Pantothenate synthetase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (2 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
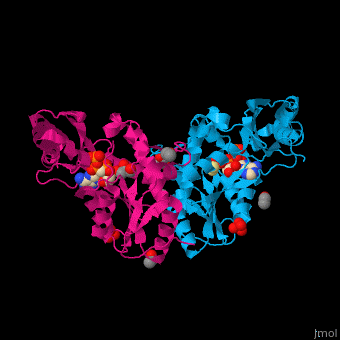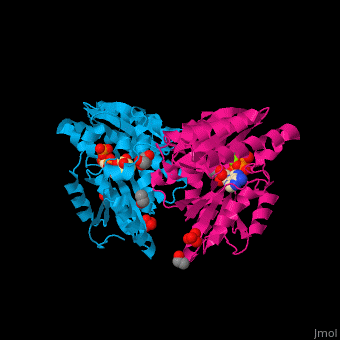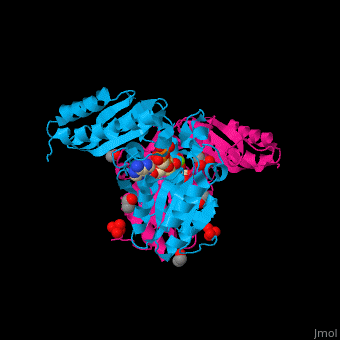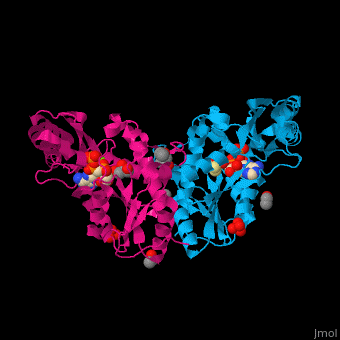
<StructureSection load='' size='450' side='right' caption='Pantothenate synthetase complex with pantoate, AMPPNP, sulfate, Mg+2 ion (green), ethanol and glycerol (PDB entry [[1n2e]])' scene='52/525165/Cv/1' pspeed='8'> | <StructureSection load='' size='450' side='right' caption='Pantothenate synthetase complex with pantoate, AMPPNP, sulfate, Mg+2 ion (green), ethanol and glycerol (PDB entry [[1n2e]])' scene='52/525165/Cv/1' pspeed='8'> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | '''Pantothenate synthetase''' (PS) catalyzes the ATP-dependent condensation of pantoate and β-alanine to form pantothenate<ref>PMID:17932772</ref>. | + | '''Pantothenate synthetase''' or '''pantoate-beta-alanine ligase''' (PS) catalyzes the ATP-dependent condensation of pantoate and β-alanine to form pantothenate<ref>PMID:17932772</ref>. |
== Relevance == | == Relevance == | ||
Pantothenate (vitamin B5) biosynthesis is essential for the virulence of ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' thus its blockage can be used as a potential drug target<ref>PMID:26486566</ref>. | Pantothenate (vitamin B5) biosynthesis is essential for the virulence of ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' thus its blockage can be used as a potential drug target<ref>PMID:26486566</ref>. | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| - | PS <scene name='52/525165/Cv/ | + | PS <scene name='52/525165/Cv/7'>active site is located at the C-terminal of the central parallel β sheet</scene>. In this structure the pantoate substrate electron density is well defined in one subunit while the nucleotide electron density is well defined in the other<ref>PMID:12717031</ref>. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. |
| - | *<scene name='52/525165/Cv/ | + | *<scene name='52/525165/Cv/8'>Pantoate binding site</scene> (chain A). |
| - | *<scene name='52/525165/Cv/ | + | *<scene name='52/525165/Cv/9'>AMPPNP binding site</scene> (chain B). |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
==3D structures of pantothenate synthetase== | ==3D structures of pantothenate synthetase== | ||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
**[[3ag5]] - SaPS – ''Staphylococcus aureus''<br /> | **[[3ag5]] - SaPS – ''Staphylococcus aureus''<br /> | ||
**[[5hg0]] - FtPS + SAM – ''Francisella tularensis''<br /> | **[[5hg0]] - FtPS + SAM – ''Francisella tularensis''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[7tot]] - PS – ''Bartonella henselae''<br /> | ||
*Pantothenate synthetase binary complex with adenosine derivatives | *Pantothenate synthetase binary complex with adenosine derivatives | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
3D structures of pantothenate synthetase
Updated on 21-August-2023
References
- ↑ Jonczyk R, Ronconi S, Rychlik M, Genschel U. Pantothenate synthetase is essential but not limiting for pantothenate biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol. 2008 Jan;66(1-2):1-14. Epub 2007 Oct 12. PMID:17932772 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11103-007-9248-6
- ↑ Hung AW, Silvestre HL, Wen S, George GP, Boland J, Blundell TL, Ciulli A, Abell C. Optimization of Inhibitors of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Pantothenate Synthetase Based on Group Efficiency Analysis. ChemMedChem. 2016 Jan 5;11(1):38-42. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201500414. Epub 2015 Oct, 21. PMID:26486566 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/cmdc.201500414
- ↑ Wang S, Eisenberg D. Crystal structures of a pantothenate synthetase from M. tuberculosis and its complexes with substrates and a reaction intermediate. Protein Sci. 2003 May;12(5):1097-108. PMID:12717031