This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Tumor necrosis factor receptor
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (12 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
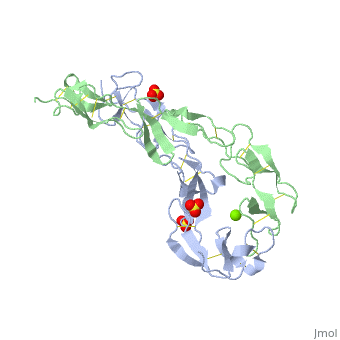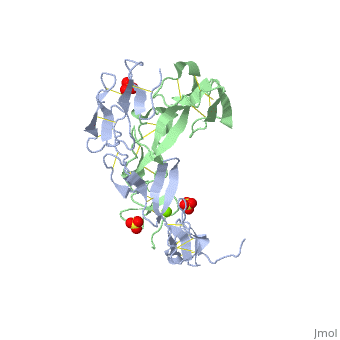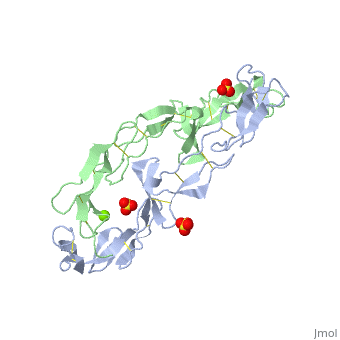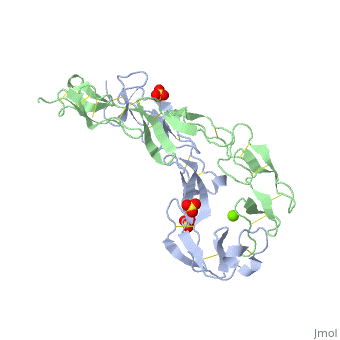
| - | <StructureSection load='1ext' size=' | + | <StructureSection load='1ext' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of human TNFR extracellular domain complex with sulfate and Mg+2 ion (green) (PDB code [[1ext]]).' scene='' pspeed='8'> |
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
* '''TNFRSF 6''' is called '''Fas''';<br /> | * '''TNFRSF 6''' is called '''Fas''';<br /> | ||
* '''TNFRSF 9''' is called '''4-1BBL''';<br /> | * '''TNFRSF 9''' is called '''4-1BBL''';<br /> | ||
| - | * '''TNFRSF | + | * '''TNFRSF 10''' see [[TRAIL]];<br /> |
* '''TNFRSF 10B''' is called '''Dr5''';<br /> | * '''TNFRSF 10B''' is called '''Dr5''';<br /> | ||
| - | * '''TNFRSF 11''' is called '''RANKL''';<br /> | ||
* '''TNFRSF 11A''' is called '''RANK''';<br /> | * '''TNFRSF 11A''' is called '''RANK''';<br /> | ||
* '''TNFRSF 11B''' is called '''Osteoprotegerin''';<br /> | * '''TNFRSF 11B''' is called '''Osteoprotegerin''';<br /> | ||
* '''TNFRSF 12''' is called '''TWEAK''';<br /> | * '''TNFRSF 12''' is called '''TWEAK''';<br /> | ||
* '''TNFRSF 12A''' is called '''TWEAKR''';<br /> | * '''TNFRSF 12A''' is called '''TWEAKR''';<br /> | ||
| - | * '''TNFRSF 13''' is called '''APRIL''';<br /> | ||
* '''TNFRSF 13B''' is called '''BAFF or sTALL-1''';<br /> | * '''TNFRSF 13B''' is called '''BAFF or sTALL-1''';<br /> | ||
* '''TNFRSF 13C''' is called '''BAFF receptor''';<br /> | * '''TNFRSF 13C''' is called '''BAFF receptor''';<br /> | ||
* '''TNFRSF 14''' is called '''LIGHT''';<br /> | * '''TNFRSF 14''' is called '''LIGHT''';<br /> | ||
| - | * '''TNFRSF 16''' is called ''' | + | * '''TNFRSF 16''' is called '''Low-affinity nerve growth factor receptor; p75NTR; p75 neurotrophin receptor''';<br /> |
* '''TNFRSF 18''' is called '''GITRL''';<br /> | * '''TNFRSF 18''' is called '''GITRL''';<br /> | ||
* '''TNFRSF 21''' is called '''Dr6''';<br /> | * '''TNFRSF 21''' is called '''Dr6''';<br /> | ||
| + | * '''TNFRSF 25''' is called '''Dr3''';<br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | See also | ||
| + | *[[Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily]] | ||
| + | *[[Cytokine receptors]] | ||
| + | *[[Receptor]] | ||
| + | *[[Immune receptors]] | ||
| - | ==See also [[Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily]]== | ||
== Relevance == | == Relevance == | ||
TRAPS - a condition characterized by recurrent episodes of fever is associated with TNFR<ref>PMID:24609716</ref>. | TRAPS - a condition characterized by recurrent episodes of fever is associated with TNFR<ref>PMID:24609716</ref>. | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| - | The extracellular domain of TNFR contains 2 to 6 cysteine-rich domains (CRD). | + | The extracellular domain of TNFR contains 2 to 6 cysteine-rich domains (CRD). The <scene name='59/590824/Cv/8'>CRD domains are ca. 40 amino-acid long and contain 4-6 cysteine residues</scene>. The CRDs are involved in binding of TNF<ref>PMID:8939750</ref>. <scene name='59/590824/Cv/9'>Mg coordination site</scene>. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
==3D structures of tumor necrosis factor receptor== | ==3D structures of tumor necrosis factor receptor== | ||
| + | [[Tumor necrosis factor receptor 3D structures]] | ||
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | **[[3u3p]], [[3u3q]], [[3u3s]], [[3u3t]], [[3u3v]] – hTNFRSF-21 cysteine-rich domain<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2dbh]] – hTNFRSF-21 CARD-like domain - NMR<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3qo4]] – hTNFRSF-21 cysteine-rich domain<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4yn0]] – hTNFRSF-21 cysteine-rich domain + amyloid beta A4 protein<br /> | ||
| - | }} | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
[[Category: Topic Page]] | [[Category: Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Wallach D, Varfolomeev EE, Malinin NL, Goltsev YV, Kovalenko AV, Boldin MP. Tumor necrosis factor receptor and Fas signaling mechanisms. Annu Rev Immunol. 1999;17:331-67. PMID:10358762 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev.immunol.17.1.331
- ↑ Lopalco G, Rigante D, Vitale A, Frediani B, Iannone F, Cantarini L. Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome managed with the couple canakinumab-alendronate. Clin Rheumatol. 2015 Apr;34(4):807-9. doi: 10.1007/s10067-014-2556-8. Epub 2014, Mar 11. PMID:24609716 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10067-014-2556-8
- ↑ Naismith JH, Devine TQ, Kohno T, Sprang SR. Structures of the extracellular domain of the type I tumor necrosis factor receptor. Structure. 1996 Nov 15;4(11):1251-62. PMID:8939750