the protein compete for the binding site: when the c-terminus is inside the binding cavity it get's an alpha helix shape, and the protein is in its "close form" (B), whereas in the "open form" (A) the c-terminus is outside of the protein and has no defined secondary structure. Binding experiments have shown that the B-form binds 15 times higher than the A-form [12], therefore considered to be the carrier of the pheromone. The complex of the A-form and the pheromone, is then considered the form that activates the receptor.
The is both pH and ligand dependent [13][14][15]. In short, the B-form (c-terminus outside the cavity) occurs only at neutral pH and in the presence of the ligand. The A-form (c-terminus inside the cavity) occurs at both low and neutral pH, yet at the latter only in the absence of ligand. Therefore, in neutral pH when the ligand is binding to the protein in its A-form, the complex formation causes a change in conformation to the B-form. However, both A and B forms are equally distributed in the lymph.
Conformation transition mechanism:
The c-terminus of the protein bears mostly . Yet on the surface of the helix there are three exceptional amino acids: Asp-132, Glu-137, and Glu-141, which are conserved in moth PBP [16]. Of these, residues (and Glu-141, if present) triggers the formation of the alpha-helix upon protonation at low pH. This causes the transition from the , to the and the ejaculation of the ligand from the binding pocket, which is replaced by the formatted alpha helix[17].
Studies on other lepidopterans that show a similar pH dependent conformation suggests that this model is a general model moth PBP[4]. Nonetheless, the enormous diversity among insects is not allowing us to assume this model is true for all insects' OBPs.
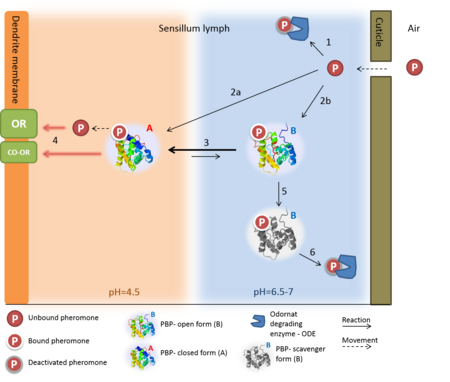
Figure 1. The events prior the neuron excitation, following the "N model" suggested by Kaissling (2009)
[18] The pheromone enters the sensillar lymph through a pore in cuticle. The pheromone can then be degraded by the ODE (1) -or- bind to the A and B protein forms (2a and 2b, respectively). When the complex arrives at the low pH near the membrane, the transition is in favor of the A-form, (3) in which the -c-terminus is forming an alpha helix inside the binding cavity, pushing out the pheromone. The activation of the complex of odorant receptor and coreceptor (OR:Orco), is induced by ether the complex of pheromone-PBP, or by the pheromone alone (5, two options). The B-form can also act as a scavenger, as it mediates the deactivation of the pheromone (6) and releases it to the ODE (6)
Receptor activation
The insect odorant receptor is a heteromer composed of a single ligand-binding OR and the OR coreceptor Orco . Orco acts as a chaperone and also play a role in signal transduction [20]. The activation of this complex begins the intracellular signal transduction. Two theories have been proposed for the activation of the odorant receptors located on the dendrite membrane. One theory suggests that the pheromone-PBP complex is needed for the activation of the OR:CO complex, while the second theory argues that the pheromone itself is sufficient for the activation of the OR:CO.
Activation by the pheromone alone
This model is supported by the pH dependent conformation transition, that is described above. The bulk of the sensillar lymph is in neutral pH (6.5-7), while environment near the dendrite membrane bears a low pH (4.5), due to the negative charges on the surface of the membrane [21], which cause the accumulation of positively charged cations near the membrane surface (20-50 nm)[18]. According to this model, the pheromone enters the sensillar lymph through a pore in the cuticle, then it can be either degraded by odorant degrading enzymes (ODE) or bind to a PBP (of both forms). Once the complex arrives to the low pH environment near the dendritic membrane the PBP will shift to the A-form, thereby releasing the ligand from the binding pocket, allowing it to activate the OR:CO-OR complex and the cellular signal transduction begins.
Activation by the complex pheromone-PBP
An alternative mode of action was proposed for the receptor activation in Drosophila melanogaster, where it was found that the complex of pheromone-PBP is required for the activity of pheromone-sensitive neurons [22][23]
3D structure of odorant binding protein
Odorant binding protein 3D structures