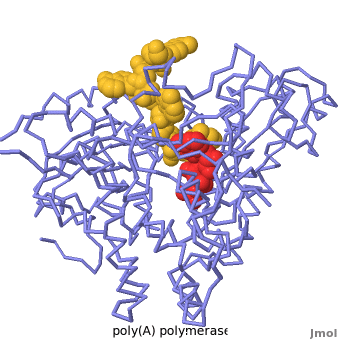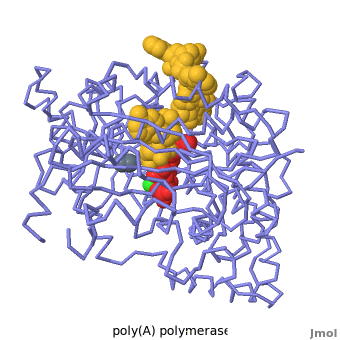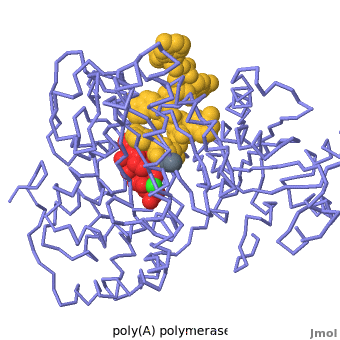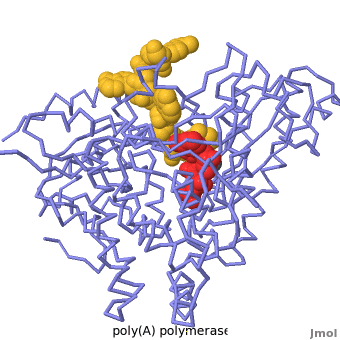
Poly(A) Polymerase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (10 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='' size=' | + | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of Yeast Poly(A) Polymerase with ATP, Mg+2 ion (green) and oligo(A) (PDB entry [[2q66]])' scene='Proteopedia:Main_page_develop/2q66_initial/3'> |
[[Image:2q66.png|left|170px]] | [[Image:2q66.png|left|170px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | __TOC__ | ||
==Function== | ==Function== | ||
[[Poly(A) Polymerase]] (polynucleotide adenylytransferase, [[EC Number|EC]] 2.7.7.19) is the enzyme responsible for adding a polyadenine tail to the 3' end of a nascent pre-mRNA transcript. Its substrates are ATP and RNA. The poly(A) tail that poly-A polymerase adds to the 3' end of the pre-mRNA transcript is important for nuclear export, translation and stability of the mRNA. | [[Poly(A) Polymerase]] (polynucleotide adenylytransferase, [[EC Number|EC]] 2.7.7.19) is the enzyme responsible for adding a polyadenine tail to the 3' end of a nascent pre-mRNA transcript. Its substrates are ATP and RNA. The poly(A) tail that poly-A polymerase adds to the 3' end of the pre-mRNA transcript is important for nuclear export, translation and stability of the mRNA. | ||
| + | *'''Star-PAP''' selects mRNA targets for polyadenylation<ref>PMID:34576144</ref>. | ||
==Determinants of ATP Recognition== | ==Determinants of ATP Recognition== | ||
| Line 14: | Line 17: | ||
</blockquote> | </blockquote> | ||
| - | </StructureSection> | ||
==3D structures of poly(A) polymerase== | ==3D structures of poly(A) polymerase== | ||
| - | + | [[Poly(A) polymerase 3D structures]] | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
Note: the regulatory subunit of Vaccinia virus Poly(A) polymerase is called '''VP39''' and the catalytic subunit name is '''VP55''' | Note: the regulatory subunit of Vaccinia virus Poly(A) polymerase is called '''VP39''' and the catalytic subunit name is '''VP55''' | ||
| Line 69: | Line 33: | ||
==Reference== | ==Reference== | ||
Mechanism of poly(A) polymerase: structure of the enzyme-MgATP-RNA ternary complex and kinetic analysis., Balbo PB, Bohm A, Structure. 2007 Sep;15(9):1117-31. PMID:[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17850751 17850751] | Mechanism of poly(A) polymerase: structure of the enzyme-MgATP-RNA ternary complex and kinetic analysis., Balbo PB, Bohm A, Structure. 2007 Sep;15(9):1117-31. PMID:[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17850751 17850751] | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
[[Category: Polynucleotide adenylyltransferase]] | [[Category: Polynucleotide adenylyltransferase]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
Note: the regulatory subunit of Vaccinia virus Poly(A) polymerase is called VP39 and the catalytic subunit name is VP55
Additional Resources
For additional information, see: Translation
For additional examples of transferases, see: Transferase
- PDB entry 2q66
Reference
Mechanism of poly(A) polymerase: structure of the enzyme-MgATP-RNA ternary complex and kinetic analysis., Balbo PB, Bohm A, Structure. 2007 Sep;15(9):1117-31. PMID:17850751
- ↑ Koshre GR, Shaji F, Mohanan NK, Mohan N, Ali J, Laishram RS. Star-PAP RNA Binding Landscape Reveals Novel Role of Star-PAP in mRNA Metabolism That Requires RBM10-RNA Association. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 15;22(18):9980. PMID:34576144 doi:10.3390/ijms22189980
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Eran Hodis, David Canner, Joel L. Sussman, OCA, Alexander Berchansky, Jaime Prilusky, David S. Goodsell, Eric Martz