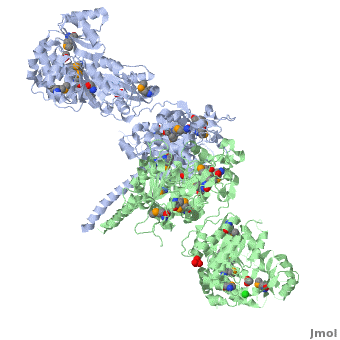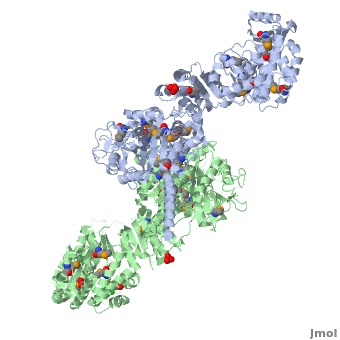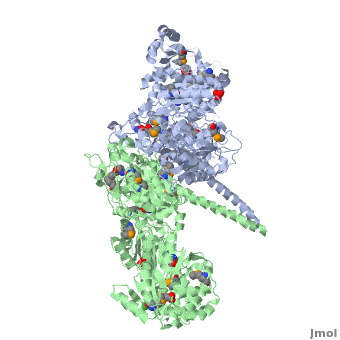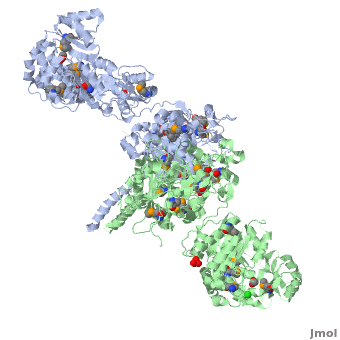
6-deoxyerythronolide B synthase (DEBS)
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (5 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' scene='40/400561/Ks-at_dimer/2' caption='6-deoxyerythronolide B synthase dimer [[2hg4]]'> | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' scene='40/400561/Ks-at_dimer/2' caption='6-deoxyerythronolide B synthase dimer [[2hg4]]'> | ||
One of the '''[[CBI Molecules]]''' being studied in the [http://www.umass.edu/cbi/ University of Massachusetts Amherst Chemistry-Biology Interface Program] at UMass Amherst and on display at the [http://www.molecularplayground.org/ Molecular Playground]. | One of the '''[[CBI Molecules]]''' being studied in the [http://www.umass.edu/cbi/ University of Massachusetts Amherst Chemistry-Biology Interface Program] at UMass Amherst and on display at the [http://www.molecularplayground.org/ Molecular Playground]. | ||
| + | __TOC__ | ||
| + | == Function == | ||
Polyketides are a large and structurally diverse class of natural products produced by bacteria, fungi, and plants. They exhibit a wide variety of biological activities including antibiotic, antitumor, anticancer, among others. | Polyketides are a large and structurally diverse class of natural products produced by bacteria, fungi, and plants. They exhibit a wide variety of biological activities including antibiotic, antitumor, anticancer, among others. | ||
| Line 8: | Line 10: | ||
[[Image:DEBS.png|left|500px|thumb|6-deoxyerythronolide B synthase (DEBS)]] | [[Image:DEBS.png|left|500px|thumb|6-deoxyerythronolide B synthase (DEBS)]] | ||
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
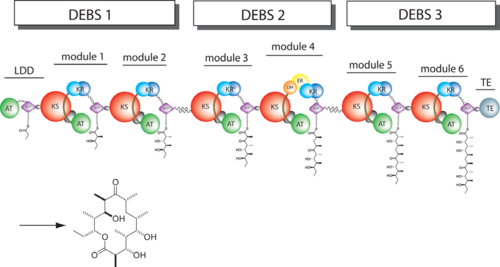
| - | The 6-deoxyerythronolide B synthase (DEBS), which catalyzes the formation of 6-dEB, consists of three large subunits, DEBS1, DEBS2 and DEBS3, each containing two modules and above 300 kD in size. There are 2 domains in the N-terminal loading module, responsible for priming the synthase with a proprionate starter unit, and 26 domains in the six extender modules, Each extender module contains at least three essential domains: a ketosynthase (KS), an acyl transferase (AT) and an acyl carrier protein (ACP). In detail, the AT domain selects the appropriate carbon extender unit and transfers the units from acyl-CoA onto the phosphopantetheine arm of ACP. The KSdomain accepts the polyketide chain from the previous module and catalyzes chain elongation reaction by adding an ACP-bound extender unit through decarboxylative condensation. | + | The '''6-deoxyerythronolide B synthase''' (DEBS), which catalyzes the formation of 6-dEB, consists of three large subunits, DEBS1, DEBS2 and DEBS3, each containing two modules and above 300 kD in size. There are 2 domains in the N-terminal loading module, responsible for priming the synthase with a proprionate starter unit, and 26 domains in the six extender modules, Each extender module contains at least three essential domains: a ketosynthase (KS), an acyl transferase (AT) and an acyl carrier protein (ACP). In detail, the AT domain selects the appropriate carbon extender unit and transfers the units from acyl-CoA onto the phosphopantetheine arm of ACP. The KSdomain accepts the polyketide chain from the previous module and catalyzes chain elongation reaction by adding an ACP-bound extender unit through decarboxylative condensation.<br /> |
| + | |||
| + | '''DEBS1''' is acylated by a diketide at module 2<ref>PMID:8952473</ref>.<br /> | ||
| + | '''DEBS3''' carries out the final two cycles in the synthesis of 6-dEB<ref>PMID:9538011</ref>. | ||
After the extender unit is added, it can be further processed by optional tailoring domains, including ketoreductases (KRs), dehydratases (DHs), and enoyl reductases (ERs), to yield a hydroxyl, enoyl, or methylene group at the beta-position. Finally, the thioesterase (TE) domain that located at the C-terminus of DEBS module 6 promotes the macrocyclization event which releases the final product, 6-dEB. <ref>PMID:17328673</ref> | After the extender unit is added, it can be further processed by optional tailoring domains, including ketoreductases (KRs), dehydratases (DHs), and enoyl reductases (ERs), to yield a hydroxyl, enoyl, or methylene group at the beta-position. Finally, the thioesterase (TE) domain that located at the C-terminus of DEBS module 6 promotes the macrocyclization event which releases the final product, 6-dEB. <ref>PMID:17328673</ref> | ||
| - | + | ==Ketosynthase-acyltransferase (KS-AT)== | |
