We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Invertase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (9 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
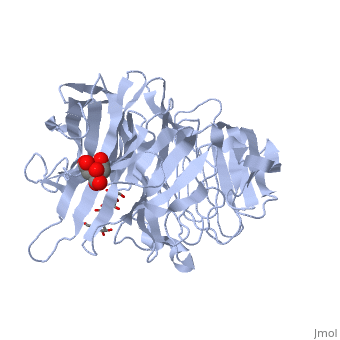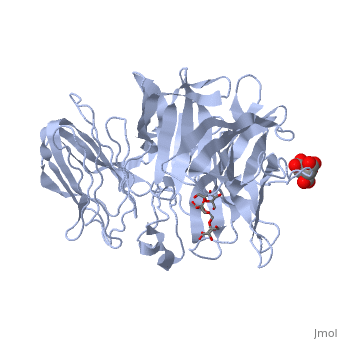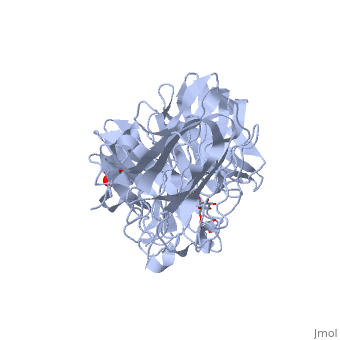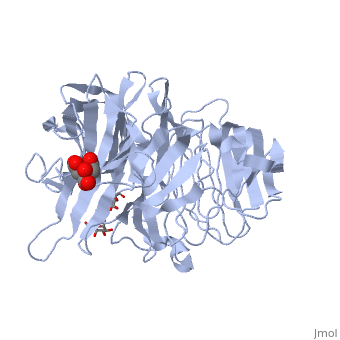
| - | <StructureSection load='1w2t' size='350' side='right' caption='Invertase complex with raffinose, citrate and sulfate (PDB code [[1w2t]]).' scene=''> | + | <StructureSection load='1w2t' size='350' side='right' caption='Invertase complex with raffinose (stick model), citrate and sulfate (PDB code [[1w2t]]).' scene=''> |
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | '''Invertase''' (INV) catalyzes the hydrolysis of sucrose into glucose and fructose<ref>PMID:4963242</ref>. INV is produced by bees which use it to make honey from nectar. | + | '''Invertase''' (INV) catalyzes the hydrolysis of sucrose into glucose and fructose<ref>PMID:4963242</ref>. INV is produced by bees which use it to make honey from nectar. |
| + | *'''Cell-wall INV''' is crucial for metabolism, growth and differentiation in plants<ref>PMID:24646208</ref>. | ||
| + | *'''Extracellular INV''' catalyzes the cleavage of the transport sugar sucrose released into the app-last<ref>PMID:12508062</ref> | ||
| + | *'''Alkaline INV''' is a tetramer which catalyzes the cleavage of sucrose<ref>PMID:8972597</ref> | ||
| + | *'''DNA INV Gin''' is found in bacteriophage Mu and catalyses the recombination between repeat sequences in vivo and in vitro<ref>PMID:3042382</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | For details in Hebrew see [[Invertase (Hebrew)]]. | ||
== Relevance == | == Relevance == | ||
INV is used in the food industry to produce fructose which is sweeter and does not crystallize easily. | INV is used in the food industry to produce fructose which is sweeter and does not crystallize easily. | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| - | The <scene name='67/676994/Cv/ | + | The <scene name='67/676994/Cv/7'>active site pocket</scene> of INV contains the catalytic residues Asp and Glu<ref>PMID:16411890</ref>. |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| Line 18: | Line 24: | ||
*Invertase | *Invertase | ||
| + | **[[4eqv]] – INV 2 – yeast<br /> | ||
**[[1uyp]] – TmINV – ''Thermotoga maritima''<br /> | **[[1uyp]] – TmINV – ''Thermotoga maritima''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4eqv]] – INV 2 – yeast<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3kf5]] – SoINV – ''Schwanniomyces occidentalis''<br /> | ||
**[[1w2t]] – TmINV (mutant) + trisaccharide<br /> | **[[1w2t]] – TmINV (mutant) + trisaccharide<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3kf5]] – SoINV – ''Schwanniomyces occidentalis''<br /> | ||
**[[3kf3]] – SoINV + fructose <br /> | **[[3kf3]] – SoINV + fructose <br /> | ||
| Line 29: | Line 35: | ||
**[[2oxb]], [[2qqu]], [[2qqv]], [[2qqw]] – AtINV (mutant) + sucrose<br /> | **[[2oxb]], [[2qqu]], [[2qqv]], [[2qqw]] – AtINV (mutant) + sucrose<br /> | ||
**[[2xqr]] – AtINV + INV inhibitor <br /> | **[[2xqr]] – AtINV + INV inhibitor <br /> | ||
| + | **[[6ttj]] – AtINV 2<br /> | ||
*Alkaline invertase | *Alkaline invertase | ||
| - | **[[5gor]] – AnINV – ''Anabaena''<br /> | + | **[[5gor]], [[5z73]] – AnINV – ''Anabaena''<br /> |
**[[5goo]], [[5gop]], [[5goq]] – AnINV + sugar <br /> | **[[5goo]], [[5gop]], [[5goq]] – AnINV + sugar <br /> | ||
| Line 39: | Line 46: | ||
**[[3uj3]] – muINV – enterobacteria phage mu<br /> | **[[3uj3]] – muINV – enterobacteria phage mu<br /> | ||
**[[4m6f]] – muINV + DNA <br /> | **[[4m6f]] – muINV + DNA <br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Extracellular invertase | ||
| + | |||
| + | **[[5xh8]], [[5xh9]] – moINV – mold<br /> | ||
| + | **[[5xha]] – moINV + fructose<br /> | ||
}} | }} | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of invertase
Updated on 07-July-2024
References
- ↑ Neumann NP, Lampen JO. Purification and properties of yeast invertase. Biochemistry. 1967 Feb;6(2):468-75. PMID:4963242
- ↑ Proels RK, Huckelhoven R. Cell-wall invertases, key enzymes in the modulation of plant metabolism during defence responses. Mol Plant Pathol. 2014 Oct;15(8):858-64. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12139. Epub 2014 May, 13. PMID:24646208 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/mpp.12139
- ↑ Roitsch T, Balibrea ME, Hofmann M, Proels R, Sinha AK. Extracellular invertase: key metabolic enzyme and PR protein. J Exp Bot. 2003 Jan;54(382):513-24. PMID:12508062
- ↑ Lee HS, Sturm A. Purification and characterization of neutral and alkaline invertase from carrot. Plant Physiol. 1996 Dec;112(4):1513-22. PMID:8972597 doi:10.1104/pp.112.4.1513
- ↑ Klippel A, Mertens G, Patschinsky T, Kahmann R. The DNA invertase Gin of phage Mu: formation of a covalent complex with DNA via a phosphoserine at amino acid position 9. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):1229-37. PMID:3042382 doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02935.x
- ↑ Alberto F, Jordi E, Henrissat B, Czjzek M. Crystal structure of inactivated Thermotoga maritima invertase in complex with the trisaccharide substrate raffinose. Biochem J. 2006 May 1;395(3):457-62. PMID:16411890 doi:http://dx.doi.org/BJ20051936