Molecular Playground banner: KS-AT The "builder" and the "gatekeeper". | Molecular Playground banner: KS-AT The "builder" and the "gatekeeper". | ||
| Line 21: | Line 26: | ||
The KS accepts the "in-progress" polyketide from its upstream module, and then catalyzes the decarboxylative condensation of ACP-bound malonyl CoA derivatives with the in-progress chain. This results in an ACP-bound β-ketothioester which is processed by any other β-carbon tailoring domains present within the module. | The KS accepts the "in-progress" polyketide from its upstream module, and then catalyzes the decarboxylative condensation of ACP-bound malonyl CoA derivatives with the in-progress chain. This results in an ACP-bound β-ketothioester which is processed by any other β-carbon tailoring domains present within the module. | ||
| - | + | ==Acyl Carrier Protein (ACP)== | |
Molecular Playground banner: "the communicator". | Molecular Playground banner: "the communicator". | ||
<scene name='6-deoxyerythronolide_B_synthase_(DEBS)/Cv/1'>Solution structure of acyl carrier protein domain from module 2 of 6-deoxyerythronolide B synthase (DEBS)</scene> ([[2ju1]]). | <scene name='6-deoxyerythronolide_B_synthase_(DEBS)/Cv/1'>Solution structure of acyl carrier protein domain from module 2 of 6-deoxyerythronolide B synthase (DEBS)</scene> ([[2ju1]]). | ||
| Line 29: | Line 34: | ||
| - | + | == Ketoreductase (KR) == | |
| - | The ketoreductase domain of a PKS is an optional tailoring domain that reduces a beta-ketoacyl ACP intermediate to the beta-hydroxy acyl ACP. <scene name='40/400561/Nadph/2'>NADPH</scene>, the co-factor for the KR domain, furnishes the hydride that is used in the reduction. | + | The ketoreductase domain of a PKS is an optional tailoring domain that reduces a beta-ketoacyl ACP intermediate to the beta-hydroxy acyl ACP. <scene name='40/400561/Nadph/2'>NADPH</scene>, the co-factor for the KR domain, furnishes the hydride that is used in the reduction. The Erythromycin <scene name='55/559997/Kr/1'>KR domain</scene> |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ==Dehydratase (DH)== | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
Molecular Playground banner: make modification on beta-keto-acyl-ACP, "the decorator". | Molecular Playground banner: make modification on beta-keto-acyl-ACP, "the decorator". | ||
<scene name='6-deoxyerythronolide_B_synthase_(DEBS)/Cv/2'>Crystal Structure of the dimeric Erythromycin Dehydratase monomer complex with sulfate and Cl- ion</scene> ([[3el6]]). | <scene name='6-deoxyerythronolide_B_synthase_(DEBS)/Cv/2'>Crystal Structure of the dimeric Erythromycin Dehydratase monomer complex with sulfate and Cl- ion</scene> ([[3el6]]). | ||
| - | + | ==Thioesterase (TE)== | |
Molecular Playground banner: cyclize the molecule, "the closer". | Molecular Playground banner: cyclize the molecule, "the closer". | ||
| Line 46: | Line 48: | ||
TE is the terminal domain in DEBS, releasing the completed polyketide from the synthase by forming a 14-membered lactone. It is able to close such a large ring by threading it into a large inner cavity which stabilizes its conformation while esterification occurs. | TE is the terminal domain in DEBS, releasing the completed polyketide from the synthase by forming a 14-membered lactone. It is able to close such a large ring by threading it into a large inner cavity which stabilizes its conformation while esterification occurs. | ||
| - | + | ||
==3D structures of 6-deoxyerythronolide B synthase== | ==3D structures of 6-deoxyerythronolide B synthase== | ||
| - | + | [[6-deoxyerythronolide B synthase 3D structures]] | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | }} | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Tsukamoto N, Chuck JA, Luo G, Kao CM, Khosla C, Cane DE. 6-deoxyerythronolide B synthase 1 is specifically acylated by a diketide intermediate at the beta-ketoacyl-acyl carrier protein synthase domain of module 2. Biochemistry. 1996 Dec 3;35(48):15244-8. PMID:8952473 doi:10.1021/bi961972f
- ↑ Jacobsen JR, Cane DE, Khosla C. Spontaneous priming of a downstream module in 6-deoxyerythronolide B synthase leads to polyketide biosynthesis. Biochemistry. 1998 Apr 7;37(14):4928-34. PMID:9538011 doi:10.1021/bi9729920
- ↑ Khosla C, Tang Y, Chen AY, Schnarr NA, Cane DE. Structure and mechanism of the 6-deoxyerythronolide B synthase. Annu Rev Biochem. 2007;76:195-221. PMID:17328673 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev.biochem.76.053105.093515
Additional Resources
For additional information, see: Cancer
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Tsung-Yi Lin, Alexander Berchansky, Lawrence Sheringham Borketey, Joel L. Sussman, Jon Amoroso, David Canner, Jaime Prilusky